
Solved Problem 3 An Old Pipe 2 M In Diameter Has A Chegg Problem 3: an old pipe 2 m in diameter has a roughness of would reduce the pipe roughness to 1 mm. e 30 mm. a 12 mm thick coating 0 a) how much the friction head loss would be reduced per kilometer of pipe, for water at 20 °c at a flow rate of 6 m3 s?. The document provides sample problems related to water flow in pipes. problem 1 involves calculating water loss from a leaking pipe given pressure differences measured upstream and downstream of the leak. problem 2 involves calculating velocity, reynolds number, and force required to produce a given flow through a syringe needle. problem 3 asks for the required pipe size to carry a given water.

Solved A 0 3m Diameter Pipe Is Connected To A 0 02m Diameter Chegg 1. the document contains worked examples of calculating flow rates and head losses in pipe systems with one or more pipes connected in parallel. 2. in example 1, the ratio of flow rates in two parallel pipes of identical diameter is calculated to be the inverse ratio of their lengths. 3. example 4 involves calculating the maximum length of the first portion of a pipe connecting two reservoirs. An, old rough surfaced, 2 m diameter concrete pipe with a manning coefficient of 0.025 carries water at a rate of 5.0 m3 s when it is half full. it is to be replaced by a new pipe with a manning coefficient of 0.012 that is also to flow half full at the same flow rate. determine the diameter of the new pipe. your solution’s ready to go!. It includes two lessons: 1) pipes in series and parallel, which describes how flow and head loss are calculated for these systems, and 2) reservoirs, which describes flow from a reservoir into a pipe. the objectives are to understand the differences between pipes in series and parallel, and to solve problems involving reservoirs. Solved problems,fundamentals of fluid flow free download as pdf file (.pdf) or read online for free. mechanic of fluids.
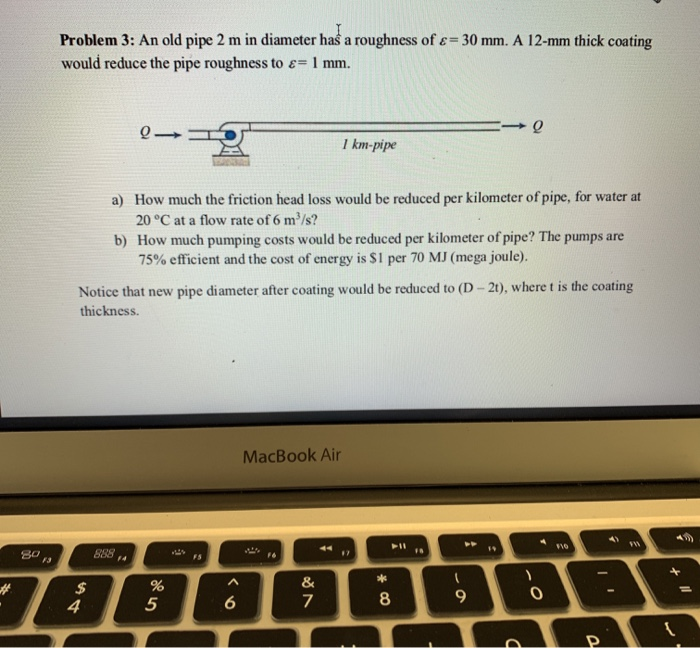
Solved Problem 3 An Old Pipe 2 M In Diameter Haš A Chegg It includes two lessons: 1) pipes in series and parallel, which describes how flow and head loss are calculated for these systems, and 2) reservoirs, which describes flow from a reservoir into a pipe. the objectives are to understand the differences between pipes in series and parallel, and to solve problems involving reservoirs. Solved problems,fundamentals of fluid flow free download as pdf file (.pdf) or read online for free. mechanic of fluids. An insulated cylindrical pipe of 0.2 m diameter has a surface temperature of 450c. it is exposed to black body surroundings at 250c. the emissivity and absorptivity of the insulation surface are 0.96 and 0.93, respectively. the convective heat transfer coefficient outside the insulation surface is 3.25 w (m2k). the stefan boltzmann constant is. Homeworkify – the only tool that you need for study smarter at no cost! with the q&a solutions search engine, you can copy and paste a chegg, course hero or homework question, and get an instant answer. start now by copy and pasting the entire homework question into the ‘type your message’ box, below:.
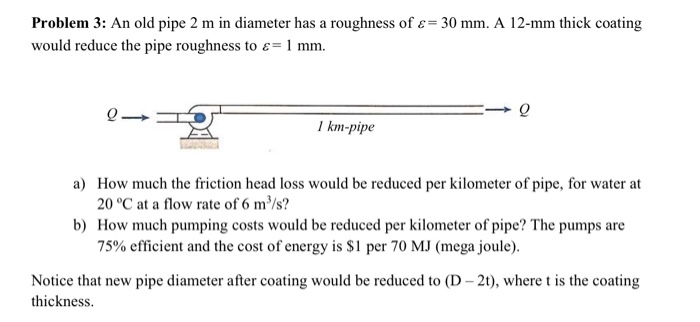
Solved Problem 3 An Old Pipe 2 M In Diameter Has A Chegg An insulated cylindrical pipe of 0.2 m diameter has a surface temperature of 450c. it is exposed to black body surroundings at 250c. the emissivity and absorptivity of the insulation surface are 0.96 and 0.93, respectively. the convective heat transfer coefficient outside the insulation surface is 3.25 w (m2k). the stefan boltzmann constant is. Homeworkify – the only tool that you need for study smarter at no cost! with the q&a solutions search engine, you can copy and paste a chegg, course hero or homework question, and get an instant answer. start now by copy and pasting the entire homework question into the ‘type your message’ box, below:.