
Irrational Numbers Definition Common Examples Diagram 55 Off Rational numbers can be written as a ratio that compares two numbers or quantities, giving a simple fraction or mixed fraction p q. these include integers or decimals terminating (finite) or recurring (repeating patterns). the denominator ‘q’ is a natural number, i.e., non zero. irrational numbers cannot be written as a ratio. Irrational numbers are all real numbers that cannot be expressed as fractions of integers. learn more about irrational numbers, the difference between rational and irrational numbers, and examples.

Irrational Numbers Definition And Examples Price Guarantee Example: 1.5 is rational, because it can be written as the ratio 3 2. Definition : can be expressed as the quotient of two integers (ie a fraction) with a denominator that is not zero. many people are surprised to know that a repeating decimal is a rational number. the venn diagram below shows examples of all the different types of rational, irrational numbers including integers, whole numbers, repeating decimals and more. set of real numbers venn diagram. The is, the rational number is expressed in the form of p q whereas it is not possible for irrational number (though both are real numbers). learn the definitions, more differences and examples based on them. definition of rational and irrational numbers the real numbers which can be represented in the form of the ratio of two integers, say p q, where q is not equal to zero are called rational. In simpler terms, rational numbers are like fractions – they show the relationship between two whole numbers. a rational numbers is any number that can be expressed as the ratio of two integers. in mathematical terms, a rational number is a number that can be written in the form p q , where p and q are integers, and q is not equal to zero.
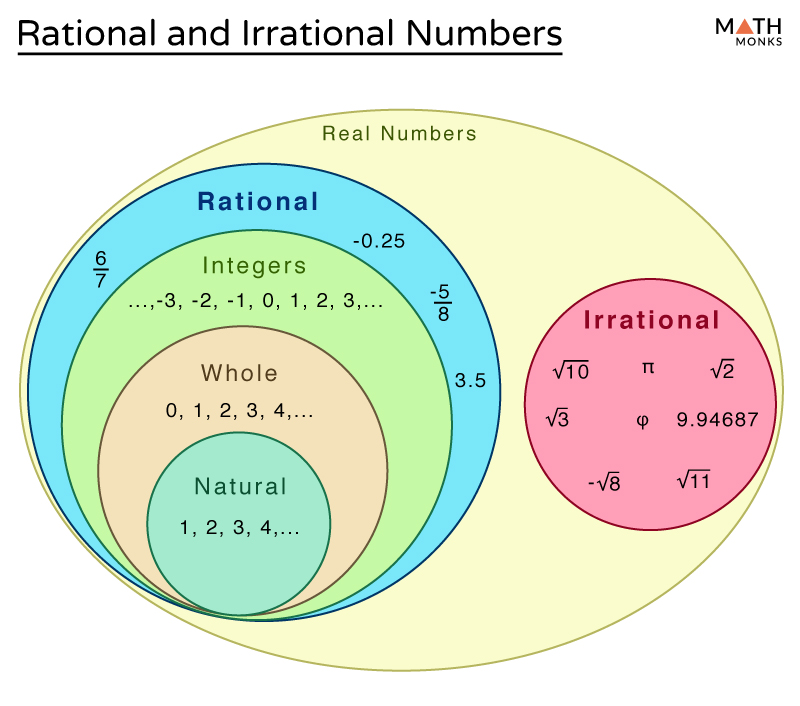
Rational And Irrational Numbers Differences Examples The is, the rational number is expressed in the form of p q whereas it is not possible for irrational number (though both are real numbers). learn the definitions, more differences and examples based on them. definition of rational and irrational numbers the real numbers which can be represented in the form of the ratio of two integers, say p q, where q is not equal to zero are called rational. In simpler terms, rational numbers are like fractions – they show the relationship between two whole numbers. a rational numbers is any number that can be expressed as the ratio of two integers. in mathematical terms, a rational number is a number that can be written in the form p q , where p and q are integers, and q is not equal to zero. It can be natural numbers, whole numbers, integers, rational numbers, and irrational numbers. irrational numbers are real numbers, but not all real numbers are irrational numbers. Rational numbers are composed of integers with a non zero denominator, whereas fractions are composed of whole numbers. for example: 5 2 5 2 a number is considered irrational if it cannot be expressed as a p q fraction of any integer p and q. the decimal extension of irrational numbers can be continuous or sporadic.
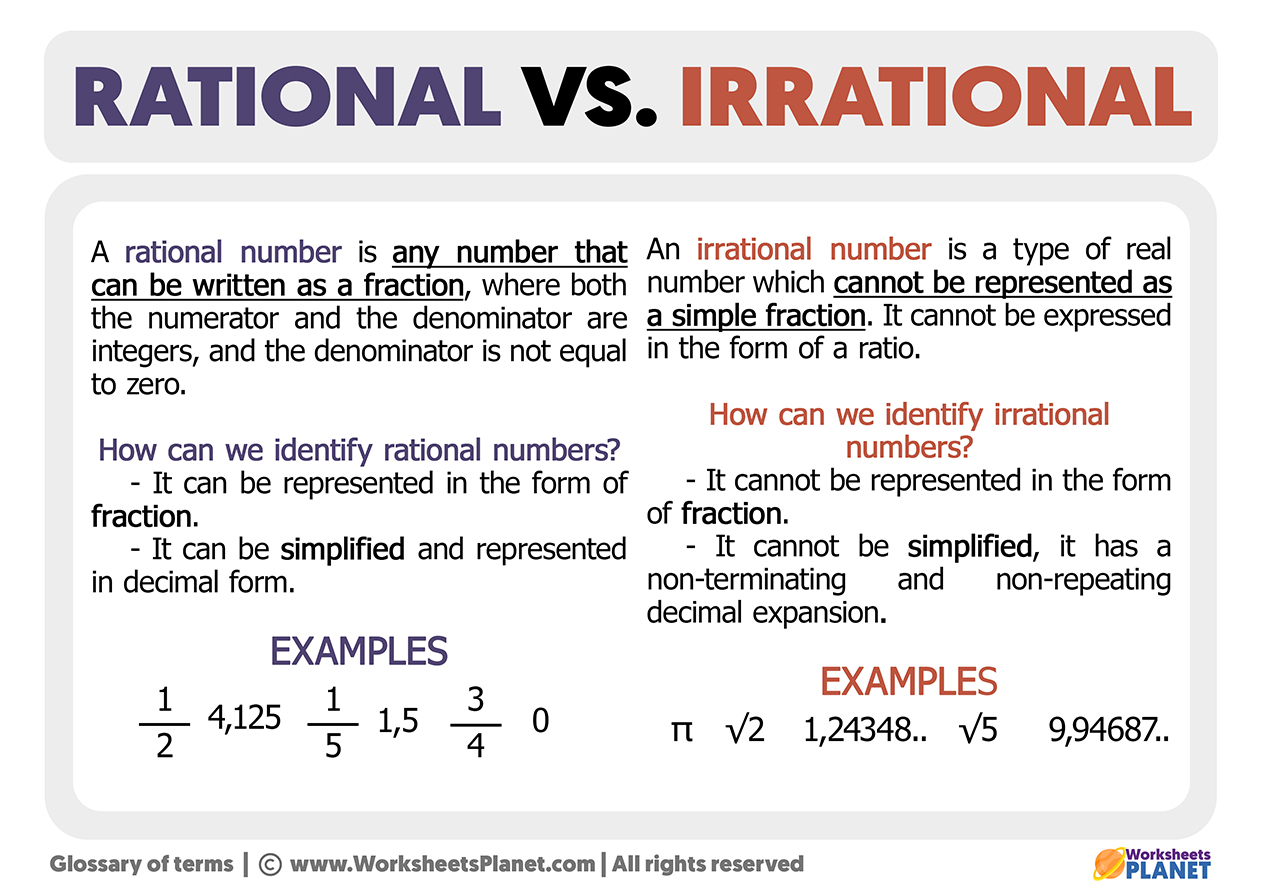
Rational And Irrational Numbers It can be natural numbers, whole numbers, integers, rational numbers, and irrational numbers. irrational numbers are real numbers, but not all real numbers are irrational numbers. Rational numbers are composed of integers with a non zero denominator, whereas fractions are composed of whole numbers. for example: 5 2 5 2 a number is considered irrational if it cannot be expressed as a p q fraction of any integer p and q. the decimal extension of irrational numbers can be continuous or sporadic.
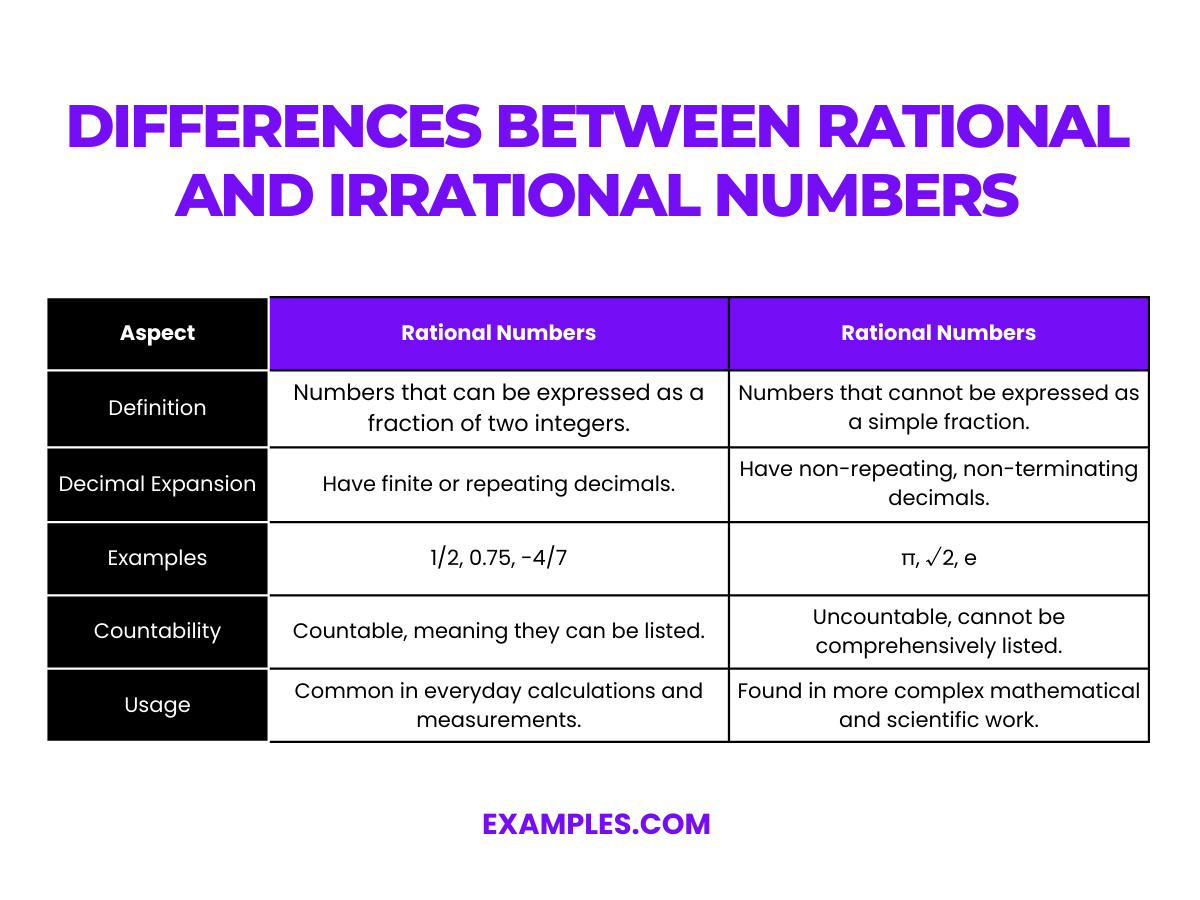
Irrational Numbers Examples Format Pdf

Rational And Irrational Numbers Pdf Unlock Success In English Math