
Solved 1 4 Points Consider A Hash Table With Collisions Chegg Question: 1. [4 points] consider a hash table with collisions resolved by chaining. assume simple uniform hashing. (a) consider the case that the number of keys (corresponding to elements) n stored in the hash table is 100 times the number of slots m. what is the average time for an unsuccessful search?. 11.2 hash tables 11.2 1 suppose we use a hash function h h to hash n n distinct keys into an array t t of length m m. assuming simple uniform hashing, what is the expected number of collisions? more precisely, what is the expected cardinality of {{k, l}: k ≠ l and h (k) = h (l)} { {k,l}: k =l and h(k) =h(l)}? under the assumption of simple uniform hashing, we will use linearity of.

Solved Question 1 A 5 Points Consider A Hash Table With Chegg In hashing, hash functions were used to generate hash values. the hash value is used to create an index for the keys in the hash table. the hash function may return the same hash value for two or more keys. when two or more keys have the same hash value, a collision happens. to handle this collision, we use collision resolution techniques. Collision resolution collision: when two keys map to the same location in the hash table. two ways to resolve collisions:. This is also called the load factor, which means how many keys hashed to 1 slot of the table. 11.2 2 demonstrate what happens when we insert the keys 5; 28; 19; 15; 20; 33; 12; 17; 10 into a hash table with collisions resolved by chaining. Computer science questions and answers (50 points) consider a hash table of size n = 7 where we are going to store integer values. the hash function is h (k) = k mod 7. draw the table that results after inserting, in the given order, the following values: 5, 15, 12, 26, 11. (a) (10 points) assume that collisions are handled by separate chaining.

Solved Analysis Of Collisions In Hash Tables Consider A Chegg This is also called the load factor, which means how many keys hashed to 1 slot of the table. 11.2 2 demonstrate what happens when we insert the keys 5; 28; 19; 15; 20; 33; 12; 17; 10 into a hash table with collisions resolved by chaining. Computer science questions and answers (50 points) consider a hash table of size n = 7 where we are going to store integer values. the hash function is h (k) = k mod 7. draw the table that results after inserting, in the given order, the following values: 5, 15, 12, 26, 11. (a) (10 points) assume that collisions are handled by separate chaining. Consider a 13 element hash table for which f (key) = key mod 13 is used with integer keys. assuming linear probing is used for collision resolution, at which location would the key 103 be inserted, if the keys 661, 182, 24 and 103 are inserted in that order?. Hash tables deal with collisions in one of two ways. option 1: by having each bucket contain a linked list of elements that are hashed to that bucket. this is why a bad hash function can make lookups in hash tables very slow. option 2: if the hash table entries are all full then the hash table can increase the number of buckets that it has and then redistribute all the elements in the table.

Solved Problem 1 Consider A Hash Table For Which Collisions Chegg Consider a 13 element hash table for which f (key) = key mod 13 is used with integer keys. assuming linear probing is used for collision resolution, at which location would the key 103 be inserted, if the keys 661, 182, 24 and 103 are inserted in that order?. Hash tables deal with collisions in one of two ways. option 1: by having each bucket contain a linked list of elements that are hashed to that bucket. this is why a bad hash function can make lookups in hash tables very slow. option 2: if the hash table entries are all full then the hash table can increase the number of buckets that it has and then redistribute all the elements in the table.

Solved In A Hash Table There Are Multiple Ways To Deal With Chegg
Collisions In Hash Table Prompts Stable Diffusion Online
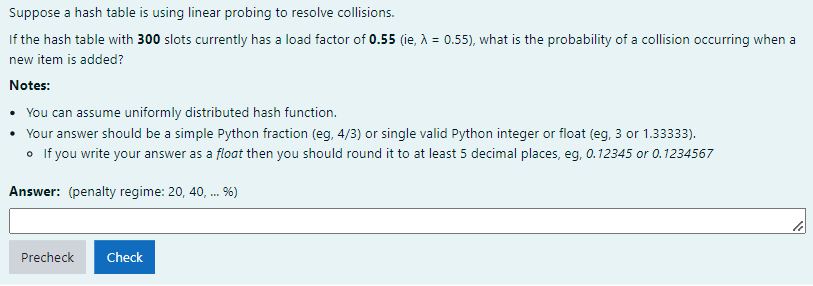
Solved Suppose A Hash Table Is Using Linear Probing To Chegg