Learn Javascript Promise Race By Practical Examples The promise.race() static method takes an iterable of promises as input and returns a single promise. this returned promise settles with the eventual state of the first promise that settles. Description the promise.race() method returns a promise from a list of promises, when the faster promise settles.
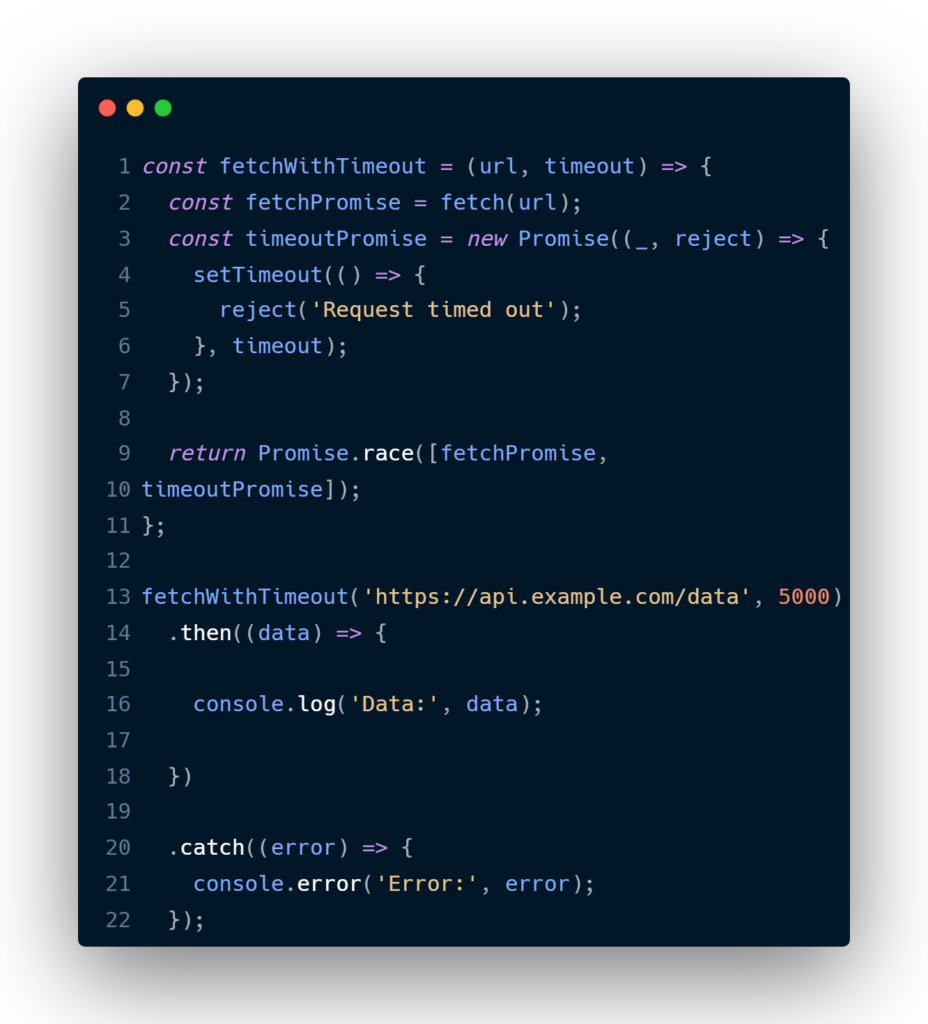
Promise Race In Javascript Mariya Baig Syntax: promise.race(iterable); parameters: iterable: an iterable object such as array, map, string, etc. having several different promises in them. example 1: this example shows the basic use of the promise.race () method in javascript. as promise2 was faster so it prints its own result which is two. With the race() you just need to get the returned promise, you needn't care about which one of the promises in the race([]) firstly returned, however, without the race, just like your example, you need to care about which one will firstly returned, and called the callback in the both success callback. In this video, i have explained what is promise.race () in javascript.schedule a meeting in case of any queries guidance counselling: calendly nave. The promise.race() static method accepts a list of promises as an iterable object and returns a new promise that fulfills or rejects as soon as there is one promise that fulfills or rejects, with the value or reason from that promise. here’s the syntax of the promise.race() method: promise.race(iterable) code language: javascript (javascript).
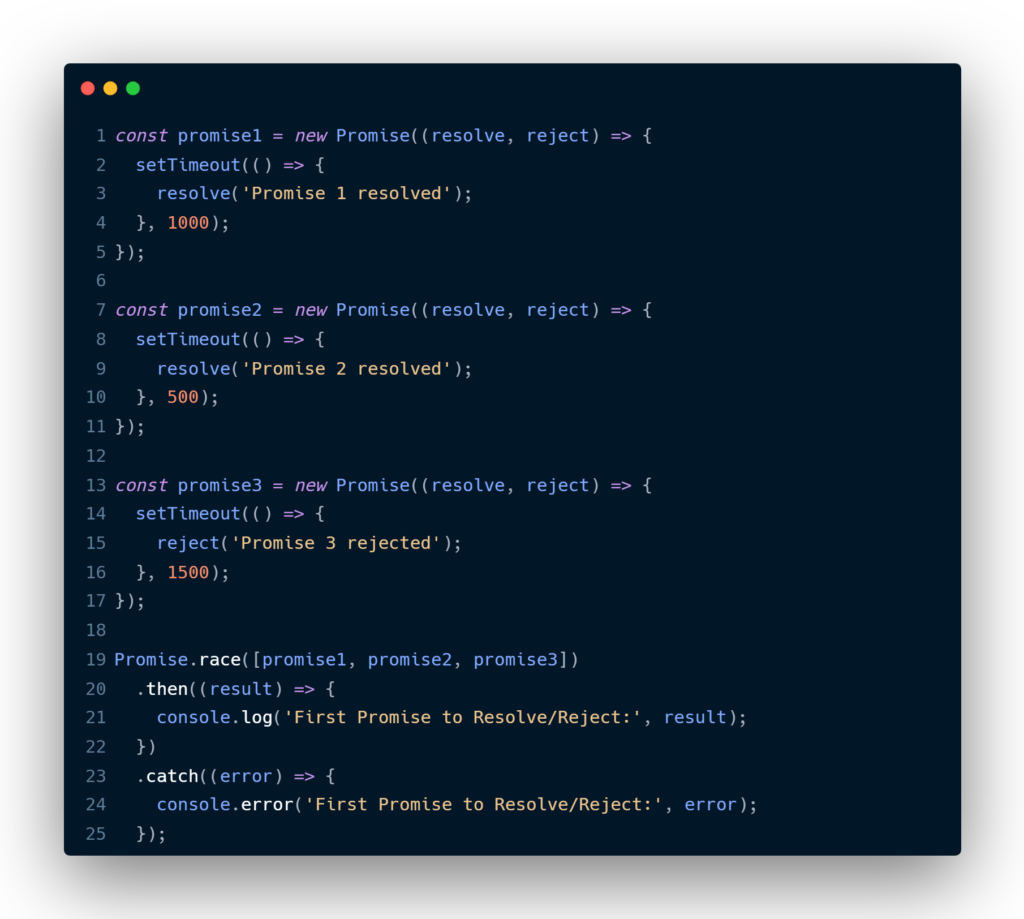
Promise Race In Javascript Mariya Baig In this video, i have explained what is promise.race () in javascript.schedule a meeting in case of any queries guidance counselling: calendly nave. The promise.race() static method accepts a list of promises as an iterable object and returns a new promise that fulfills or rejects as soon as there is one promise that fulfills or rejects, with the value or reason from that promise. here’s the syntax of the promise.race() method: promise.race(iterable) code language: javascript (javascript). In previous articles we learned about how promise work and discussed about then catch and finally methods. today we will be discussing: promise.all () promise.allsettled () difference usecase of promise.all () and promise.allsettled () promise.race () promise.any () difference usecase of promise.race () and promise.any () all these methods take array of promises as an input but deals. Javascript’s promise.race () is the perfect tool for this scenario, and today we’ll explore everything you need to know about this powerful feature. promise.race () takes an array of promises and returns a new promise that resolves or rejects as soon as the first promise in the array settles.

Promise Race In Javascript Mariya Baig In previous articles we learned about how promise work and discussed about then catch and finally methods. today we will be discussing: promise.all () promise.allsettled () difference usecase of promise.all () and promise.allsettled () promise.race () promise.any () difference usecase of promise.race () and promise.any () all these methods take array of promises as an input but deals. Javascript’s promise.race () is the perfect tool for this scenario, and today we’ll explore everything you need to know about this powerful feature. promise.race () takes an array of promises and returns a new promise that resolves or rejects as soon as the first promise in the array settles.