
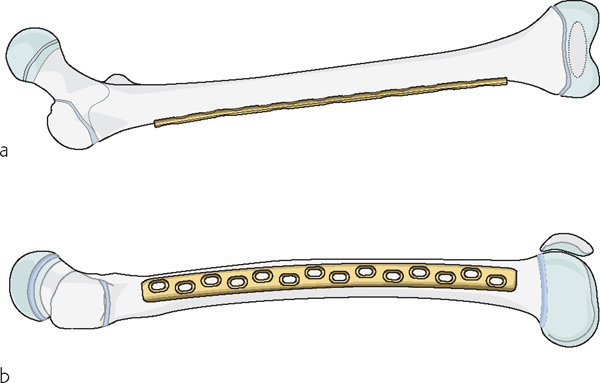
Pediatric Fractures Pdf Bone Surgical Specialties 10.1055 b 0040 176953 12 principles of pediatric fracture managementgeorge gantsoudes introduction children are not small adults. they have different anatomy (physes, thicker periosteum, etc.), different physiology (faster healing), and have the potential to remodel angulated fractures. this chapter will discuss the unique treatment of pediatric fractures about the elbow, forearm, knee, and. Fractures are common in children. nearly one of three children will have at least one fracture during childhood (3). orthopaedic surgeons, pediatricians, emergency room, personnel and primary care physicians will all be commonly exposed to fractures and other musculoskeletal trauma in children and, therefore, must have an understanding of the basic diagnostic and treatment principles. the.

Common Pediatric Fractures Pdf Anatomical Terms Of Location Bone Children break bones more easily than adults so pediatric fractures are very common. there are several unique features of the pediatric musculoskeletal system that need to be considered in management decisions of all of these injuries growth plates, plasticity, callus formation, remodeling potential, and partial breaks are some of the key ones. Musculoskeletal musculoskeletal structure of infants & children bones are more porous and less dense rapid bone growth: facilitates healing and growing pains most childhood disorders are in the long bones. fractures heal is less time in children than in adults. the approximate healing times for the femoral shaft are as follows: neonatal period 2 to 3 weeks early childhood 4 weeks later. 23.1 pediatric fractures—introduction rodrigo pesantez, chang wug oh 625 1 introduction 625 1.1 special features of pediatric fractures 625 1.2 general principles in treating pediatric fractures 625 1.3 indications for operative treatment 625 1.4 indications and contraindications for minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis (mipo) in pediatric fractures 626 2 surgical anatomy 626 2.1 femoral. The fatigue fracture is seen when repetitive abnormal stress is imposed on normal bone, and this is what is most frequently seen in a typical pediatric population participating in sports. the insufficiency fracture occurs with normal stress on abnormal bone, and the type of patient affected may be anorexic or have metabolic bone disease.
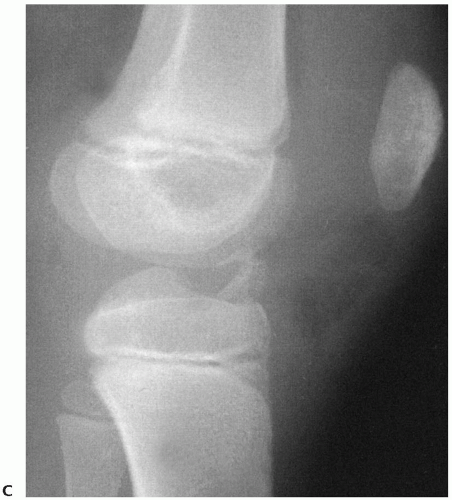
Pediatric Fractures Introduction Musculoskeletal Key 23.1 pediatric fractures—introduction rodrigo pesantez, chang wug oh 625 1 introduction 625 1.1 special features of pediatric fractures 625 1.2 general principles in treating pediatric fractures 625 1.3 indications for operative treatment 625 1.4 indications and contraindications for minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis (mipo) in pediatric fractures 626 2 surgical anatomy 626 2.1 femoral. The fatigue fracture is seen when repetitive abnormal stress is imposed on normal bone, and this is what is most frequently seen in a typical pediatric population participating in sports. the insufficiency fracture occurs with normal stress on abnormal bone, and the type of patient affected may be anorexic or have metabolic bone disease. Understanding these key differences in pediatric bone composition and metabolism is essential for clinicians when assessing growth, treating fractures, and managing orthopedic conditions in children. The most common classification scheme for pediatric ankle fractures is the salter harris method for physeal fractures. the lauge hansen classification used in adults can be modified for pediatric ankle fractures and aids in conceptualizing the reduction technique by reversing the fracture pattern.
Pediatric Fractures Musculoskeletal Key Understanding these key differences in pediatric bone composition and metabolism is essential for clinicians when assessing growth, treating fractures, and managing orthopedic conditions in children. The most common classification scheme for pediatric ankle fractures is the salter harris method for physeal fractures. the lauge hansen classification used in adults can be modified for pediatric ankle fractures and aids in conceptualizing the reduction technique by reversing the fracture pattern.
Pediatric Fractures Musculoskeletal Key
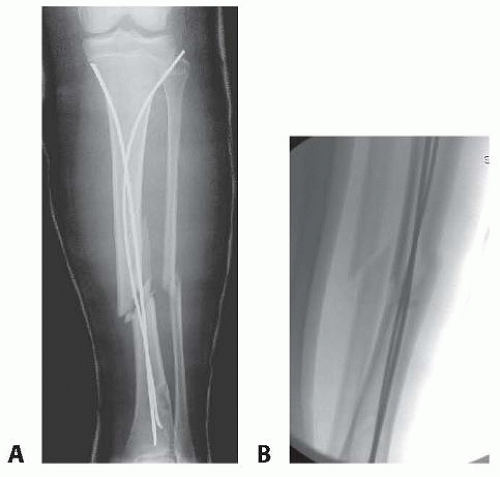
Pediatric Tibial Fractures Musculoskeletal Key

Pediatric Forearm Fractures Musculoskeletal Key