
Comparison Of Bone Modeling And Remodeling Activities Bone Remodeling Bone is a dynamic tissue that is constantly adapting its structure. it is initially formed during development through either an intramembranous or endochondral ossification process. once formed, the bone grows and changes shape by modeling, a process in which either bone formation or bone resorption occurs on a given bone surface. bone remodeling functions to renew the skeleton and involves. Bone modeling occurs by removal of bone from one site and formation of bone at different sites. the bone regeneration process persists even after skeletal maturity by periodic replacement of old bone with newly formed bone at the same location, called remodeling.
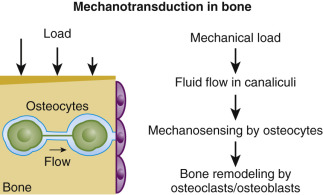
Bone Modeling And Remodeling Neupsy Key Bone modeling adapts structure to loading by changing bone size and shape and removes damage and so maintains bone strength. remodeling is initiated by damage producing osteocyte apoptosis, which signals the location of damage via the osteocyte canalicular system to endosteal lining cells that form the canopy of a bone remodeling compartment (brc). Despite the tremendous efforts of researchers studying bone remodeling for more than 50 years, the intrinsic spatial, biomolecular, and mechanotransduction complexities in bone remodeling continue. Bone modeling defines skeletal development and growth but continues throughout life and contributes to the periosteal expansion, just as remodeling based resorption is responsible for the medullary expansion seen in long bones with aging. treatments of osteoporosis affect remodeling as well as modeling. Bone remodeling is an essential, delicately balanced physiological process of coordinated activity of bone cells that remove and deposit new bone tissue in the adult skeleton. due to the complex nature of this process, many mathematical models of bone remodeling have been developed.
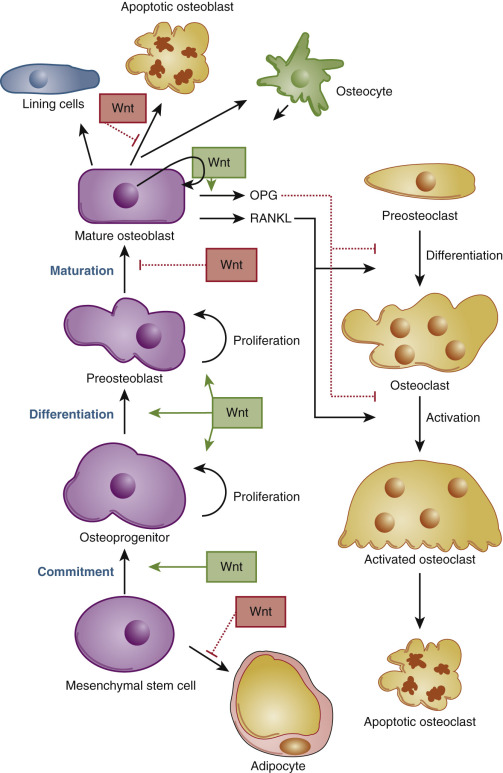
Bone Modeling And Remodeling Neupsy Key Bone modeling defines skeletal development and growth but continues throughout life and contributes to the periosteal expansion, just as remodeling based resorption is responsible for the medullary expansion seen in long bones with aging. treatments of osteoporosis affect remodeling as well as modeling. Bone remodeling is an essential, delicately balanced physiological process of coordinated activity of bone cells that remove and deposit new bone tissue in the adult skeleton. due to the complex nature of this process, many mathematical models of bone remodeling have been developed. This chapter discusses bone structure, cells, and extracellular matrix, the mechanical and chemical stimulants and inhibitors of bone activity, and the interaction among these components that leads to bone formation and remodeling both in physiologic situations and in response to injury. Remodeling based bone resorption and formation are coupled on the same surface and contribute to calcium homeostasis, while modeling based bone formation and resorption occur on different surfaces, such as during growth, to change skeletal shape; of importance, the aging skeleton can also include bone modeling (1, 2).

Pdf Modeling Bone Remodeling This chapter discusses bone structure, cells, and extracellular matrix, the mechanical and chemical stimulants and inhibitors of bone activity, and the interaction among these components that leads to bone formation and remodeling both in physiologic situations and in response to injury. Remodeling based bone resorption and formation are coupled on the same surface and contribute to calcium homeostasis, while modeling based bone formation and resorption occur on different surfaces, such as during growth, to change skeletal shape; of importance, the aging skeleton can also include bone modeling (1, 2).