
Meiosis Basic Anatomy And Physiology Biochemistry Notes Meiosis Updated meiosis video. join the amoeba sisters as they explore the meiosis stages with vocabulary including chromosomes, centromeres, centrioles, spindle fibers, and crossing over. Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like interphase, mitosis, sexual reproduction and more.
Meiosis About Meiosis Updated meiosis video. join the amoeba sisters as they explore the meiosis stages with vocabulary including chromosomes, centromeres, centrioles, spindle fibers, and crossing over. Meiosis (updated)be the first to ask a question about this topic. Learn about meiosis in cells. get the definition, a diagram and list of steps, and look at its function in biology. Meiosis articles from across nature portfolio meiosis is the generation of germ cells (eggs and sperm). in meiosis, dna replication is followed by two division cycles: meiosis i, which segregates.
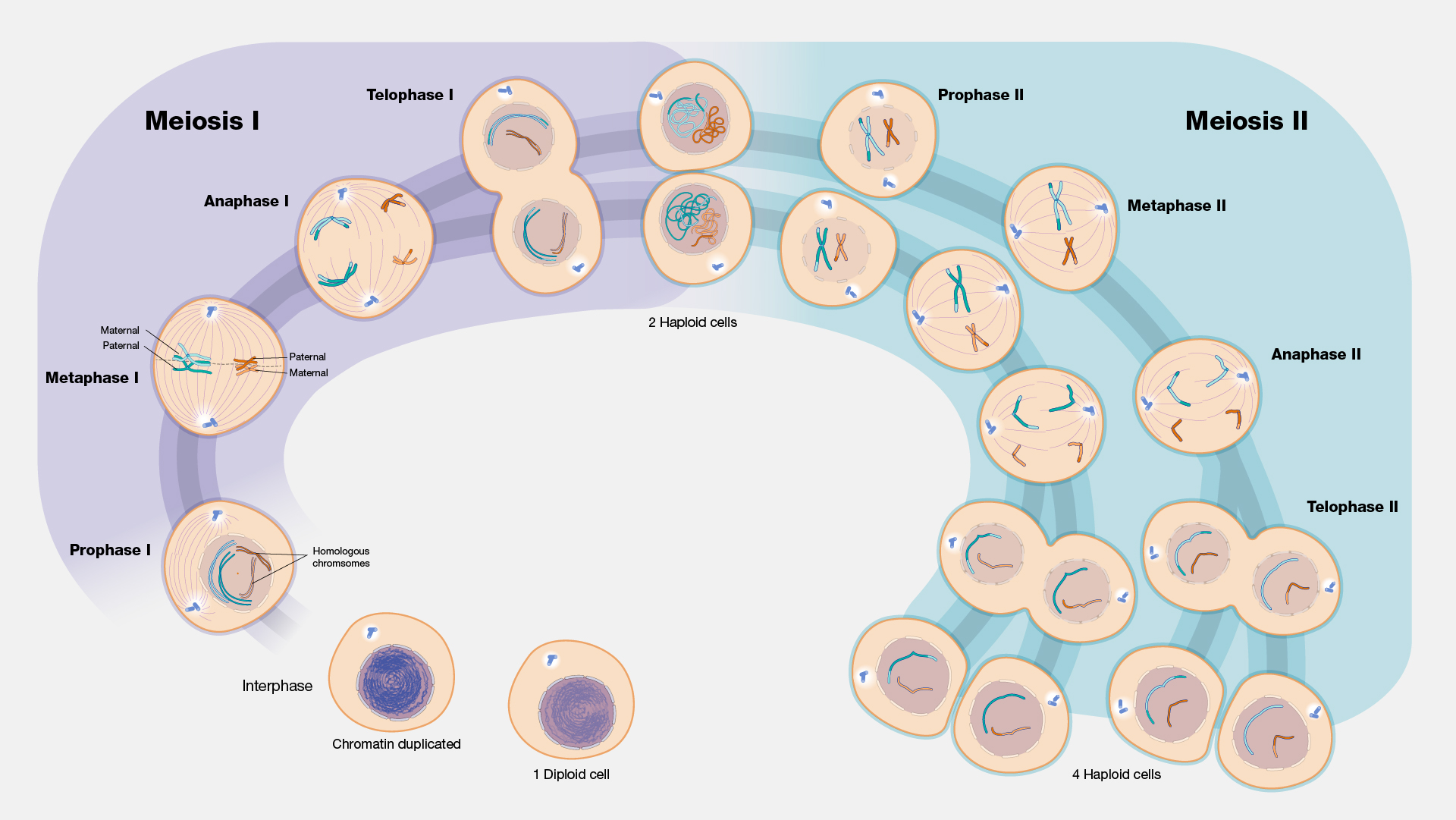
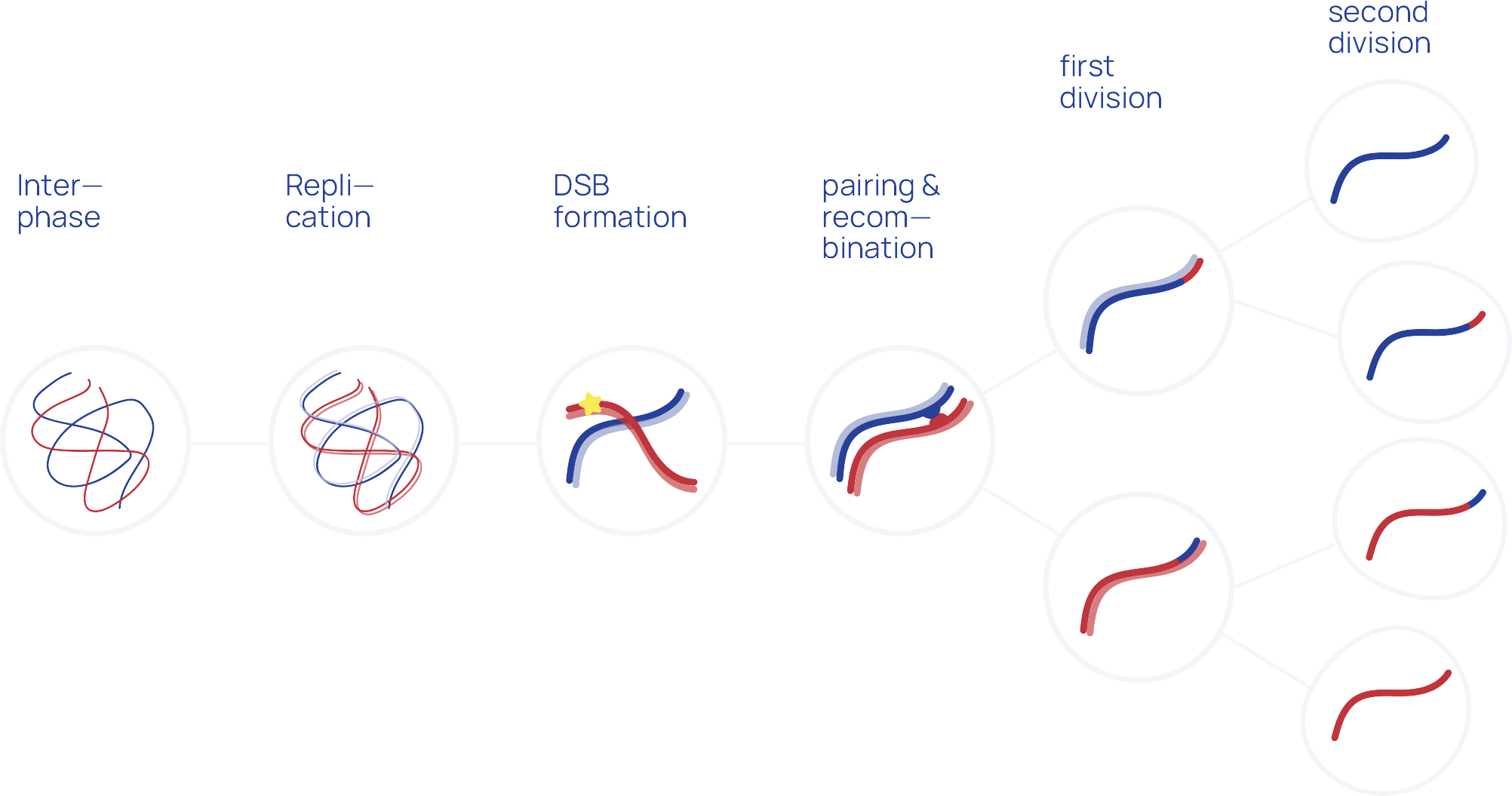
Meiosis Learn about meiosis in cells. get the definition, a diagram and list of steps, and look at its function in biology. Meiosis articles from across nature portfolio meiosis is the generation of germ cells (eggs and sperm). in meiosis, dna replication is followed by two division cycles: meiosis i, which segregates. Updated meiosis video. join the amoeba sisters as they explore the meiosis stages with vocabulary including chromosomes, centromeres, centrioles, spindle fibers, and crossing over. Meiosis is an essential event that generates haploid gametes from diploid progenitors in all sexually reproducing organisms. it involves a single round of dna replication followed by two rounds of chromosome segregation: separating homologous chromosomes (homologs; meiosis i [mi]), then sister chromatids (meiosis ii [mii]).
Meiosis Updated meiosis video. join the amoeba sisters as they explore the meiosis stages with vocabulary including chromosomes, centromeres, centrioles, spindle fibers, and crossing over. Meiosis is an essential event that generates haploid gametes from diploid progenitors in all sexually reproducing organisms. it involves a single round of dna replication followed by two rounds of chromosome segregation: separating homologous chromosomes (homologs; meiosis i [mi]), then sister chromatids (meiosis ii [mii]).