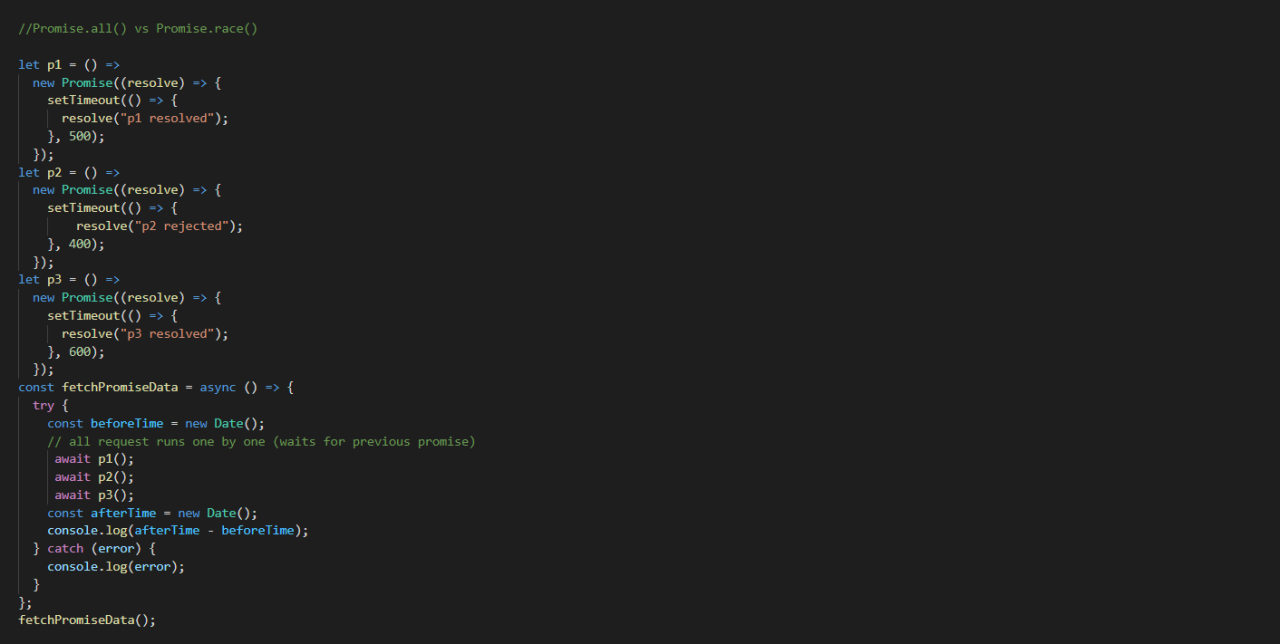
Promise All Race Allsettled Any In previous articles we learned about how promise work and discussed about then catch and finally methods. today we will be discussing: promise.all () promise.allsettled () difference usecase of promise.all () and promise.allsettled () promise.race () promise.any () difference usecase of promise.race () and promise.any () all these methods take array of promises as an input but deals. From mdn, also, unlike promise.race (), which returns the first settled value, this method returns the first resolved value. this method will ignore all rejected promises up until the first promise that resolves. so that brings me to, the difference between resolved and settled.

Promise Race Promise All Promise Allsettled Javascript Methods 47 Javascript promises: race, all, allsettled, and then fernando doglio technical manager at globant. author of books and maker of software things. find me online at fdoglio . This comprehensive guide covers the usage of promise.all (), promise.allsettled (), promise.race (), and promise.any () in javascript. learn when to use each method, their syntax, and how to handle errors. explore practical examples and best practices to master asynchronous programming with these powerful promise utilities. Javascript promises: promise.all vs promise.allsettled vs promise.race vs promise.any on your way to become a “javascript superstar” and “promises whizz”, you’ll need to master the. In this article, i’ve explained the promise methods: all (), any (), race (), allsettled () along with their polyfills. promise.all () it accepts an iterable of promises as its argument and returns a promise if all promises resolve, then the returned promise is resolved with an array of fulfilled values.

Promise Apis рџ ґ All Allsettled Race Any Javascript promises: promise.all vs promise.allsettled vs promise.race vs promise.any on your way to become a “javascript superstar” and “promises whizz”, you’ll need to master the. In this article, i’ve explained the promise methods: all (), any (), race (), allsettled () along with their polyfills. promise.all () it accepts an iterable of promises as its argument and returns a promise if all promises resolve, then the returned promise is resolved with an array of fulfilled values. Since the introduction of promises in es2015, javascript has supported exactly two promise combinators: the static methods promise.all and promise.race. two new proposals are currently making their way through the standardization process: promise.allsettled, and promise.any. with those additions, there’ll be a total of four promise combinators in javascript, each enabling different use cases. Rejection of promise.all () : fail fast behavior promise.all() shows fail fast behavior, that is, promise.all () asynchronously rejects with the value of the promise that rejected, if any of the passed in elements are rejected. for example, if we pass in two promises that resolve after a timeout and one promise that rejects immediately, then promise.all () will reject immediately. it does not.

Javascript Promises Promise All Vs Promise Allsettled Vs Promise Race Since the introduction of promises in es2015, javascript has supported exactly two promise combinators: the static methods promise.all and promise.race. two new proposals are currently making their way through the standardization process: promise.allsettled, and promise.any. with those additions, there’ll be a total of four promise combinators in javascript, each enabling different use cases. Rejection of promise.all () : fail fast behavior promise.all() shows fail fast behavior, that is, promise.all () asynchronously rejects with the value of the promise that rejected, if any of the passed in elements are rejected. for example, if we pass in two promises that resolve after a timeout and one promise that rejects immediately, then promise.all () will reject immediately. it does not.

The Difference Between Promise All Vs Promise Allsettled Vs Promise
Javascript Promise Apis Explained When To Use All Allsettled