
Fluorescence Vs Phosphorescence What S The Difference This Vs That Fluorescence and phosphorescence are both forms of photoluminescence, where materials absorb light and then re emit it, but they differ in how long the glow. Phosphorescence: this phenomenon allows the rocks to absorb light and re emit it slowly, providing a long lasting glow. minerals like calcite and willemite are popular for their phosphorescent properties. fluorescence: unlike phosphorescence, fluorescing minerals glow only under a uv light source and stop glowing once the light is removed. sodalite and hackmanite are common examples.

Fluorescence Vs Phosphorescence What S The Difference Fluorescence, phosphorescence, incandescence and so on… with the single exception of iridescence, all of these phenomena involve the emission of energy in the form of light. with the exceptions of chemiluminescence (including bioluminescence) and radioluminescence, they involve also the initial absorption of energy. Phosphorescence is a phenomenon exhibited in several fluorescent minerals where the mineral continues to glow even after the uv light source has been removed. the glow slowly fades, and after several seconds (or minutes in a few cases) is no longer visible to the eye. only few minerals phosphoresce; phosphorescence is only noted as interesting mineral property, rarely as a diagnostic. Fluorescence typically results in shorter wavelengths (e.g., blue or green light), while phosphorescence can emit longer wavelengths (e.g., yellow or red light) due to different electronic transitions. how do temperature and environment affect fluorescence and phosphorescence?. Luminescence can be defined as the radiation emitted by a molecule or an atom on return to ground state from excited state after initial absorption of energy. both fluorescence and phosphorescence are type of photoluminescence which involves absorption of energy and excitation of atom to higher energy level followed by emission of.

Fluorescence Vs Phosphorescence Vs Luminescence Tabular Form Fluorescence typically results in shorter wavelengths (e.g., blue or green light), while phosphorescence can emit longer wavelengths (e.g., yellow or red light) due to different electronic transitions. how do temperature and environment affect fluorescence and phosphorescence?. Luminescence can be defined as the radiation emitted by a molecule or an atom on return to ground state from excited state after initial absorption of energy. both fluorescence and phosphorescence are type of photoluminescence which involves absorption of energy and excitation of atom to higher energy level followed by emission of. 153 likes, tiktok video from vt (@vt.physics): “can rocks really glow? fluorescence vs phosphorescence explained fluorescence and phosphorescence are both forms of photoluminescence, where materials absorb light and then re emit it, but they differ in how long the glow lasts. fluorescent materials glow almost immediately when exposed to light and stop glowing as soon as the light source is. Fluorescence and phosphorescence are two distinct processes that involve the emission of light by certain substances. while fluorescence is characterized by its short lived emission, dependence on excitation light, and sensitivity to environmental factors, phosphorescence exhibits persistence, phosphorescence delay, and a red shift in emitted.
Fluorescence Vs Phosphorescence How Light Emission Works 153 likes, tiktok video from vt (@vt.physics): “can rocks really glow? fluorescence vs phosphorescence explained fluorescence and phosphorescence are both forms of photoluminescence, where materials absorb light and then re emit it, but they differ in how long the glow lasts. fluorescent materials glow almost immediately when exposed to light and stop glowing as soon as the light source is. Fluorescence and phosphorescence are two distinct processes that involve the emission of light by certain substances. while fluorescence is characterized by its short lived emission, dependence on excitation light, and sensitivity to environmental factors, phosphorescence exhibits persistence, phosphorescence delay, and a red shift in emitted.
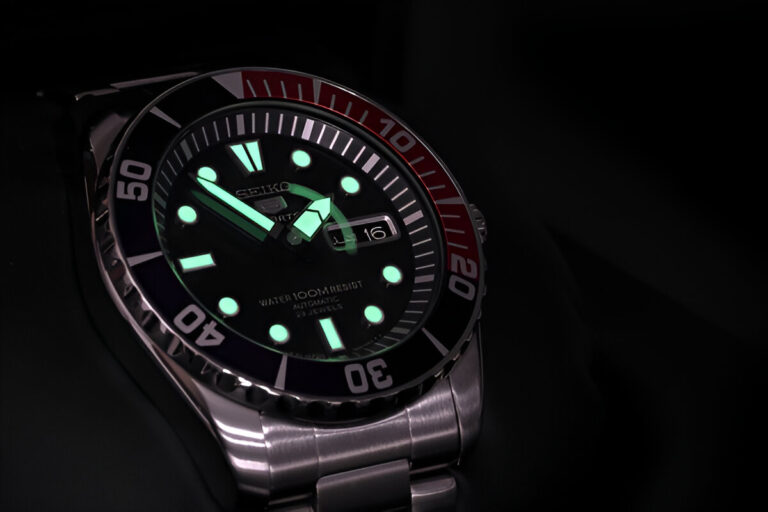

Fluorescence Vs Phosphorescence How Light Emission Works