
Addressing Disparities In Type 2 Diabetes Care Advancing health equity: diabetes key points some racial and ethnic minority groups and groups with lower socioeconomic status have higher rates of diabetes. cdc's division of diabetes translation (ddt) works to reduce and one day eliminate health disparities for people with or at risk for type 2 diabetes. Definitions of health disparities, health equity, and sdoh table 1 displays definitions of key terms. differences in diabetes risk and outcomes can result from multiple contributors, including biological, clinical, and nonclinical factors (1). a substantial body of scientific literature demonstrates the adverse impact of a particular type of difference, health disparities (16) in diabetes (1.

Addressing Disparities In Type 2 Diabetes Care In diabetes, understanding and mitigating the impact of sdoh are priorities due to disease prevalence, economic costs, and disproportionate population burden (12 – 14). in 2013, the american diabetes association (ada) published a scientific statement on socioecological determinants of prediabetes and type 2 diabetes (15). Rates of type 2 diabetes in the u.s. vary significantly across geographies social determinants of health—factors that include access to food, housing, education and healthcare— play a key role in these disparities. lack of access to healthy and affordable foods can increase the likelihood of developing type 2 diabetes. Addressing the multifactorial challenge of therapeutic inertia requires eforts that bring together multidisciplinary diabetes care teams, people with diabetes, community organizations, health systems, payors, technology providers, and policymakers to efect change.11 to further support people with diabetes, rdns and ndtrs may benefit from. The ddt program employs preventative and education programs to identify and address healthcare disparities in patient populations at greater risk of prediabetes, type 2 diabetes mellitus (t2dm), and diabetes related complications.

Addressing Disparities In Type 2 Diabetes Care Addressing the multifactorial challenge of therapeutic inertia requires eforts that bring together multidisciplinary diabetes care teams, people with diabetes, community organizations, health systems, payors, technology providers, and policymakers to efect change.11 to further support people with diabetes, rdns and ndtrs may benefit from. The ddt program employs preventative and education programs to identify and address healthcare disparities in patient populations at greater risk of prediabetes, type 2 diabetes mellitus (t2dm), and diabetes related complications. There are numerous other disparities in diabetes care including prescribing diferences, access to care inequities, health insurance variations (eg, medicaid vs commer cial insurance), and myriad other social determinants of health (eg, low health literacy) that can impact diabetes care. Type 2 diabetes disparities in the usa persist in both the prevalence of disease and diabetes related complications. we conducted a literature review related to diabetes prevention, management, and complications across racial and ethnic groups in the usa. the objective of this review is to summarise the current understanding of diabetes disparities by examining differences between and within.

Diabetes Disparities There are numerous other disparities in diabetes care including prescribing diferences, access to care inequities, health insurance variations (eg, medicaid vs commer cial insurance), and myriad other social determinants of health (eg, low health literacy) that can impact diabetes care. Type 2 diabetes disparities in the usa persist in both the prevalence of disease and diabetes related complications. we conducted a literature review related to diabetes prevention, management, and complications across racial and ethnic groups in the usa. the objective of this review is to summarise the current understanding of diabetes disparities by examining differences between and within.
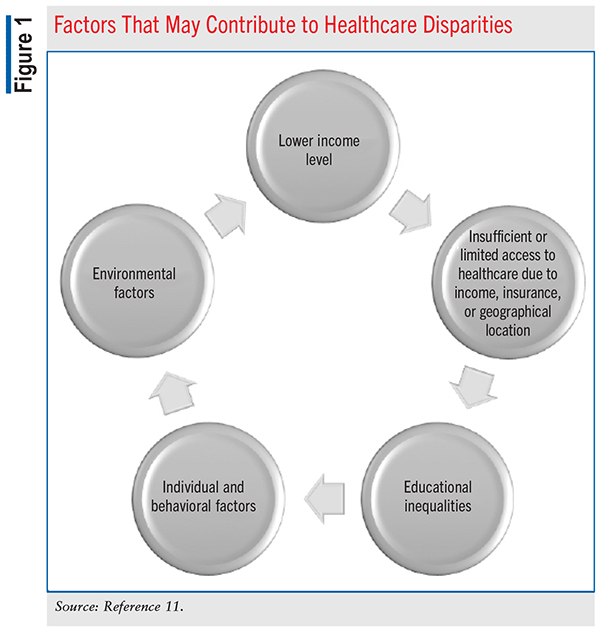
Healthcare Disparities In Diabetes Care