
301 Moved Permanently Analog signals are continuous and vary smoothly over time, while digital signals are discrete and represented by a series of discrete values. understanding the difference between these signals is important in telecommunications, electronics, and signal processing. Signal that are continuous as time varying in nature are analog signals signals which are discrete are called digital signals. analog signals analog signal is a form of electrical energy (voltage, current, or electromagnetic power) for which there is a linear relationship between electrical quantity and the value that the signal represents.

301 Moved Permanently Analog and digital signals are used to transmit information, usually through electric signals. in both these technologies, the information, such as any audio or video, is transformed into electric signals. the difference between analog and digital technologies is that in analog technology, information is translated into electric pulses of varying amplitude. in digital technology, translation. Analog process the violin sequence is an example of an analog process have a continuously varying signal transfers from one medium to the next keeping its basic shape great moments in etymology: analogy is a related word many old technologies are analog (pre computer) why is digital better?. Learn the key differences between analog and digital signals, their characteristics, and applications in this comprehensive guide. Analog and digital signals are the bedrock of modern electronics and information technology. while both serve the fundamental purpose of conveying information, they differ significantly in their representation, transmission, processing, and susceptibility to noise. this article delves into the core distinctions between these two signal types, providing a comprehensive overview for technology.

Analog And Digital Signals In Computer Networking 5 Differences Learn the key differences between analog and digital signals, their characteristics, and applications in this comprehensive guide. Analog and digital signals are the bedrock of modern electronics and information technology. while both serve the fundamental purpose of conveying information, they differ significantly in their representation, transmission, processing, and susceptibility to noise. this article delves into the core distinctions between these two signal types, providing a comprehensive overview for technology. An analog signal is a continuous signal, whereas digital signals are time separated signals. analog signal is denoted by sine waves while digital signals are denoted by square waves. analog signal uses a continuous range of values that help you to represent information; on the other hand, digital signal uses discrete 0 and 1 to represent. A signal is an electromagnetic or electrical current that carries data from one system or network to another. in electronics, a signal is often a time varying voltage that is also an electromagnetic wave carrying information, though it can take on other forms, such as current. there are two main types of signals used in electronics: analog and digital signals. this article discusses the.
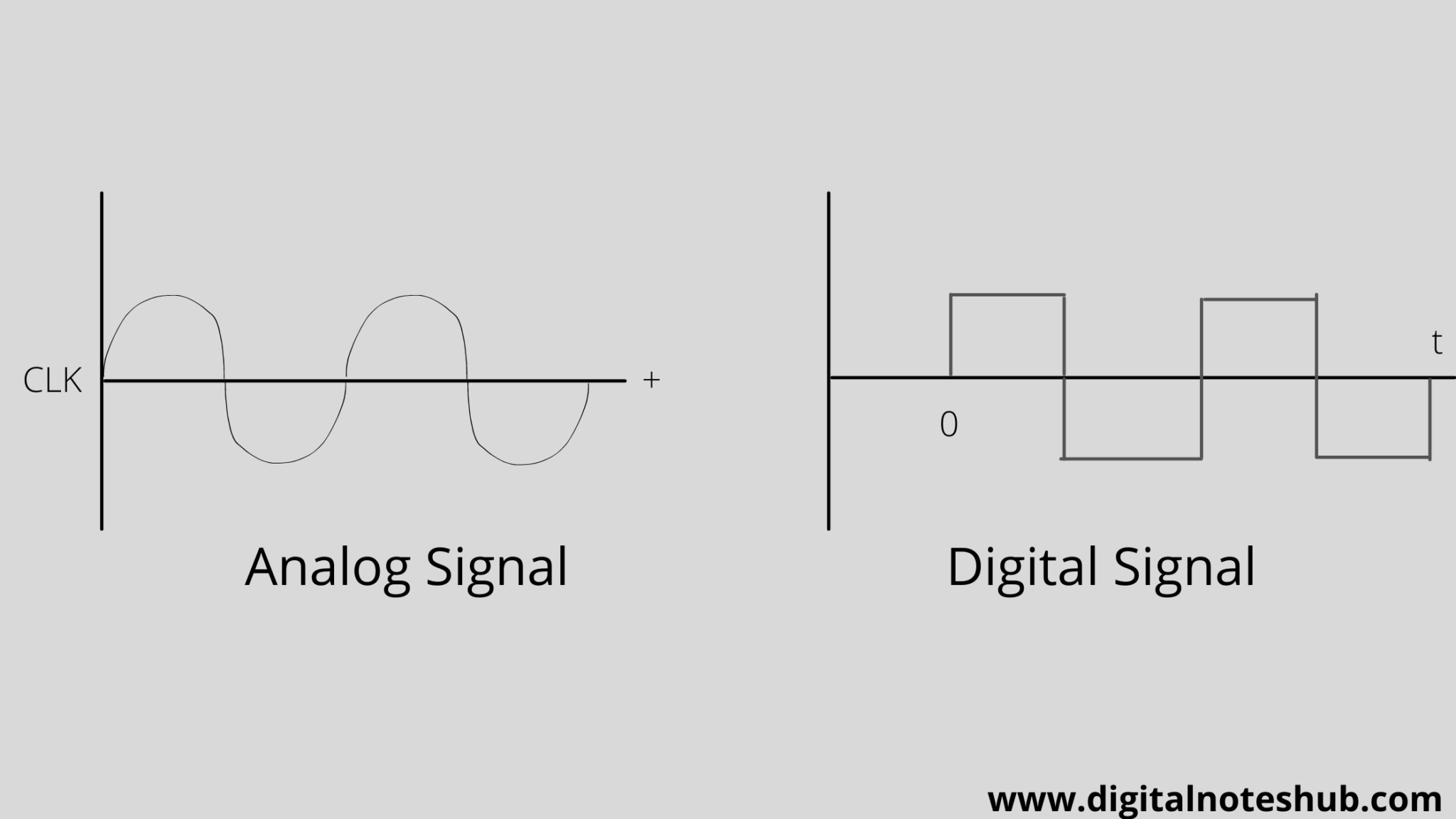
Analog And Digital Signals In Computer Networking 5 Differences An analog signal is a continuous signal, whereas digital signals are time separated signals. analog signal is denoted by sine waves while digital signals are denoted by square waves. analog signal uses a continuous range of values that help you to represent information; on the other hand, digital signal uses discrete 0 and 1 to represent. A signal is an electromagnetic or electrical current that carries data from one system or network to another. in electronics, a signal is often a time varying voltage that is also an electromagnetic wave carrying information, though it can take on other forms, such as current. there are two main types of signals used in electronics: analog and digital signals. this article discusses the.