
Future Forecast 2025 A Deep Dive Into The Next Generation Second Home The class template std::future provides a mechanism to access the result of asynchronous operations: . an asynchronous operation (created via std::async, std::packaged task, or std::promise) can provide a std::future object to the creator of that asynchronous operation. A future<t> is something that in the future will give you a t. lets try a different explanation: a future represents the result of an asynchronous operation, and can have two states: uncompleted or completed. most likely, as you aren't doing this just for fun, you actually need the results of that future<t> to progress in your application. you.

Future Forecast 2025 A Deep Dive Into The Next Generation Second Home If the future is the result of a call to std::async that used lazy evaluation, this function returns immediately without waiting. this function may block for longer than timeout duration due to scheduling or resource contention delays. Atomic compare exchange weak atomic compare exchange weak explicit atomic compare exchange strong atomic compare exchange strong explicit. Lazy evaluation is performed: . the first call to a non timed wait function on the std::future that std::async returned to the caller will evaluate invoke (std:: move (g), std:: move (xyz)) in the thread that called the waiting function (which does not have to be the thread that originally called std::async), where. It is valid to move from a future object for which valid() is false. contents . 1 parameters; 2 return value;.

Future Forecast 2025 A Deep Dive Into The Next Generation Second Home Lazy evaluation is performed: . the first call to a non timed wait function on the std::future that std::async returned to the caller will evaluate invoke (std:: move (g), std:: move (xyz)) in the thread that called the waiting function (which does not have to be the thread that originally called std::async), where. It is valid to move from a future object for which valid() is false. contents . 1 parameters; 2 return value;. The get member function waits (by calling wait()) until the shared state is ready, then retrieves the value stored in the shared state (if any). A future statement is a directive to the compiler that a particular module should be compiled using syntax or semantics that will be available in a specified future release of python. the future statement is intended to ease migration to future versions of python that introduce incompatible changes to the language.

Future Forecast 2025 A Deep Dive Into The Next Generation Second Home The get member function waits (by calling wait()) until the shared state is ready, then retrieves the value stored in the shared state (if any). A future statement is a directive to the compiler that a particular module should be compiled using syntax or semantics that will be available in a specified future release of python. the future statement is intended to ease migration to future versions of python that introduce incompatible changes to the language.

Future Forecast 2025 A Deep Dive Into The Next Generation Second Home

Future Forecast 2025 A Deep Dive Into The Next Generation Second Home
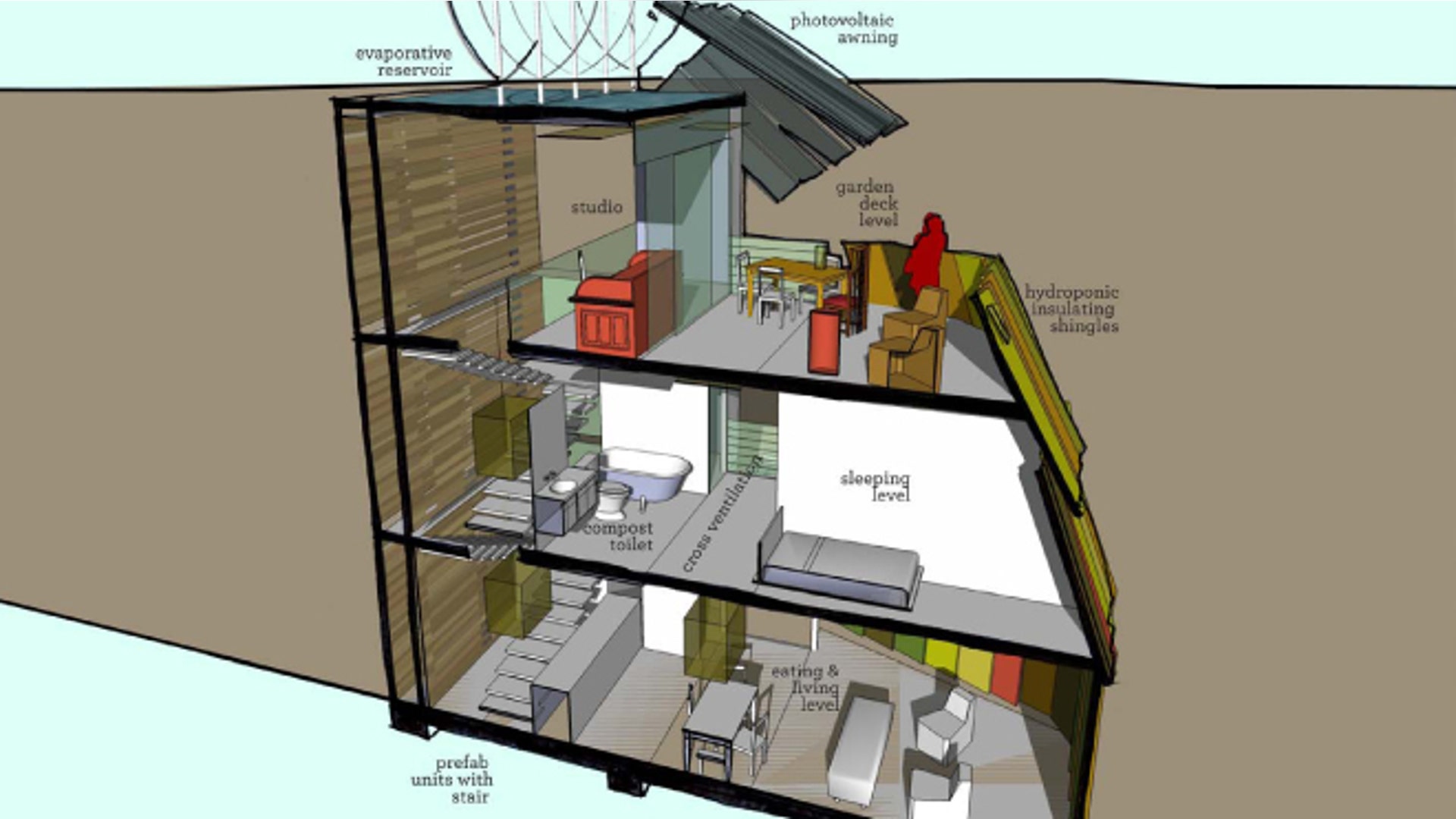
The Future Home Of 2025 Fox News