
Concave Mirror Ray Diagram Pdf Thin lens equation (4 of 6) concave mirror, object distance less then f step by step science classic crew neck comfortsoft t shirt. For a concave mirror, object can be kept at different positionshence, we take different casescase 1 object is placed at infinityin this case, object ab is kept far away from mirror (almost at infinite distance)so, we draw rays parallel to principal axissince ray parallel to principal axis passes t.

Concave And Convex Mirror Ray Diagrams Step by step method for drawing ray diagrams the method for drawing ray diagrams for concave mirror is described below. the method is applied to the task of drawing a ray diagram for an object located beyond the center of curvature (c) of a concave mirror. yet the same method works for drawing a ray diagram for any object location. 1. pick a point on the top of the object and draw two incident. Ray diagrams for concave mirrors for the following mirrors and corresponding object positions, construct ray diagrams. then describe the location of the image, orientation (upright or inverted) of the image, the relative size of the image (larger or smaller than object), and the type of image (real or virtual). for case 4, merely construct the ray diagram. Once the incident rays strike the mirror, reflect them according to the two rules of reflection for concave mirrors, which you verified in part a. the ray that passes through the focal point on the way to the mirror will reflect and travel away from the mirror parallel to the principal axis. (use a ruler to accurate draw the path). The sign conventions for the given quantities in the mirror equation and magnification equations are as follows: fis if the mirror is a concave mirror fis if the mirror is a convex mirror diis if the image is a real image and located on the object's side of the mirror. diis if the image is a virtual image and located behind the mirror.

Ray Diagrams Of Concave Mirror Once the incident rays strike the mirror, reflect them according to the two rules of reflection for concave mirrors, which you verified in part a. the ray that passes through the focal point on the way to the mirror will reflect and travel away from the mirror parallel to the principal axis. (use a ruler to accurate draw the path). The sign conventions for the given quantities in the mirror equation and magnification equations are as follows: fis if the mirror is a concave mirror fis if the mirror is a convex mirror diis if the image is a real image and located on the object's side of the mirror. diis if the image is a virtual image and located behind the mirror. The video introduces the important components of a ray diagram for concave mirrors, including the principal axis, center of curvature (c), and focal point (f). it explains how to draw ray diagrams for objects placed at different distances from the mirror, such as beyond c, at c, between c and f,. Drawing ray diagrams for concave mirrors concave mirrors the mid point of a curved mirror is called the vertex. the principal axis is an imaginary horizontal line drawn through the vertex. vertex.
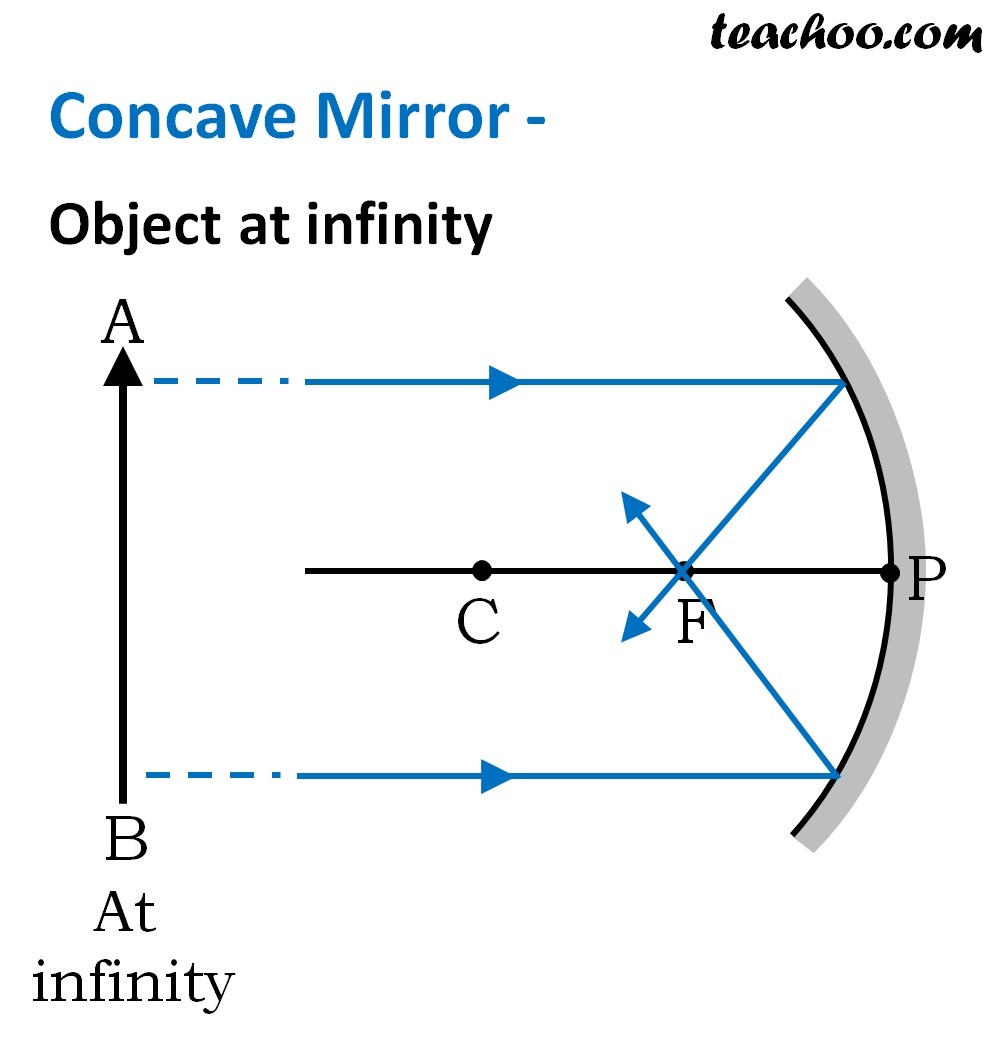
Concave And Convex Mirror Ray Diagrams The video introduces the important components of a ray diagram for concave mirrors, including the principal axis, center of curvature (c), and focal point (f). it explains how to draw ray diagrams for objects placed at different distances from the mirror, such as beyond c, at c, between c and f,. Drawing ray diagrams for concave mirrors concave mirrors the mid point of a curved mirror is called the vertex. the principal axis is an imaginary horizontal line drawn through the vertex. vertex.
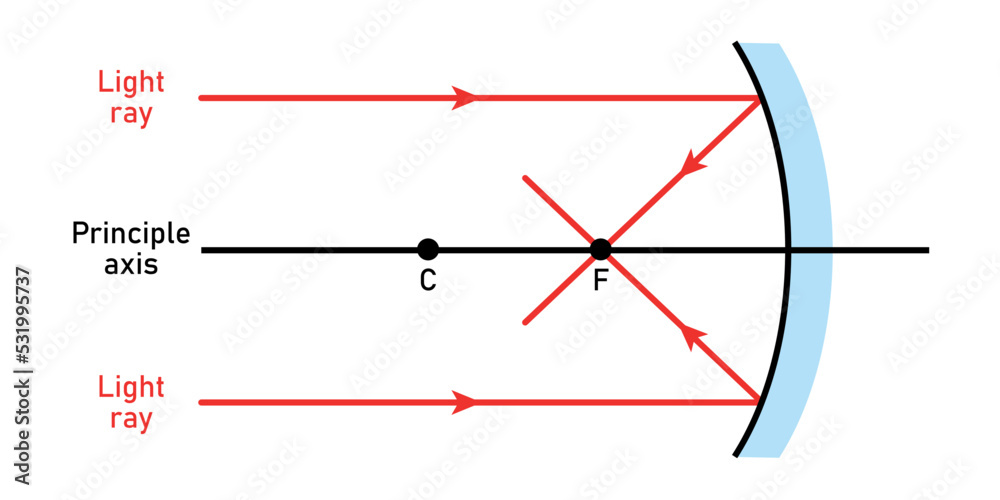
Ray Diagrams For Concave Mirror Vector Illustration Stock Vector
Ray Diagram Concave Mirror Get Physics Help