
Design And Comparison Migration Between Ipv4 And Ipv6 Transition Abstract and figures ipv4 which is the old version of internet protocol has a new successor named ip next generation (ipng) or ipv6 developed by internet engineering task force (ietf). The purpose of this study is to configure the network with address allocation, router configuration with ospf routing protocol, implementation of dual stack, tunnels namely manual tunnel, gre ipv4 tunnel, isatap and 6to4 tunnel that allows the communication between the ipv4 and ipv6 network hosts.
Pdf Design And Comparison Migration Between Ipv4 And Ipv6 Transition Dual stack is one of the ipv4 ipv6 compatible mechanism by running both ipv4 stack and ipv6 stack in a single node. 6 to 4 tunneling mechanism encrypts ipv6 packets in ipv4 packets to make communications possible, from ipv6 network over ipv4 network. this has been configured using gns3 simulator and packet tracer 6.1. The migration from ipv4 to ipv6 is a something of an evident in the long term, however, ipv6 does not only provides ip address space there are some other advantages including long term cost savings and better performance. 2.1 what is the difference between ipv4 and ipv6? internet protocol version 4 (ipv4) is the fourth version of the internet protocol used to identify ip addresses on a network. This thesis focuses on the design and implementation issues that accompany a migration of the monterey security enhanced architecture (mysea) from internet protocol version four (ipv4) to ipv6. the research for this thesis consists of two major parts: a functional comparison between the ipv4 and ipv6 designs, and a prototype implementation of mysea in an ipv6 environment.
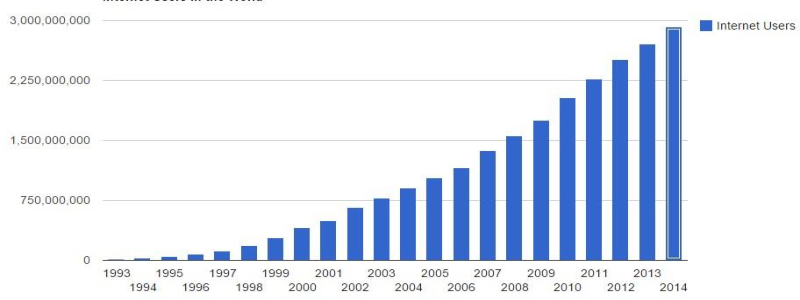
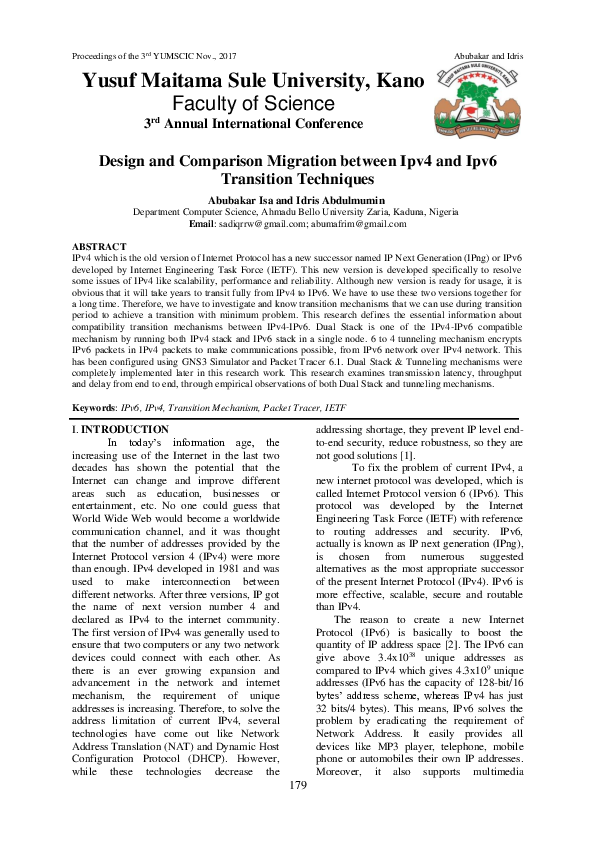
Figure 4 From Design And Comparison Migration Between Ipv4 And Ipv6 2.1 what is the difference between ipv4 and ipv6? internet protocol version 4 (ipv4) is the fourth version of the internet protocol used to identify ip addresses on a network. This thesis focuses on the design and implementation issues that accompany a migration of the monterey security enhanced architecture (mysea) from internet protocol version four (ipv4) to ipv6. the research for this thesis consists of two major parts: a functional comparison between the ipv4 and ipv6 designs, and a prototype implementation of mysea in an ipv6 environment. This paper discusses ways to migrate from ipv4 to ipv6,it uses gns3 to simulate three ways used in transition to ip6 and svolarwinds to analysis three parameters of network performance latency, packet loss.we tried to present in this paper a groundwork examination of ipv6 in network migration and performance analysis, in which determine that. The reason to create a new internet protocol (ipv6) is basically to boost the quantity of ip address space [2]. the ipv6 can give above 3.4x1038 unique addresses as compared to ipv4 which gives 4.3x109 unique addresses (ipv6 has the capacity of 128 bit 16 bytes’ address scheme, whereas ipv4 has just 32 bits 4 bytes). this means, ipv6 solves the problem by eradicating the requirement of.
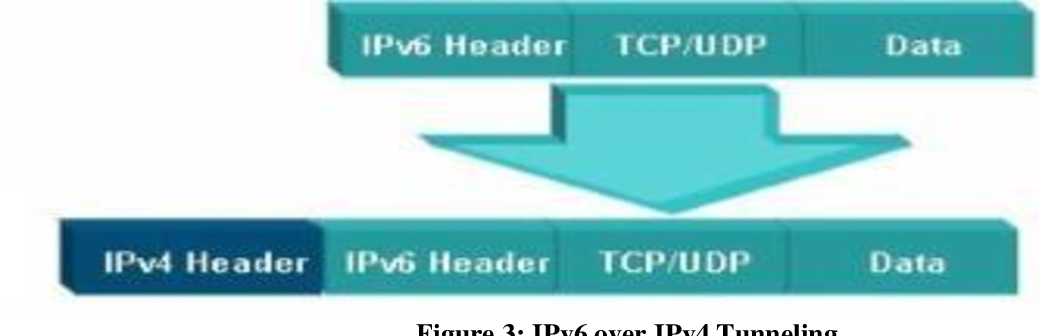
Figure 4 From Design And Comparison Migration Between Ipv4 And Ipv6 This paper discusses ways to migrate from ipv4 to ipv6,it uses gns3 to simulate three ways used in transition to ip6 and svolarwinds to analysis three parameters of network performance latency, packet loss.we tried to present in this paper a groundwork examination of ipv6 in network migration and performance analysis, in which determine that. The reason to create a new internet protocol (ipv6) is basically to boost the quantity of ip address space [2]. the ipv6 can give above 3.4x1038 unique addresses as compared to ipv4 which gives 4.3x109 unique addresses (ipv6 has the capacity of 128 bit 16 bytes’ address scheme, whereas ipv4 has just 32 bits 4 bytes). this means, ipv6 solves the problem by eradicating the requirement of.
Figure 6 From Design And Comparison Migration Between Ipv4 And Ipv6

Table 1 From Design And Comparison Migration Between Ipv4 And Ipv6