
25 Ordinal Variables Examples 2025 Ordinal variables are variables that have categories with a specific order or ranking to them, but the distances between the categories are not known or consistent (babbie et al., 2007). examples include rating scales like “low”, “medium”, and “high” or education levels such as “elementary”, “high school”, and “college”. In statistics, we use data to answer interesting questions. but not all data is created equal. there are actually four different data measurement scales that are used to categorize different types of data: 1. nominal 2. ordinal 3. interval 4. ratio in this post, we define each measurement scale and provide examples of variables that can be used with each scale. nominal the simplest measurement.
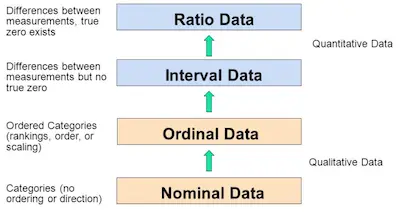
Examples Of Ordinal Variables What is ordinal data? | examples & definition published on june 9, 2024 by julia merkus, ma revised on may 19, 2025 ordinal data is categorized into ranks, with each category having a natural order. however, the spacing between these categories is not clearly uniform or quantifiable. for instance, consider the variable “college degree,” which can be categorized into the following levels. What is ordinal data? ordinal data is a categorical data type where the variables have a natural, ordered sequence. this means the categories can be ranked, but the intervals between the ranks aren’t necessarily equal. think of it like a race where you know who came in first, second, and third, but you don’t know by how much they won. Ordinal is the second of 4 hierarchical levels of measurement: nominal, ordinal, interval, and ratio. the levels of measurement indicate how precisely data is recorded. while nominal and ordinal variables are categorical, interval and ratio variables are quantitative. nominal data differs from ordinal data because it cannot be ranked in an order. Ordinal variables are an essential part of data analysis in various fields, including social sciences, marketing, and health research. they help researchers measure and interpret ordered data, offering insights into attitudes, preferences, and behavioral patterns. this guide explains the definition, purpose, and examples of ordinal variables, providing clarity on their role in research and.

Exploring Ordinal Data Examples And Uses Mind The Graph Blog Ordinal is the second of 4 hierarchical levels of measurement: nominal, ordinal, interval, and ratio. the levels of measurement indicate how precisely data is recorded. while nominal and ordinal variables are categorical, interval and ratio variables are quantitative. nominal data differs from ordinal data because it cannot be ranked in an order. Ordinal variables are an essential part of data analysis in various fields, including social sciences, marketing, and health research. they help researchers measure and interpret ordered data, offering insights into attitudes, preferences, and behavioral patterns. this guide explains the definition, purpose, and examples of ordinal variables, providing clarity on their role in research and. Ordinal data can be used to calculate summary statistics, e.g., frequency distribution, median, and mode, range of variables. ordinal data has a median. ordinal variables ordinal variables are categorical variables with ordered possible values. they can be considered as “in between” categorical and quantitative variables. Variables with a natural order but no quantitative difference in values are labeled using the ordinal data. ordinal data are a higher degree of measurement since they provide more information than nominal data. examples of ordinal data the following are some instances of variables that can be measured using ordinal data:.

Descriptive Statistics Of Ordinal Variables Download Scientific Diagram Ordinal data can be used to calculate summary statistics, e.g., frequency distribution, median, and mode, range of variables. ordinal data has a median. ordinal variables ordinal variables are categorical variables with ordered possible values. they can be considered as “in between” categorical and quantitative variables. Variables with a natural order but no quantitative difference in values are labeled using the ordinal data. ordinal data are a higher degree of measurement since they provide more information than nominal data. examples of ordinal data the following are some instances of variables that can be measured using ordinal data:.

Ordinal Variables Data Presentation And Visualization Researchgate

Descriptive Statistics For Ordinal Variables Download Scientific Diagram