
Checked Vs Unchecked Exception Java Architect Journey In java, an exception is an unwanted or unexpected event that occurs during the execution of a program, i.e., at run time, that disrupts the normal flow of the program’s instructions. in java, there are two types of exceptions: checked exception: these exceptions are checked at compile time, forcing the programmer to handle them explicitly. In this article, we discussed the difference between checked and unchecked exceptions. we also provided some code examples to show when to use checked or unchecked exceptions.

Java Checked And Unchecked Exceptions Example Codevscolor Learn the difference between checked vs unchecked exceptions in java, with simple explanations and examples. learn java exception handling best practices. An exception's type determines whether an exception is checked or unchecked. all exception types that are direct or indirect subclasses of class runtimeexception are unchecked exception. Java’s exception handling mechanism uses these two categories of exceptions to give developers a structured way to identify, catch, and handle errors. knowing the distinction between checked and unchecked exceptions helps in creating robust applications while also maintaining code clarity. what are exceptions in java?. Understanding java checked and unchecked exceptions exception handling is an essential aspect of any programming language, as it allows developers to handle unexpected situations that may arise.

Java Checked And Unchecked Exceptions Example Codevscolor Java’s exception handling mechanism uses these two categories of exceptions to give developers a structured way to identify, catch, and handle errors. knowing the distinction between checked and unchecked exceptions helps in creating robust applications while also maintaining code clarity. what are exceptions in java?. Understanding java checked and unchecked exceptions exception handling is an essential aspect of any programming language, as it allows developers to handle unexpected situations that may arise. In java, exceptions are either checked or unchecked. checked exceptions must be explicitly caught or propagated by the programmer, whereas unchecked exceptions are not required to be handled by the programmer (the programmer can let them automatically propagate). in this section, we will see two short programs. one containing code that potentially throws an unchecked exception and another that. Learn the key differences between checked and unchecked exceptions in java, along with practical examples and best practices.
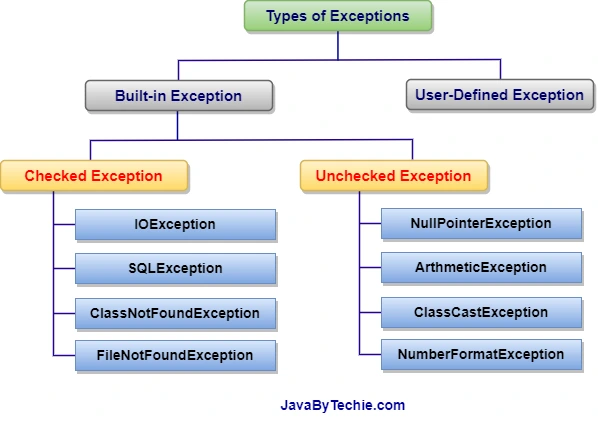
Checked Vs Unchecked Exception In Java Javabytechie In java, exceptions are either checked or unchecked. checked exceptions must be explicitly caught or propagated by the programmer, whereas unchecked exceptions are not required to be handled by the programmer (the programmer can let them automatically propagate). in this section, we will see two short programs. one containing code that potentially throws an unchecked exception and another that. Learn the key differences between checked and unchecked exceptions in java, along with practical examples and best practices.