
Solved 20 Consider The Power System Shown In Figure 1 Chegg Consider the power system shown in the figure below, showing a grid connected generator. assume that the generator is not connected to the grid yet, and that it is protected with an over current relay connected as a differential relay. (14 pts) (this problem is identical to prob 11.3 in the w&w text; if you worked it in advance and brought the solution with you, you may turn in that as your solution to this part of the exam.) consider the three bus network shown in the figure below where x12=0.2pu, x13=0.4pu and x23=0.25 pu. the [x] matrix for this system is also given below:.

Solved Consider The Power System Shown Below In Which The Chegg Hw7 solution ee 4721 introduction to power system analysis fall 2021 homework solution problem consider the circuit shown in the figure below. obtain an. Textbook problem solution for three phase power system analysis, including impedance diagram and voltage calculations. For the power system shown in the figure below, the specifications of the components are the following: g1:25 kv, 100 mva, x = 9% g2:25 kv, 100 mva, x = 9% t1: 25 kv 220 kv, 90 mva, x = 12% t2: 220 kv 25 kv, 90 mva, x = 12% line1:220 kv, x = 150 ohms choose 25 kv as the base voltage at the generator g1, and 200 mva as the mva base. Let's understand the concept of per unit system by solving an example. in the one line diagram below, the impedance of various components in a power system, typically derived from their nameplates, are presented. the task now is to normalize these values using a common base.

Solved Consider The Simplified Electric Power System Shown Chegg For the power system shown in the figure below, the specifications of the components are the following: g1:25 kv, 100 mva, x = 9% g2:25 kv, 100 mva, x = 9% t1: 25 kv 220 kv, 90 mva, x = 12% t2: 220 kv 25 kv, 90 mva, x = 12% line1:220 kv, x = 150 ohms choose 25 kv as the base voltage at the generator g1, and 200 mva as the mva base. Let's understand the concept of per unit system by solving an example. in the one line diagram below, the impedance of various components in a power system, typically derived from their nameplates, are presented. the task now is to normalize these values using a common base. The one line diagram of a three phase power system is as shown in figure 32. impedances are marked in per unit on a 100 mva, 400 kv base. the load at bus 2 is s2 = 15.93 mw −j33.4 mvar, and at bus 3 is s3 = 77 mw j14 mvar. it is required to hold the voltage at bus 3 at 4006 0 kv. working in per unit, determine the voltage at buses 2 and 1. Convert all actual resistance, inductive and capacitive reactance values to per unit using the zbase for each particular part of the power system where each r, x etc. is located. carry out all calculations in per unit, solving for the per unit bus voltage magnitudes and bus phase angles, line currents, and transmission losses.

Solved Consider The Power System Shown In The Figure Below Chegg The one line diagram of a three phase power system is as shown in figure 32. impedances are marked in per unit on a 100 mva, 400 kv base. the load at bus 2 is s2 = 15.93 mw −j33.4 mvar, and at bus 3 is s3 = 77 mw j14 mvar. it is required to hold the voltage at bus 3 at 4006 0 kv. working in per unit, determine the voltage at buses 2 and 1. Convert all actual resistance, inductive and capacitive reactance values to per unit using the zbase for each particular part of the power system where each r, x etc. is located. carry out all calculations in per unit, solving for the per unit bus voltage magnitudes and bus phase angles, line currents, and transmission losses.
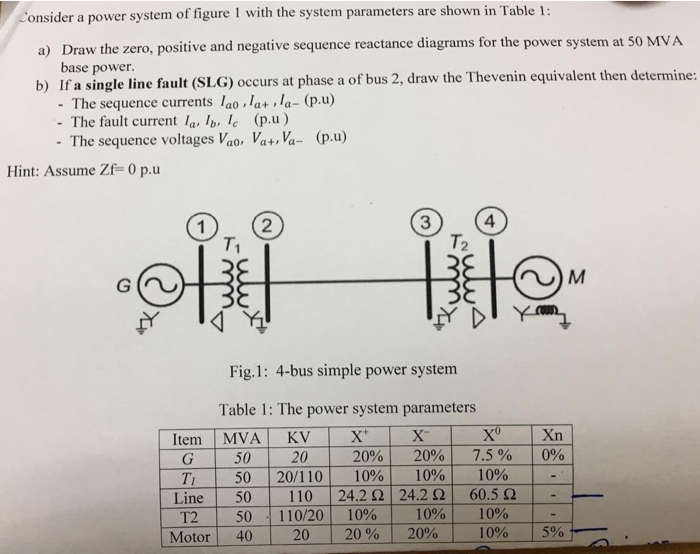
Solved Consider A Power System Of Figure 1 With The System Chegg