
Checked Vs Unchecked Exceptions In Java Checked exceptions represent invalid conditions in areas outside the immediate control of the program like memory, network, file system, etc. any checked exception is a subclass of exception. unlike unchecked exceptions, checked exceptions must be either caught by the caller or listed as part of the method signature using the throws keyword. In this article, we discussed the difference between checked and unchecked exceptions. we also provided some code examples to show when to use checked or unchecked exceptions.
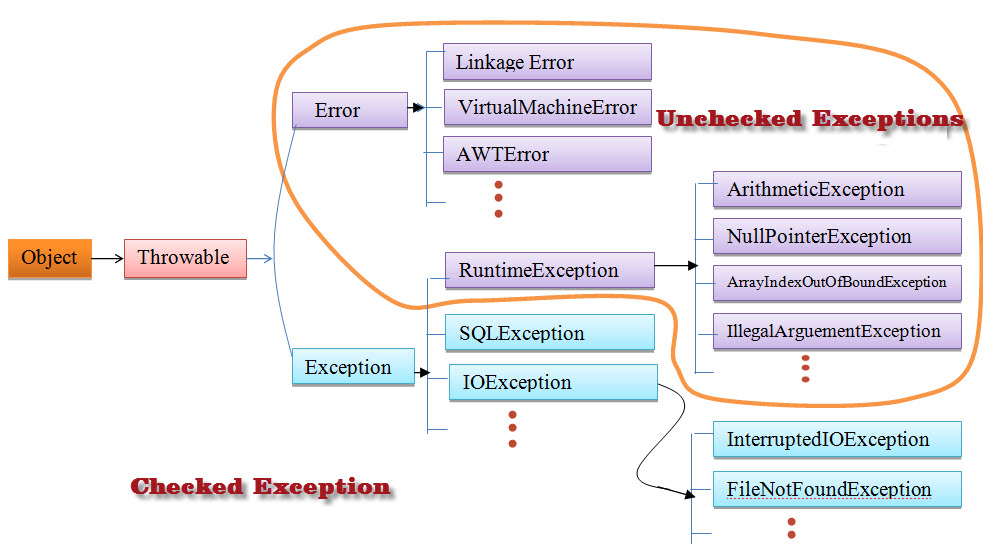
Checked Exceptions Vs Unchecked Exceptions In Java Java4coding Learn the difference between checked vs unchecked exceptions in java, with simple explanations and examples. learn java exception handling best practices. Joshua bloch in "effective java" said that use checked exceptions for recoverable conditions and runtime exceptions for programming errors (item 58 in 2nd edition) let's see if i understan. Understanding the difference between checked vs. unchecked exceptions is vital for java professionals aiming to write resilient, maintainable code. by handling exceptions effectively and applying best practices, developers can ensure that their applications provide a smooth user experience, even in the face of unexpected runtime issues. In java, exceptions are either checked or unchecked. checked exceptions must be explicitly caught or propagated by the programmer, whereas unchecked exceptions are not required to be handled by the programmer (the programmer can let them automatically propagate). in this section, we will see two short programs. one containing code that potentially throws an unchecked exception and another that.
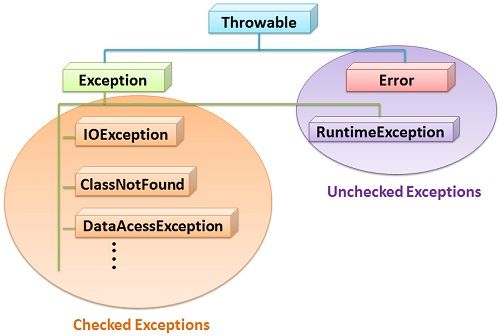
Checked Exceptions Vs Unchecked Exceptions Riset Understanding the difference between checked vs. unchecked exceptions is vital for java professionals aiming to write resilient, maintainable code. by handling exceptions effectively and applying best practices, developers can ensure that their applications provide a smooth user experience, even in the face of unexpected runtime issues. In java, exceptions are either checked or unchecked. checked exceptions must be explicitly caught or propagated by the programmer, whereas unchecked exceptions are not required to be handled by the programmer (the programmer can let them automatically propagate). in this section, we will see two short programs. one containing code that potentially throws an unchecked exception and another that. Checked exceptions vs. unchecked exceptions in java. any exception which is must to handle or catch it while writing the program is called checked exception. any exception which is not mandatory to handle or catch it while writing the program or executing the program is called unchecked exception. Inheriting from runtimeexception sets apart checked vs. unchecked exceptions in java, and that small change can have a big impact on your code.
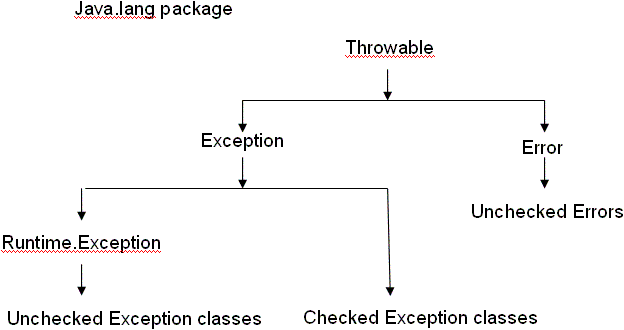
Checked Exceptions Vs Unchecked Exceptions Checked exceptions vs. unchecked exceptions in java. any exception which is must to handle or catch it while writing the program is called checked exception. any exception which is not mandatory to handle or catch it while writing the program or executing the program is called unchecked exception. Inheriting from runtimeexception sets apart checked vs. unchecked exceptions in java, and that small change can have a big impact on your code.