
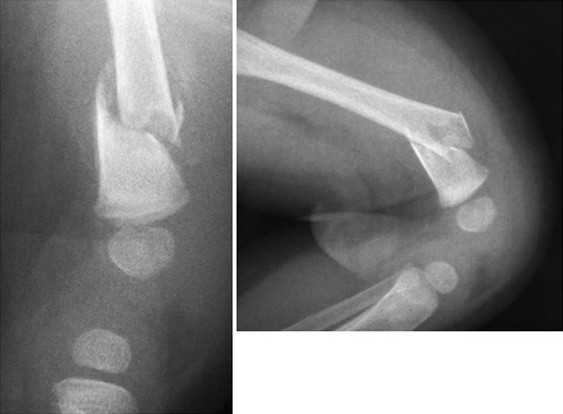
Musculoskeletal Disorders Fractures Pdf Bone Injury 4) list 4 conditions with similar presentation to child abuse (shownotes) 5) list causes of pathologic fractures in children. 6) what is the utility of blood culture, esr and crp in a child with suspected septic arthritis of the hip? 7) what the mechanism of a lateral elbow condyle fracture and how are they managed? (shownotes). Fractures are common injuries in children, occurring in 10 25% of cases. the most common sites are the distal forearm, supracondylar humerus, and lateral condyle of the humerus. etiologies include falls, bicycle accidents, sports injuries, birth related fractures, stress fractures, and child abuse. treatment depends on the type and location of the fracture, with options including closed.
Children S Fractures Musculoskeletal Key This document provides an overview of pediatric musculoskeletal disorders including: kyphosis, lordosis, and scoliosis their causes, types, and treatment including bracing and spinal fusion surgery. common fractures in children and their treatment involving reduction, retention with casting or traction. rheumatoid arthritis in children including the different classifications of. Summarize common diagnostic tests (laboratory and radiology) utilized when evaluating a musculoskeletal concern. compare and contrast the pathophysiology, clinical presentation, management, and follow up of the most common musculoskeletal concerns seen in primary care. describe education needs related to the most common musculoskeletal concerns. The pediatric musculoskeletal system differs from the adult musculoskeletal system in many ways, including anatomical, physiological, and psychological differences. these differences will result in differences in clinical and radiological presentation. in this chapter the specific knowledge essential for radiologists who deal with musculoskeletal diseases in children will be discussed with a. A broad differential diagnosis for a child with recurrent fractures includes trauma (both accidental and inflicted), genetic disorders, endocrine disorders, nutritional deficiency, chronic renal disease, medication or invasive neoplastic bone fragility; key investigations include laboratory investigations assessing mineral metabolism, plain.

Paediatric Fractures Pdf The pediatric musculoskeletal system differs from the adult musculoskeletal system in many ways, including anatomical, physiological, and psychological differences. these differences will result in differences in clinical and radiological presentation. in this chapter the specific knowledge essential for radiologists who deal with musculoskeletal diseases in children will be discussed with a. A broad differential diagnosis for a child with recurrent fractures includes trauma (both accidental and inflicted), genetic disorders, endocrine disorders, nutritional deficiency, chronic renal disease, medication or invasive neoplastic bone fragility; key investigations include laboratory investigations assessing mineral metabolism, plain. Musculoskeletal disorders and treatment case report: open access diaphyseal femur fractures in children: a preliminary study comparing the use of elastic stable intramedullary nailing (esin. The anatomy of the pediatric musculoskeletal system is unique and reflects the active growth and development that occurs during childhood. fracture classification, treatment approach, and types of complications are directly related to this unique anatomy. in general, both injury patterns and treatment approaches in children in whom closure of the physes (growth plates) has already occurred is.

Fractures In Children Ppt Musculoskeletal disorders and treatment case report: open access diaphyseal femur fractures in children: a preliminary study comparing the use of elastic stable intramedullary nailing (esin. The anatomy of the pediatric musculoskeletal system is unique and reflects the active growth and development that occurs during childhood. fracture classification, treatment approach, and types of complications are directly related to this unique anatomy. in general, both injury patterns and treatment approaches in children in whom closure of the physes (growth plates) has already occurred is.