Brain Mri Demonstrating Cerebellar Atrophy A Brain Magnetic Cerebral atrophy is the morphological presentation of brain parenchymal volume loss that is frequently seen on cross sectional imaging. rather than being a primary diagnosis, it is the common endpoint for a range of disease processes that affect the central nervous system. Brain atrophy (cerebral atrophy) is a loss of neurons and connections between neurons. different conditions cause brain atrophy, including cerebral palsy, dementia and infectious diseases. symptoms and severity of brain atrophy depend on the specific disease and location of damage. treatment involves managing the underlying disorder.

Figure Progressive Brain Atrophy Was Detected By Structural Mri First Dementia with lewy bodies (dlb): in contrast to other forms of dementia usually no specific abnormalities. so when we study the mr images we should score in a systematic way for global atrophy, focal atrophy and for vascular disease (i.e. infarcts, white matter lesions, lacunes). Brain atrophy (cerebral atrophy) is the loss of brain cells called neurons, as well as the connections that help cells communicate. it can result from different diseases that damage the brain. Introduction interpreting the diagnostic significance of moderate to severe global cerebral atrophy (gca) is a conundrum for many clinicians, who visually interpret structural brain magnetic resonance imaging (mri) in routine clinical practice. Brain imaging: when it comes to parenchymal volume loss in the brain, neuroimaging techniques such as mri (magnetic resonance imaging) and ct (computed tomography) scans come into play. these imaging methods can unveil brain atrophy and volume loss in specific regions.

Brain Mri Of The Patient At 64 Years Of Age December 2017 Brain Mri Introduction interpreting the diagnostic significance of moderate to severe global cerebral atrophy (gca) is a conundrum for many clinicians, who visually interpret structural brain magnetic resonance imaging (mri) in routine clinical practice. Brain imaging: when it comes to parenchymal volume loss in the brain, neuroimaging techniques such as mri (magnetic resonance imaging) and ct (computed tomography) scans come into play. these imaging methods can unveil brain atrophy and volume loss in specific regions. Here, we studied the clinical brain imaging characteristics of part focusing on neuroanatomical vulnerability by applying a previously validated multiregion visual atrophy scale. we analysed 26 cases with confirmed part with paired clinical magnetic resonance imaging (mri) acquisitions. Brain atrophy is one of the most common neuropathologic findings in patients infected with hiv. both head ct and structural brain mri can demonstrate brain atrophy (fig. 18.2 a). ct was used to evaluate hiv associated brain atrophy, primarily in clinical settings, over the last three decades. studies in perinatally hiv infected children using ct scan often showed cerebral atrophy, basal.

Brain Atrophy In Structural Mri Using Visual Rating Scales A Medial Here, we studied the clinical brain imaging characteristics of part focusing on neuroanatomical vulnerability by applying a previously validated multiregion visual atrophy scale. we analysed 26 cases with confirmed part with paired clinical magnetic resonance imaging (mri) acquisitions. Brain atrophy is one of the most common neuropathologic findings in patients infected with hiv. both head ct and structural brain mri can demonstrate brain atrophy (fig. 18.2 a). ct was used to evaluate hiv associated brain atrophy, primarily in clinical settings, over the last three decades. studies in perinatally hiv infected children using ct scan often showed cerebral atrophy, basal.
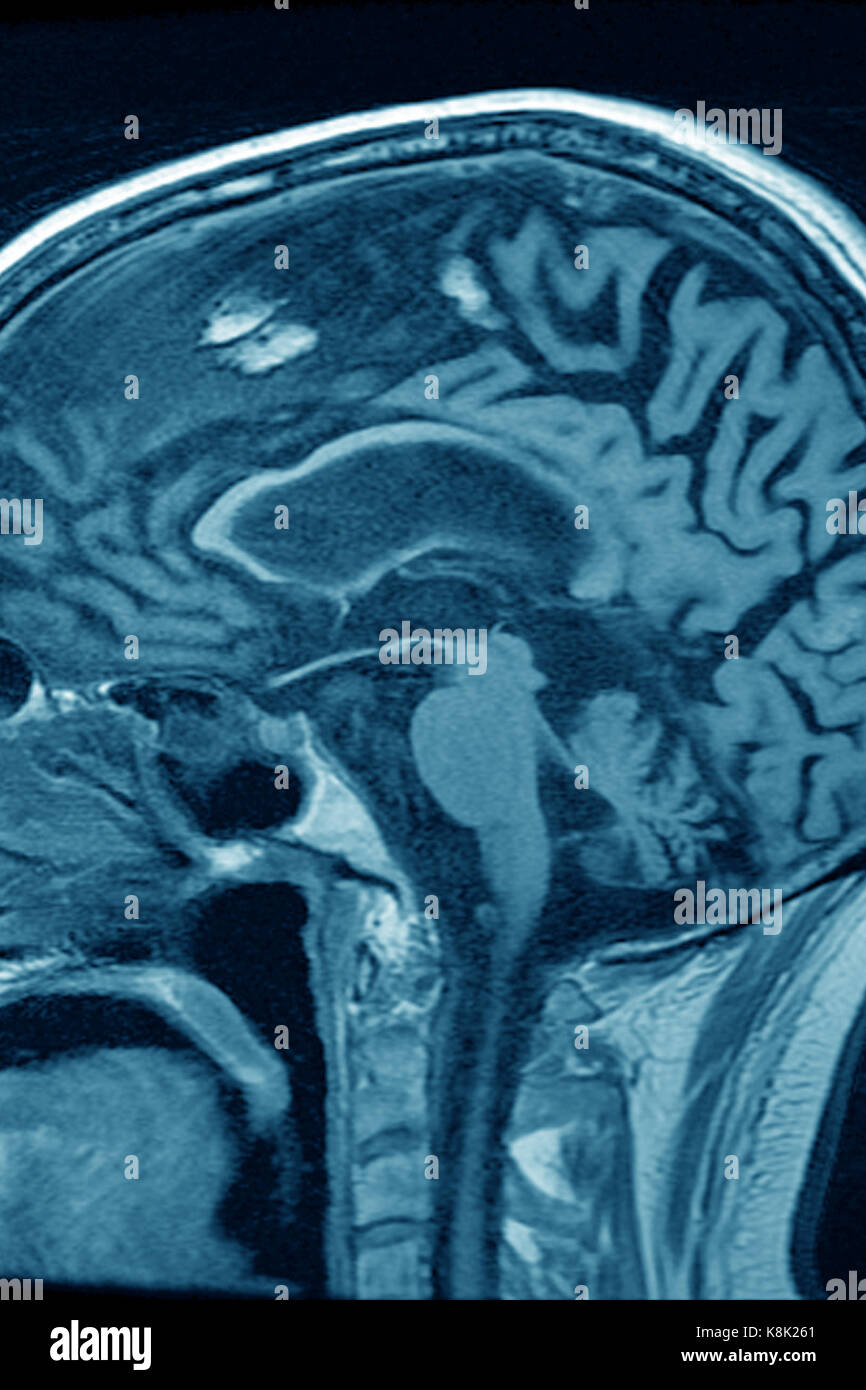
Cerebral Atrophy Mri Stock Photo 160229385 Alamy

Brain Atrophy Mri Stock Photo Download Image Now Alzheimer S