
Raster Vs Vector Data Formats In Gis Equator What are data models in gis? spatial data models in gis are understood as a set of mathematical and other constructs that are used to generate a computer based representation of geographical entities, phenomena, and processes, within the real world. the two basic data models in gis would be – as you might have guessed – the raster and vector data models. Spatial data observations focus on locations. every house, every tree, and every city has its own unique latitude and longitude coordinates. the two primary types of spatial data are vector and raster data in a gis. but what is the difference between raster and vector data? when should we use raster and when should we use vector features? find out more about the spatial data models commonly used.
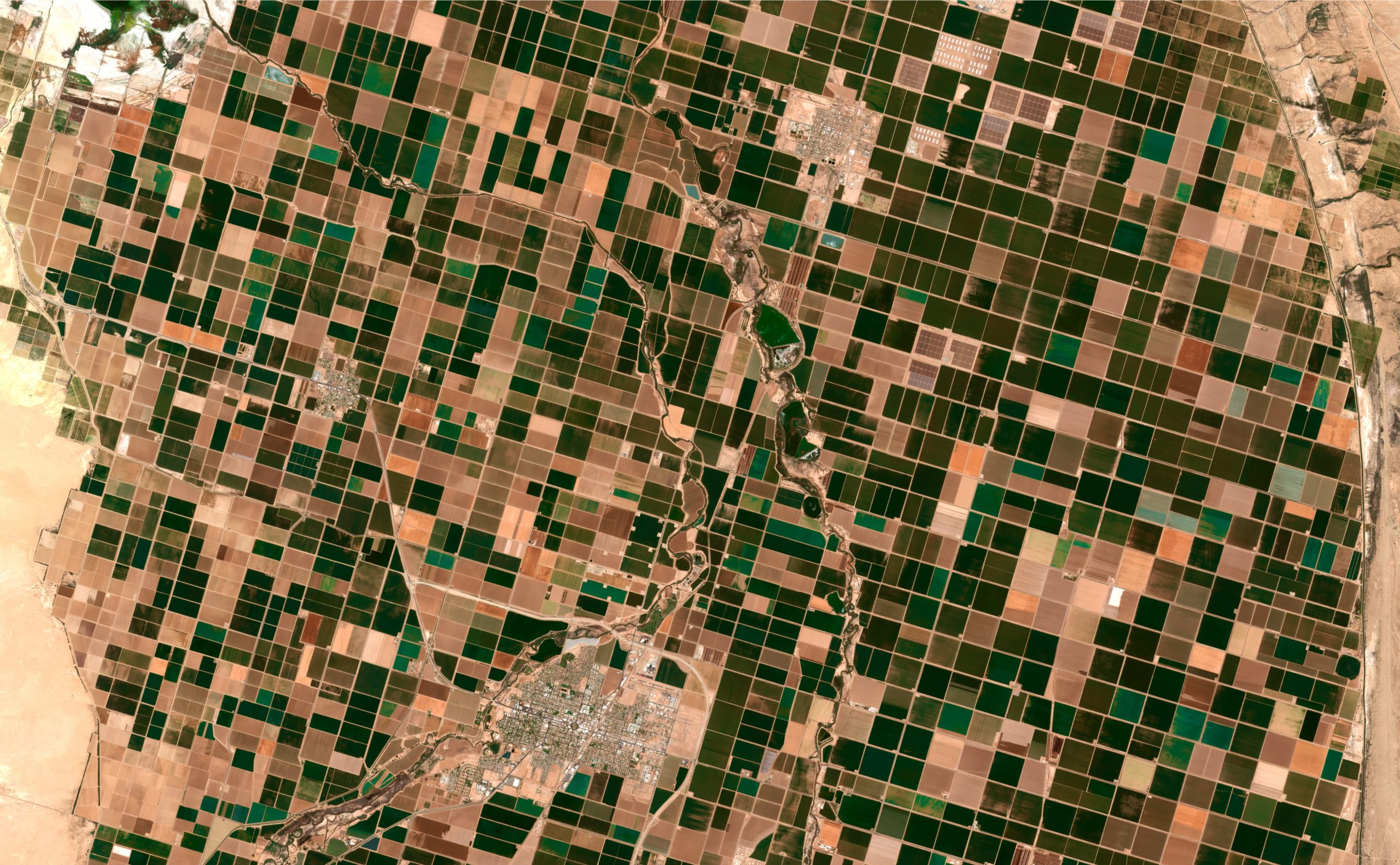

Raster Vs Vector Data Formats In Gis Equator The difference between vector and raster data in gis in this article, we will cover the fundamental differences between raster and vector data. geospatial data can be represented using either vector data type or raster. the two data types are very different in their internal representation, the operations you can do on them as well as their look and feel. the figures below show a. Geographic information system (gis) data formats are essential for storing and managing spatial information. the most common gis data formats are vector and raster formats. vector data represents geographic features using geometric shapes such as points, lines, and polygons. each feature has additional information (so called attribute data), such as names or types, stored in a table. points. Mastering raster and vector data in gis requires understanding their unique characteristics, applications, and analytical techniques. raster data excels in continuous surface analysis and remote sensing applications, while vector data is ideal for precise spatial representation and network analysis. This article will give a detailed look at vector data vs raster data. after reading this, you should be able to make a sound decision on which to use.
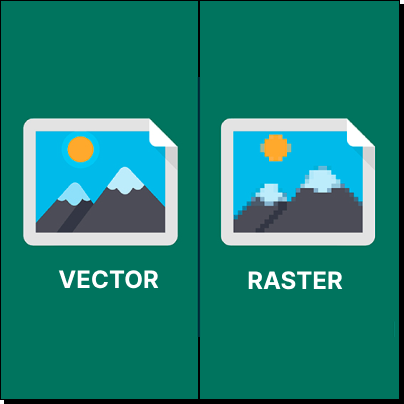
Raster Vs Vector Data Formats In Gis Equator Mastering raster and vector data in gis requires understanding their unique characteristics, applications, and analytical techniques. raster data excels in continuous surface analysis and remote sensing applications, while vector data is ideal for precise spatial representation and network analysis. This article will give a detailed look at vector data vs raster data. after reading this, you should be able to make a sound decision on which to use. Vector vs raster: a simple way of identifying whether data is in a vector or raster format is to keep zooming in and see if you see the pixels. it is a raster file if you can see those pixels, otherwise it is a vector file. in figure 6, you can see how a series of polygons would be represented as raster data. Geographic information systems (gis) are powerful tools for spatial analysis, utilizing two primary data representations: raster and vector formats. understanding the nuanced characteristics of these data types is crucial for professionals working in cartography, environmental science, urban planning, and geospatial analysis.
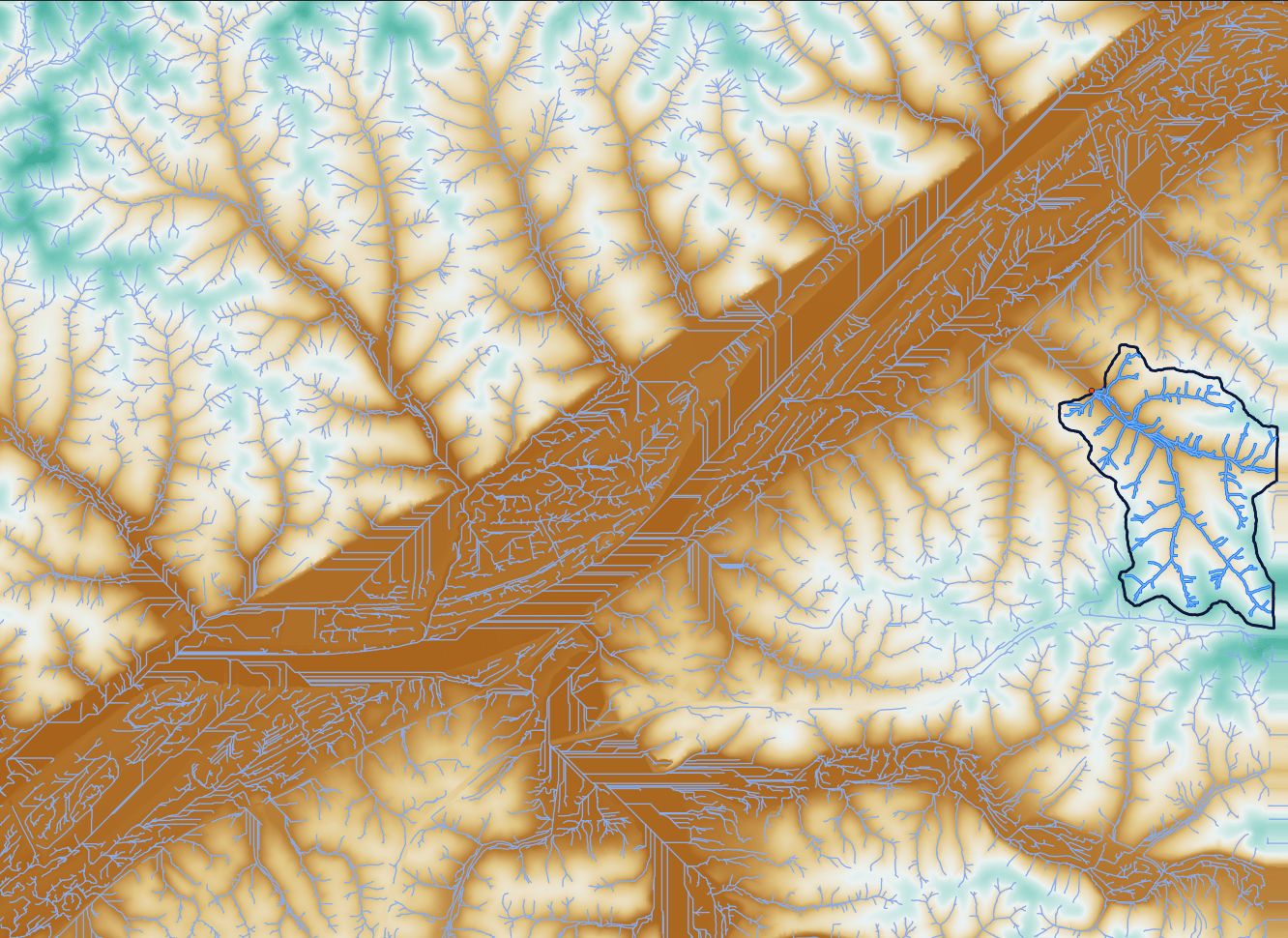
Raster Vs Vector Data Formats In Gis Equator Vector vs raster: a simple way of identifying whether data is in a vector or raster format is to keep zooming in and see if you see the pixels. it is a raster file if you can see those pixels, otherwise it is a vector file. in figure 6, you can see how a series of polygons would be represented as raster data. Geographic information systems (gis) are powerful tools for spatial analysis, utilizing two primary data representations: raster and vector formats. understanding the nuanced characteristics of these data types is crucial for professionals working in cartography, environmental science, urban planning, and geospatial analysis.