
Resultant Force Pdf Force Mechanical Engineering Effort force vs. resultant force mechanical advantage and efficiency simple and compound machines review of simple machines lever, inclined plane, pulley, wheel and axle. This document discusses simple machines and their characteristics. it defines simple machines as devices that make work easier by transmitting force through a mechanical advantage. examples of simple machines discussed include levers, pulleys, gears, inclined planes, screws, and the wheel and axle. key terms like effort, load, mechanical advantage, velocity ratio, and efficiency are defined.

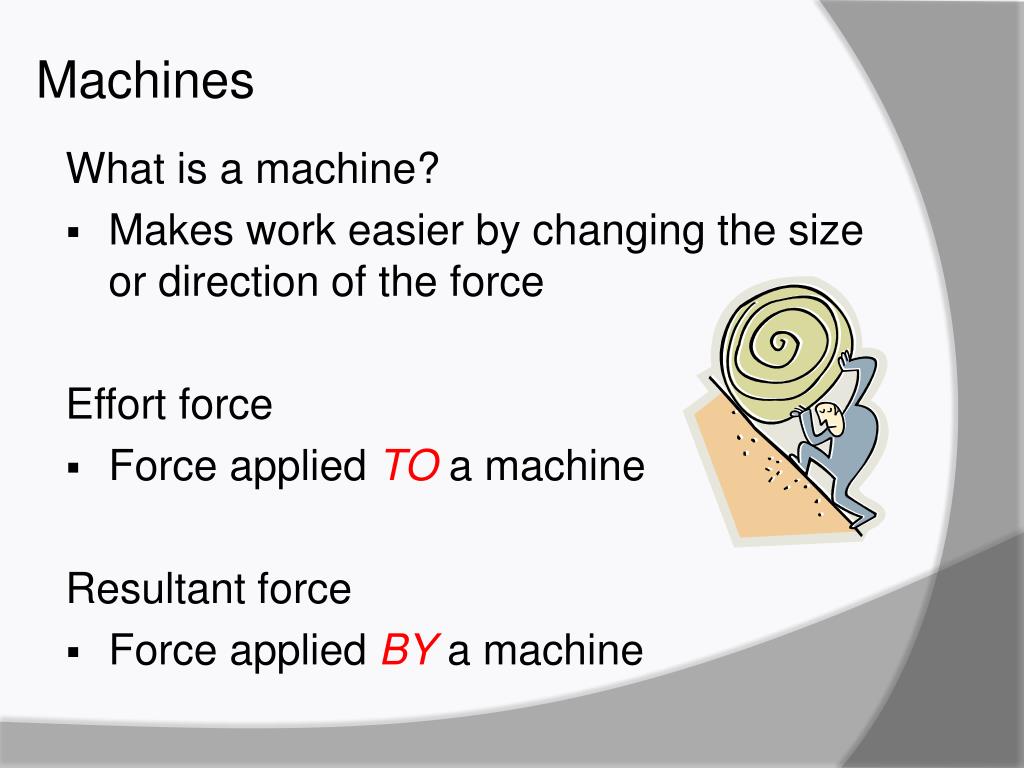
Ppt What Is A Machine Effort Force Vs Resultant Force Mechanical Problems with friction, we have two components of the force – normal reaction and sliding friction force. the friction force opposes the impending direction of motion. same direction of impending motion assumed. so friction force direction is same. normal reaction force direction reversed. resultant rn is not same; not even opposite of each. Resultant force: if a number of forces, p, q, r etc. are acting simultaneously on a particle, then it is possible to find out a single force which could replace them i.e., which would produce the same effect as produced by all the given forces. What is mechanical advantage mechanical advantage (ma) is a method of showing how machines can make life easier for humans when they are used properly. when simple machines are used, they reduce the amount of effort needed to perform a task. 2 types of ma actual mechanical advantage (ama) – the ratio of load force to effort force for a machine. The force exerted by the link de has a known line of action but unknown magnitude. it is determined by summing moments about c. with the force on the link de known, the sum of forces in the x and y directions may be used to find the force components at c. with member ace as a free body, check the solution by summing moments about a.

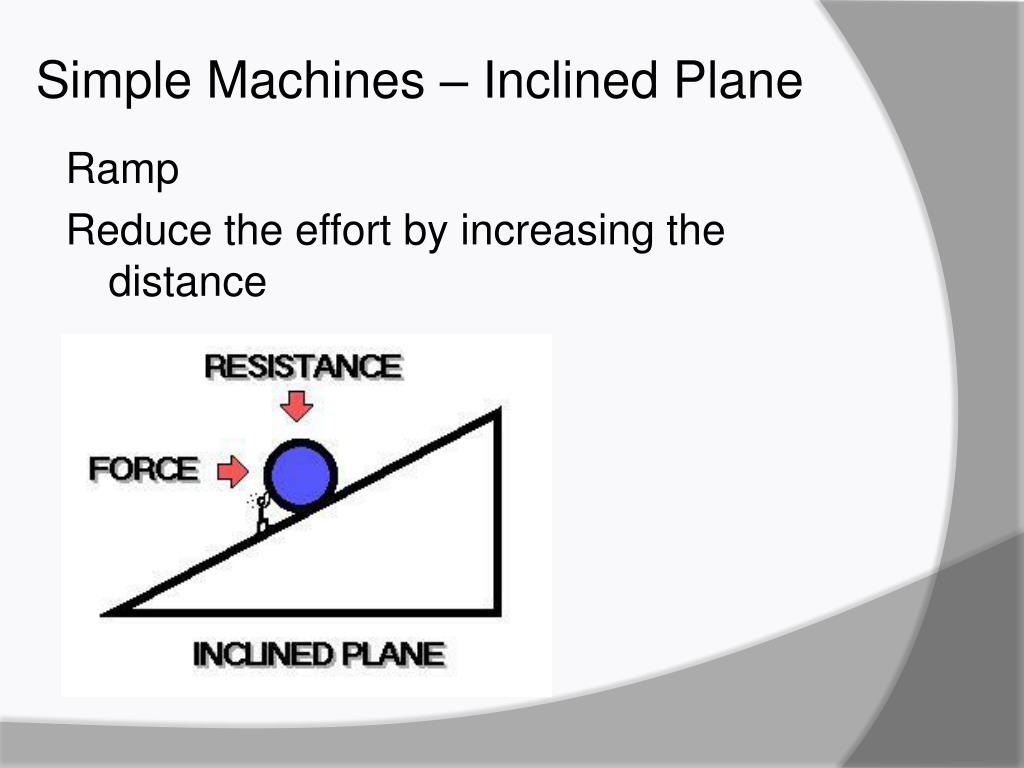
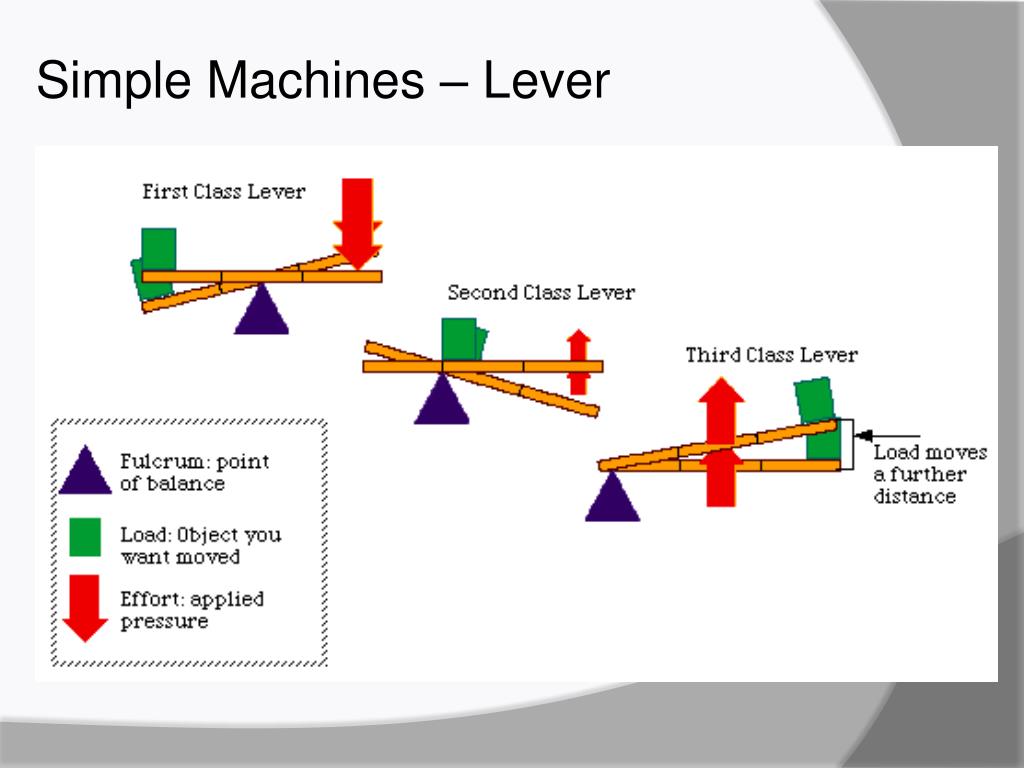
Ppt What Is A Machine Effort Force Vs Resultant Force Mechanical What is mechanical advantage mechanical advantage (ma) is a method of showing how machines can make life easier for humans when they are used properly. when simple machines are used, they reduce the amount of effort needed to perform a task. 2 types of ma actual mechanical advantage (ama) – the ratio of load force to effort force for a machine. The force exerted by the link de has a known line of action but unknown magnitude. it is determined by summing moments about c. with the force on the link de known, the sum of forces in the x and y directions may be used to find the force components at c. with member ace as a free body, check the solution by summing moments about a. The document provides an overview of the concepts related to forces, including their classification, composition, and methods for determining resultant forces such as the parallelogram, triangle, and polygon laws. it discusses different types of forces—coplanar, non coplanar, collinear, non collinear, concurrent, non concurrent, parallel, and non parallel. an example is presented involving. Effort force vs. resultant force mechanical advantage and efficiency simple and compound machines review of simple machines lever, inclined plane, pulley, wheel and axle.

Ppt What Is A Machine Effort Force Vs Resultant Force Mechanical The document provides an overview of the concepts related to forces, including their classification, composition, and methods for determining resultant forces such as the parallelogram, triangle, and polygon laws. it discusses different types of forces—coplanar, non coplanar, collinear, non collinear, concurrent, non concurrent, parallel, and non parallel. an example is presented involving. Effort force vs. resultant force mechanical advantage and efficiency simple and compound machines review of simple machines lever, inclined plane, pulley, wheel and axle.
Ppt What Is A Machine Effort Force Vs Resultant Force Mechanical
Ppt What Is A Machine Effort Force Vs Resultant Force Mechanical
Ppt What Is A Machine Effort Force Vs Resultant Force Mechanical