
Solved A Specimen With A Length Of 50 Mm Width Of 20 Mm And Chegg A specimen with a length of 50 mm, width of 20 mm and thickness of 5 mm is subjected to a tensile test and the results obtained are given below. determine the ultimate tensile strength of the specimen. The results of a tensile test are: diameter of specimen 20 mm, gauge length 50 mm, load at limit of proportionality 80 kn, extension at limit of proportionality 0.075 mm, maximum load 100 kn, and final length at point of fracture 60 mm. determine (a) young's modulus of elasticity, (b) the ultimate tensile strength, (c) the stress at the limit.
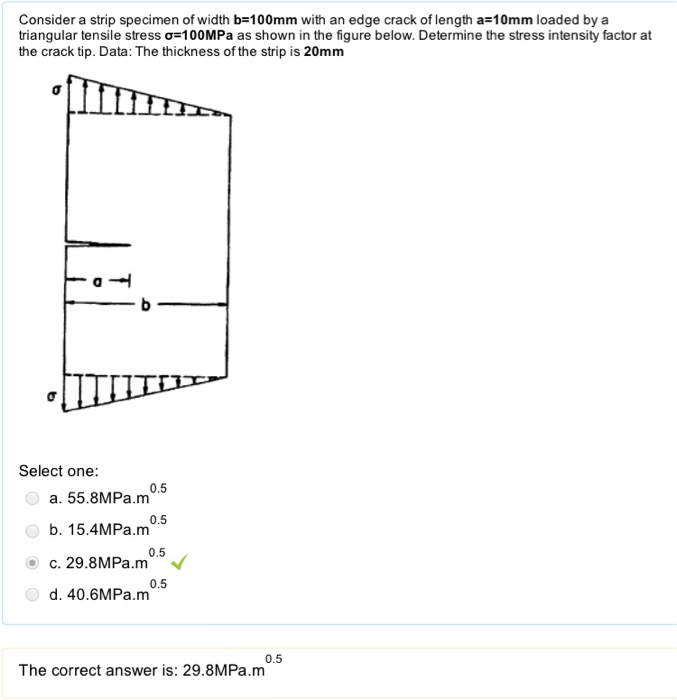
Solved Consider A Strip Specimen Of Width B 100mm With An Chegg The gage length was 50 mm. load (n) elongation (mm) load (n) elongation (mm) 0 0 46 200 1.25 6 310 0.010 52 400 2.50 12 600 0.020 58 500 4.50 18 800 0.030 68 000 7.50 25 100 0.040 59 000 12.5 31 300 0.050 67 800 15.5 37 900 0.060 65 000 20.0 40 100 0.163 65 500 fracture 41 600 0.433 plot the stress strain diagram and determine the following. A steel tensile test specimen has a cross sectional area of 100 mm2 and a gauge length of 50 mm, the gradient of the elastic section is 410 x 103 n mm. determine the modulus of elasticity. In this figure, the gauge length (l0) is the length over which the elongation of the specimen is measured. the minimum parallel length (lc) is the minimum length over which the specimen must maintain a constant cross sectional area before the test load is applied. the lengths l0, lc. li and the cross sectional area (a) are all specified in bs 18. Measure and record the beam width (b), beam thickness (t), and length (l) of the test section. mark a section of specimen and measure the effective length. start the computer and select automatic application icon. n main menu select specimen preparation. select tensile test for rectangular bar.
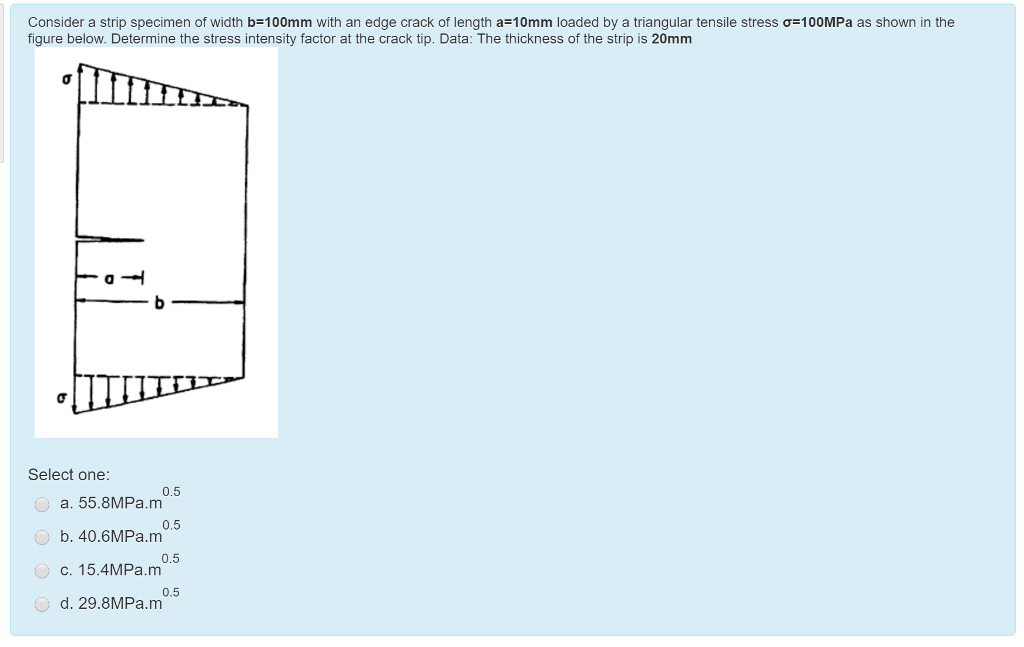
Solved Consider A Strip Specimen Of Width B 100mm With An Chegg In this figure, the gauge length (l0) is the length over which the elongation of the specimen is measured. the minimum parallel length (lc) is the minimum length over which the specimen must maintain a constant cross sectional area before the test load is applied. the lengths l0, lc. li and the cross sectional area (a) are all specified in bs 18. Measure and record the beam width (b), beam thickness (t), and length (l) of the test section. mark a section of specimen and measure the effective length. start the computer and select automatic application icon. n main menu select specimen preparation. select tensile test for rectangular bar. Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like (strength and ductility in tension) a tensile test uses a test specimen that has a gage length of 50 mm and an area = 200 mm2 . during the test the specimen yields under a load of 98,000 n. the corresponding gage length = 50.23 mm. this is the 0.2 percent yield point. the maximum load of 168,000 n is reached at a gage length = 64. The same metal is now tested in a compression test in which the starting height of the specimen = 50 mm and its diameter = 20 mm. if the cross section increases uniformly, determine the load required to compress the specimen to a height of 30 mm. (10) 2.3 a bending test is used on an experimental cemented carbide material.
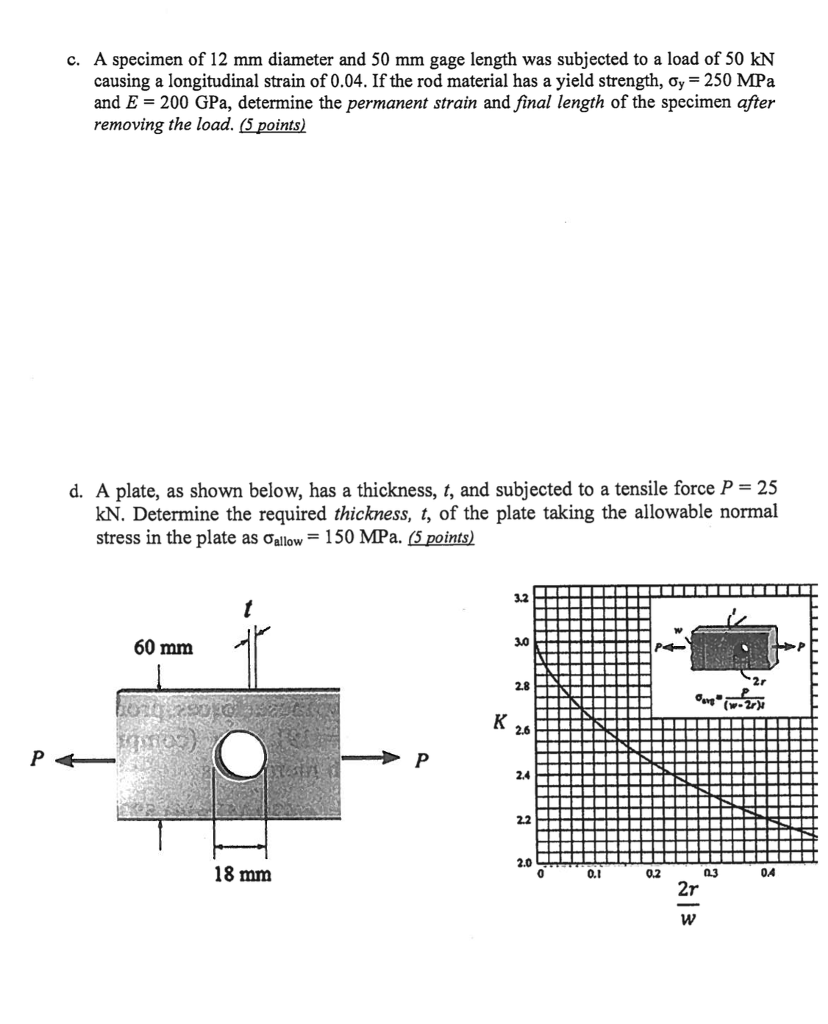
Solved A Specimen Of 12 Mm Diameter And 50 Mm Gage Length Chegg Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like (strength and ductility in tension) a tensile test uses a test specimen that has a gage length of 50 mm and an area = 200 mm2 . during the test the specimen yields under a load of 98,000 n. the corresponding gage length = 50.23 mm. this is the 0.2 percent yield point. the maximum load of 168,000 n is reached at a gage length = 64. The same metal is now tested in a compression test in which the starting height of the specimen = 50 mm and its diameter = 20 mm. if the cross section increases uniformly, determine the load required to compress the specimen to a height of 30 mm. (10) 2.3 a bending test is used on an experimental cemented carbide material.