
Hash Tables Hash Functions Pdf Mathematical Proof Expected Value Typically it is correct to say that the output of a hash function is a hash (aslo known as a hash value or a hash sum). however, sometimes people refer to the function itself as a hash. this is technically incorrect, but usually overlooked as it is generally understood (in context) that the person meant hash function. If the data set consists of sha 1 hashes strings that are deliberately chosen so that their sha 1 hash starts with the byte 0, then taking the first byte doesn't satisfy randomness either. in fact, there is no hash function that satisfies randomness for all datasets: for any hash function (with at least two buckets), a data set consisting.

Hash Tables 2 Pdf Computing Algorithms In fact, this is a more general question. in a lot of the old (and current) literature on hashing, the advice is that the hash function should be taken modulo a prime number (e.g. hash tables should have a prime size). for a hash function to be as useful as possible, its range needs to be relatively uniform, even when its domain is not. As far as i and this page know, there are no collisions (2 inputs with the same output) found in sha 256 (yet). what would happen if a collision were to be found, 1. would it be easier to. Hash值是通过一个计算函数把难以比较的字符串或者其他类型的数据映射成一个整数,最常用的就是映射a~z的hash值,变成hash[(str(i) ‘a’]这个数是一个十进制数,这个十进制数把它映射到0 25,也就是数组下标,但通常来说是映射成1 26,因为方便计算,这是最简单的hash值,然后这个hash值映射成下标. The answer to your second question, about the time complexity of computing the hash function, is that it takes time linear in the size of the data item. most hash functions used in this context are "rolling hash", in which a small has value is being updated as the data item is read. this ensures that the time complexity is indeed linear.

9 Hash Function And Hash Table Pdf Database Index Array Data Hash值是通过一个计算函数把难以比较的字符串或者其他类型的数据映射成一个整数,最常用的就是映射a~z的hash值,变成hash[(str(i) ‘a’]这个数是一个十进制数,这个十进制数把它映射到0 25,也就是数组下标,但通常来说是映射成1 26,因为方便计算,这是最简单的hash值,然后这个hash值映射成下标. The answer to your second question, about the time complexity of computing the hash function, is that it takes time linear in the size of the data item. most hash functions used in this context are "rolling hash", in which a small has value is being updated as the data item is read. this ensures that the time complexity is indeed linear. I am looking for a good way to hash the two numbers together into a deterministic 64 bit integer. tabular hashing with randomly generated keys works wonderfully, but i was wondering if there was a faster non iterative alternative. the target is to minimize the number of collisions between two unique sets of a and b. The hash nodes are a little bigger, but all of the hash values to check are in the same cache line. if you're particularly lucky, the compiler may even turn this into a simd operation for you. if the hash table is stored on disk, variations of this technique can improve locality much more than open addressing, at the cost of using extra space.
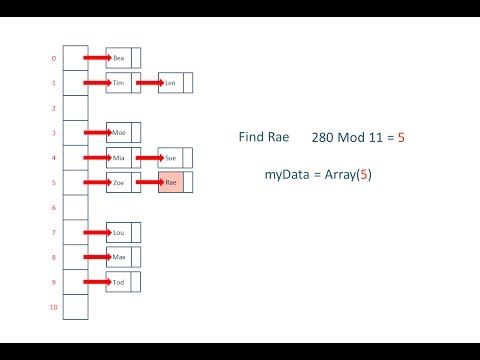
Hash Tables And Hash Functions Empower Youth I am looking for a good way to hash the two numbers together into a deterministic 64 bit integer. tabular hashing with randomly generated keys works wonderfully, but i was wondering if there was a faster non iterative alternative. the target is to minimize the number of collisions between two unique sets of a and b. The hash nodes are a little bigger, but all of the hash values to check are in the same cache line. if you're particularly lucky, the compiler may even turn this into a simd operation for you. if the hash table is stored on disk, variations of this technique can improve locality much more than open addressing, at the cost of using extra space.