
Introduction To Spatial Data Vector And Raster Spatial data observations focus on locations. every house, every tree, and every city has its own unique latitude and longitude coordinates. the two primary types of spatial data are vector and raster data in a gis. but what is the difference between raster and vector data? when should we use raster and when should we use vector features? find out more about the spatial data models commonly used. Harmen romeijn demonstrates how vector data compares to raster in gis, and different tools used for analysis. read on to find out more.

Raster And Vector Data In Gis Spatial Vision The changes in the cell value reflect the spatial variation of the phenomenon. for example, figure 5 shows an annual average temperature layer in raster format; the temperature variation across space can be observed. Understanding the difference between vector and raster data is fundamental for gis. these two types of spatial data are the backbone of gis analyses and mapping, each with its unique characteristics, advantages, and applications. Spatial data is the foundation of geographic information systems (gis), helping us analyze and visualize geographic features. in gis, spatial data is primarily categorized into vector and raster formats. The difference between vector and raster data in gis in this article, we will cover the fundamental differences between raster and vector data. geospatial data can be represented using either vector data type or raster. the two data types are very different in their internal representation, the operations you can do on them as well as their look and feel. the figures below show a.

Raster And Vector Data In Gis Spatial Vision Spatial data is the foundation of geographic information systems (gis), helping us analyze and visualize geographic features. in gis, spatial data is primarily categorized into vector and raster formats. The difference between vector and raster data in gis in this article, we will cover the fundamental differences between raster and vector data. geospatial data can be represented using either vector data type or raster. the two data types are very different in their internal representation, the operations you can do on them as well as their look and feel. the figures below show a. Geographic information systems (gis) have revolutionized how we analyze and visualize spatial data. at the core of gis lie two fundamental data types: raster and vector. The vector model is used for high quality cartography and where accuracy and precision are important, such as for cadastral (property) applications. the raster data model is useful for image picture storage and is well suited to many spatial modeling operations (as optimum corridor route selection, modeling surface storm runoff, and forest fire spread).
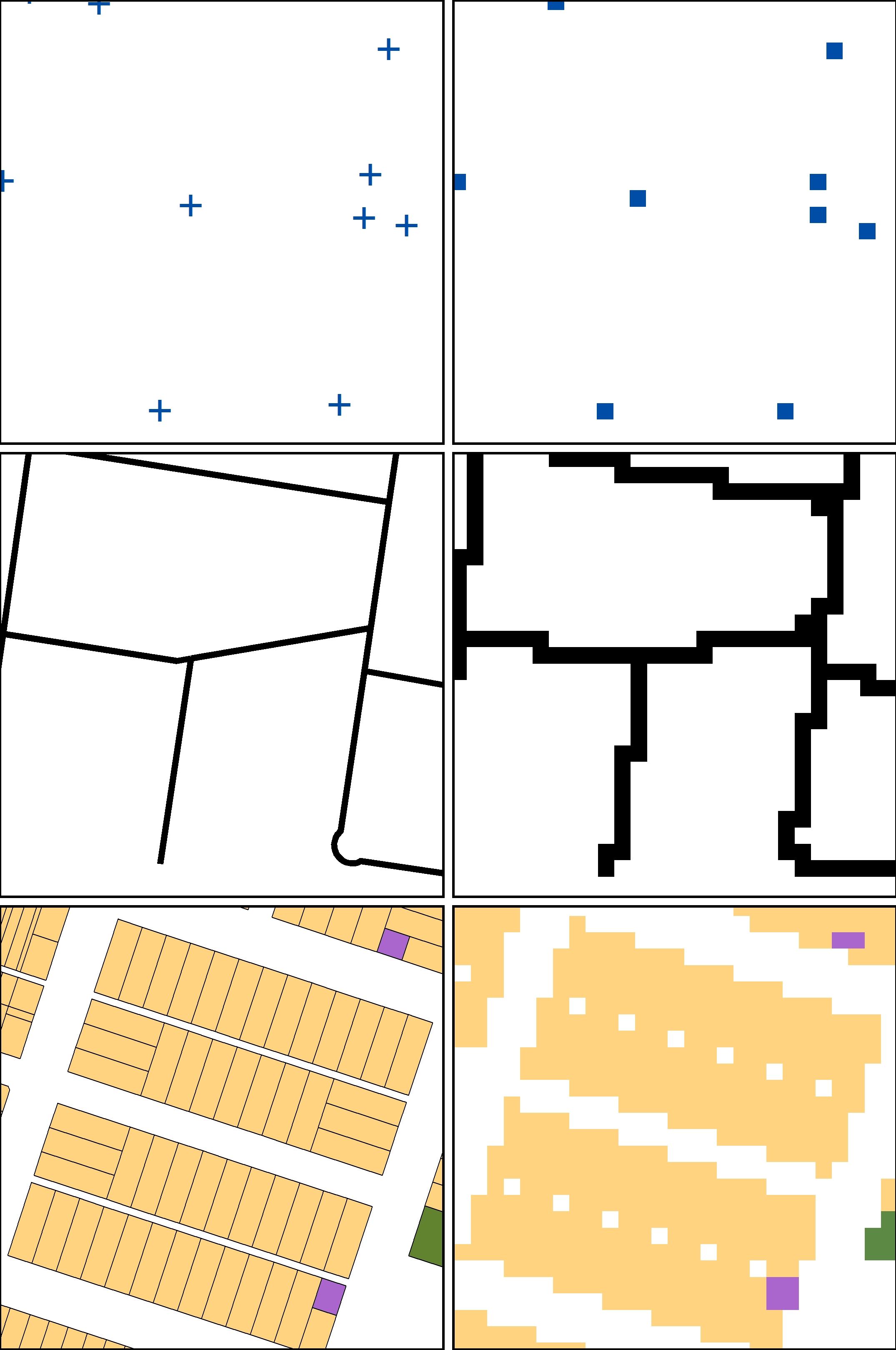
Raster And Vector Data In Gis Spatial Vision Geographic information systems (gis) have revolutionized how we analyze and visualize spatial data. at the core of gis lie two fundamental data types: raster and vector. The vector model is used for high quality cartography and where accuracy and precision are important, such as for cadastral (property) applications. the raster data model is useful for image picture storage and is well suited to many spatial modeling operations (as optimum corridor route selection, modeling surface storm runoff, and forest fire spread).

Raster And Vector Data In Gis Spatial Vision