
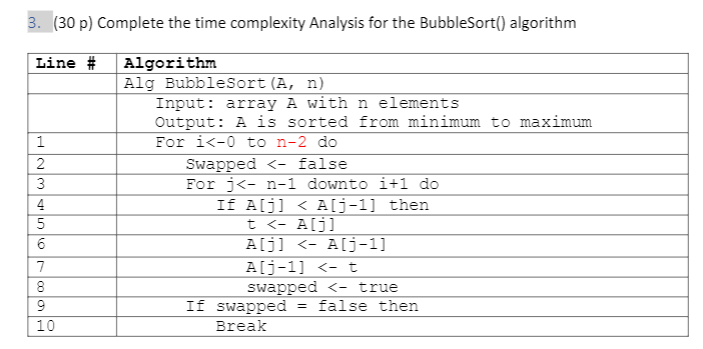
Solved 3 30 P Complete The Time Complexity Analysis For Chegg 3. (30 p) complete the time complexity analysis for the bubblesort () algorithm line # algorithm alg bubblesort (a, n) input: array a with n elements output: a is sorted from minimum to maximum 1 for i< 0 to n 2 do 2 swapped < false 3 for j< n 1 downto i 1 do 4 if a [j] <a [j 1] then 5 t < a [j] 6 aljl < alj 1] 7 aj 1] < t 8 swapped < true 9 if swapped = false then break 6 10 b. call. An algorithm with time complexity o(f(n)) and processing time t(n) = cf(n), where f(n) is a known function of n, spends 10 seconds to process 1000 data items. how much time will be spent to process 100,000 data items if f(n) = n and f(n) = n3?.

Solved 3 30p Complete The Time Complexity Analysis For Chegg Learn how to calculate the time complexity of algorithms with detailed notes and examples. boost your programming skills now!. 3. o(n m) time, o(1) space explanation: the first loop is o (n) and the second loop is o (m). since n and m are independent variables, so we can't say which one is the leading term. therefore time complexity of the given problem will be o (n m). since variables size does not depend on the size of the input, therefore space complexity will be constant or o (1) 2. what is the time complexity. Let's take your own recurrence t (n) = 3t (n 2) n for example. this recurrence is actually saying that the algorithm represented by it is such that, (time to solve a problem of size n) = (time taken to solve 3 problems of size n 2) n the n at the end is the cost of merging the results of those 3 n 2 sized problems. Question: week 3: complexity analysis and divide and conquerpart 3: theoretical questions (25 points)question 8: divide and conquer approach (10 points) (a) what is the divide and conquer approach in algorithm design? (2 points) (b) provide two examples of algorithms that use the divide and conquer approach and explain how they.
Solved 3 30 P Complete The Time Complexity Analysis For Chegg Let's take your own recurrence t (n) = 3t (n 2) n for example. this recurrence is actually saying that the algorithm represented by it is such that, (time to solve a problem of size n) = (time taken to solve 3 problems of size n 2) n the n at the end is the cost of merging the results of those 3 n 2 sized problems. Question: week 3: complexity analysis and divide and conquerpart 3: theoretical questions (25 points)question 8: divide and conquer approach (10 points) (a) what is the divide and conquer approach in algorithm design? (2 points) (b) provide two examples of algorithms that use the divide and conquer approach and explain how they. An analysis of the computer memory required involves the of the algorithm. 1. time complexity 2. space complexity. which of these considerations are important reasons for studying the computational complexity of algorithm?. Methods of complexity analysis asymptotic analysis create recurrence relation and solve this relates problem size of original problem to number and size of sub problems solved different performance measures are of interest worst case (often easiest to analyze; need one ‘bad’ example) best case (often easy for same reason).

Solved 3 30 P Complete The Time Complexity Analysis For Chegg An analysis of the computer memory required involves the of the algorithm. 1. time complexity 2. space complexity. which of these considerations are important reasons for studying the computational complexity of algorithm?. Methods of complexity analysis asymptotic analysis create recurrence relation and solve this relates problem size of original problem to number and size of sub problems solved different performance measures are of interest worst case (often easiest to analyze; need one ‘bad’ example) best case (often easy for same reason).