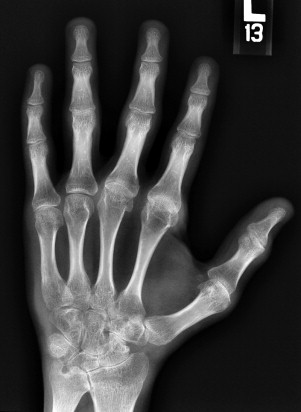
Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis Musculoskeletal Key Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis, also known as JA, causes the immune system to become overactive and cause damage to the body The most common area would be the joints WebMD provides information on popular vitamins and supplements including side effects, drug interactions, user ratings and reviews, medication over dose, warnings, and uses
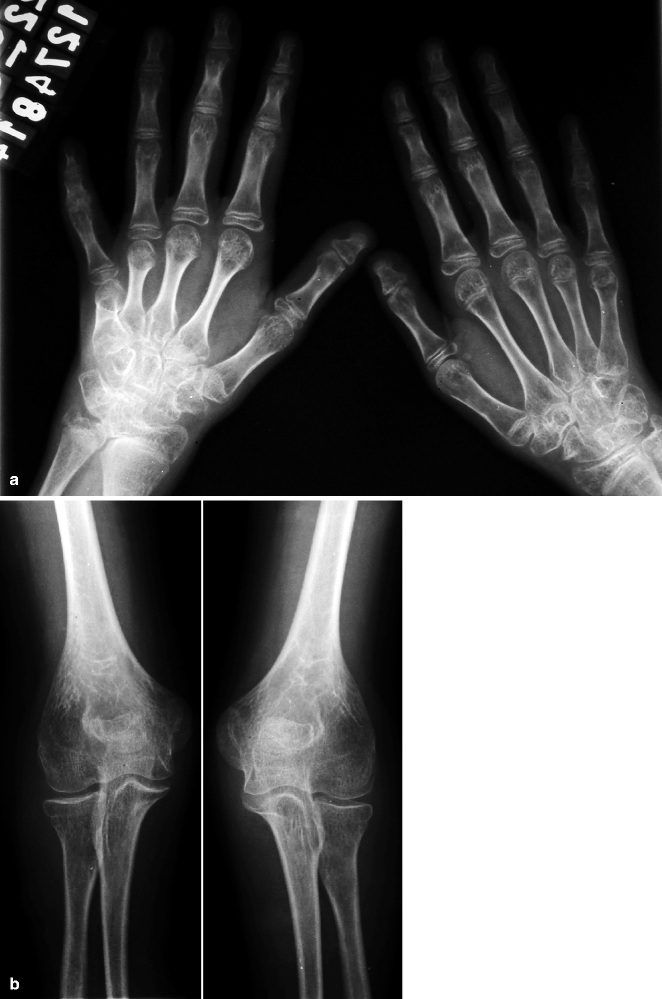
Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis Musculoskeletal Key DUBLIN--(BUSINESS WIRE)--The "Systemic Idiopathic Juvenile Arthritis - Pipeline Review, H2 2018" drug pipelines has been added to ResearchAndMarketscom's offering Systemic Idiopathic Juvenile Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis (JIA) is a relatively rare disease, affecting 30 to 150 children per 100,000 per year in Europe1 "Systemic JIA is a specific type of juvenile idiopathic arthritis Juvenile idiopathic arthritis (JIA) also known as a pediatric rheumatic disease, is the most common type of arthritis found in children under the age of 16 years Some children may experience Juvenile idiopathic arthritis (JIA) is a childhood immune disease where the immune system attacks the body, in particular the lining of the joints It is the most common type of arthritis in children
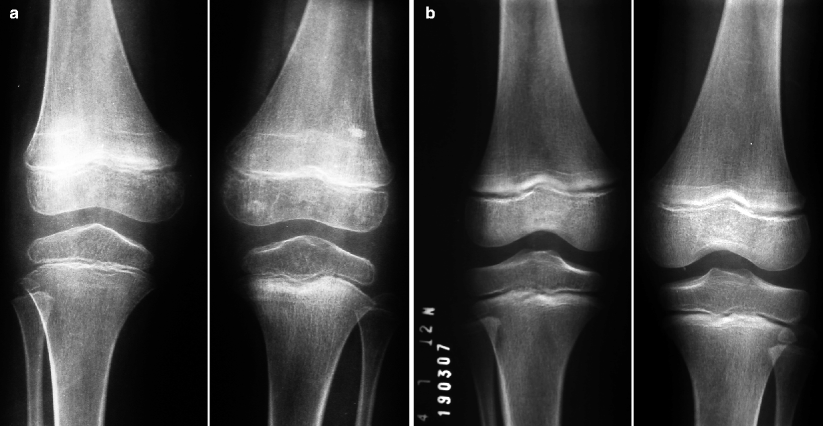
Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis Musculoskeletal Key Juvenile idiopathic arthritis (JIA) also known as a pediatric rheumatic disease, is the most common type of arthritis found in children under the age of 16 years Some children may experience Juvenile idiopathic arthritis (JIA) is a childhood immune disease where the immune system attacks the body, in particular the lining of the joints It is the most common type of arthritis in children March 13, 2012 — The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has okayed Pfizer's decision to stop a long-term postmarketing safety study of celecoxib (Celebrex) in patients with juvenile
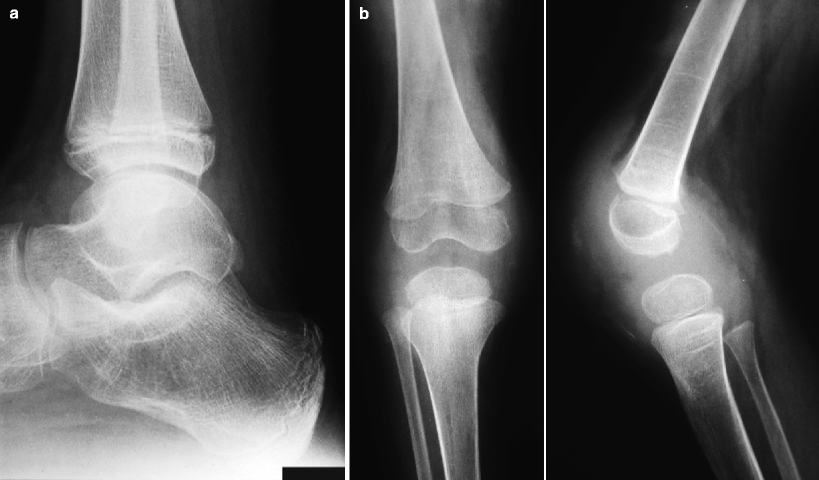
Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis Musculoskeletal Key March 13, 2012 — The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has okayed Pfizer's decision to stop a long-term postmarketing safety study of celecoxib (Celebrex) in patients with juvenile