
Cross Section Of The Mar Del Plata Canyon Head Area At The Location Of Cross section of the mar del plata canyon head area at the location of sites t300 and geob13830, which are separated one from each other by cold water coral (cwc) mounds. Cross‐section of the mar del plata canyon head area at the location of sites t300 and geob13830, which are separated one from each other by cold‐water coral (cwc) mounds. upper left corner.

Cross Section Of The Mar Del Plata Canyon Head Area At The Location Of The head of the mar del plata canyon is located in the middle slope, mid way between the la plata and the ewing terrace (fig. 3). the canyon has a length of ∼130 km and is almost 18 km wide in the center of the ewing terrace. The mar del plata (mdp) canyon at the argentine continental margin is incorporated into a major contourite depositional system, built by the incursion of southern sourced water masses affecting the seafloor at different waters depths. the new sedimentological, morphological and hydro acoustic data provide novel insights into contour and turbidity current interactions in mid slope (blind. Since sedimentation processes in the mar del plata canyon indicate a response to changes of aaiw contour current strength related to late glacial holocene variability, the sediments deposited within the canyon are a great climate archive for paleoceanographic reconstructions. Find local businesses, view maps and get driving directions in google maps.

Cross Section B B Through The La Plata Canyon Area Showing Location Since sedimentation processes in the mar del plata canyon indicate a response to changes of aaiw contour current strength related to late glacial holocene variability, the sediments deposited within the canyon are a great climate archive for paleoceanographic reconstructions. Find local businesses, view maps and get driving directions in google maps. A variety of gravel to cobble sized rocks, recovered from the mar del plata canyon area and interpreted as ice rafted debris, represents the first evidence that large icebergs have floated in the falkland (malvinas) current from the southern polar high latitudes far northward. The head region of the mar del plata canyon does not show clear indications of relatively recent failures close to the head region. a possible explanation is the location of the head region on the broad and flat terrace, which might have stopped or significantly slowed down further headward erosion of the canyon.

The Study Area And Rock Distribution A Bathymetric Map Of The Mar A variety of gravel to cobble sized rocks, recovered from the mar del plata canyon area and interpreted as ice rafted debris, represents the first evidence that large icebergs have floated in the falkland (malvinas) current from the southern polar high latitudes far northward. The head region of the mar del plata canyon does not show clear indications of relatively recent failures close to the head region. a possible explanation is the location of the head region on the broad and flat terrace, which might have stopped or significantly slowed down further headward erosion of the canyon.
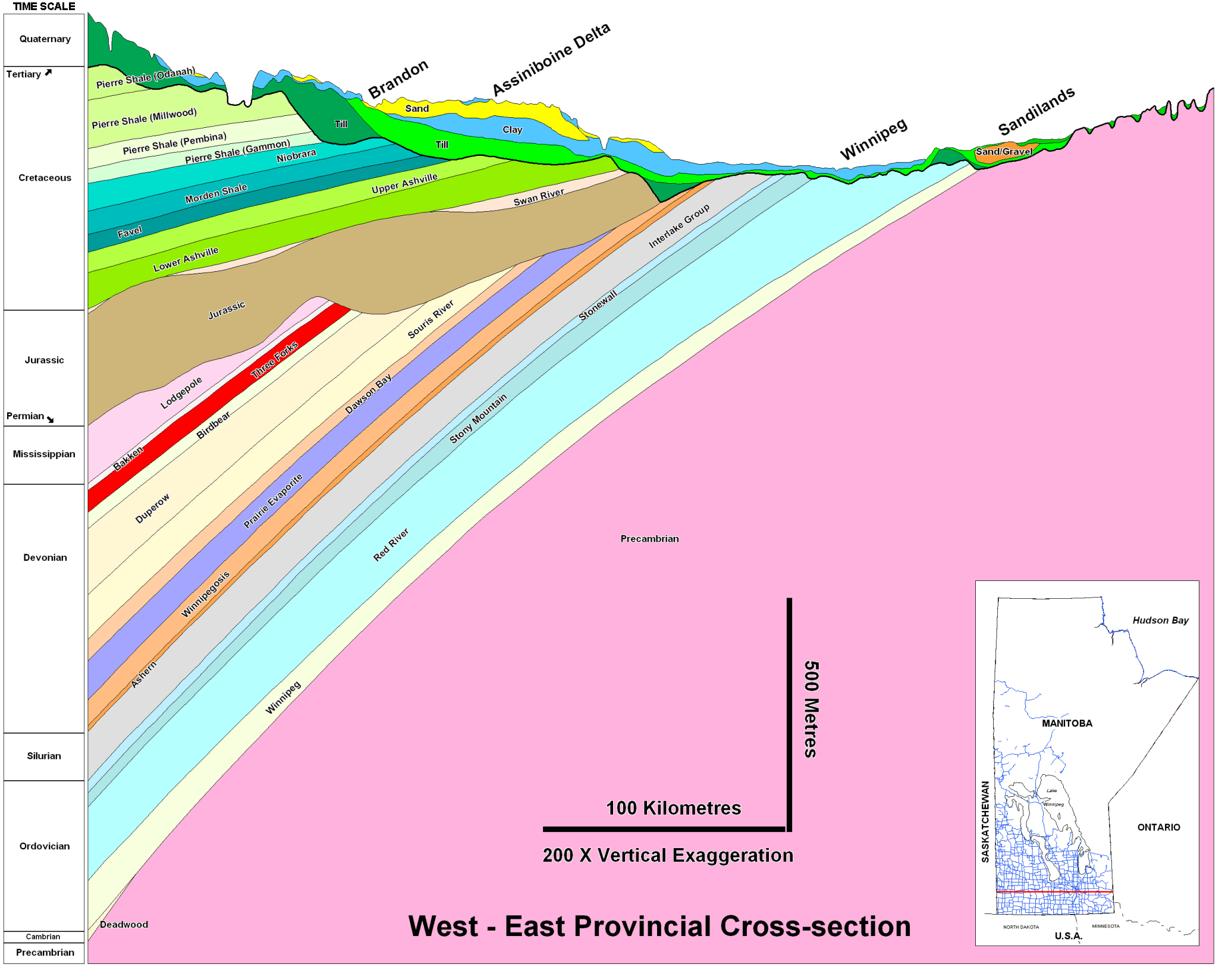
Large Cross Section Map Of Manitoba Geological Survey Mineral

Map Of Mar Del Plata Illustrating Location Of Study Area And The

A Measurements Of High Turbidity At The Southern Fl Ank Of The Mar