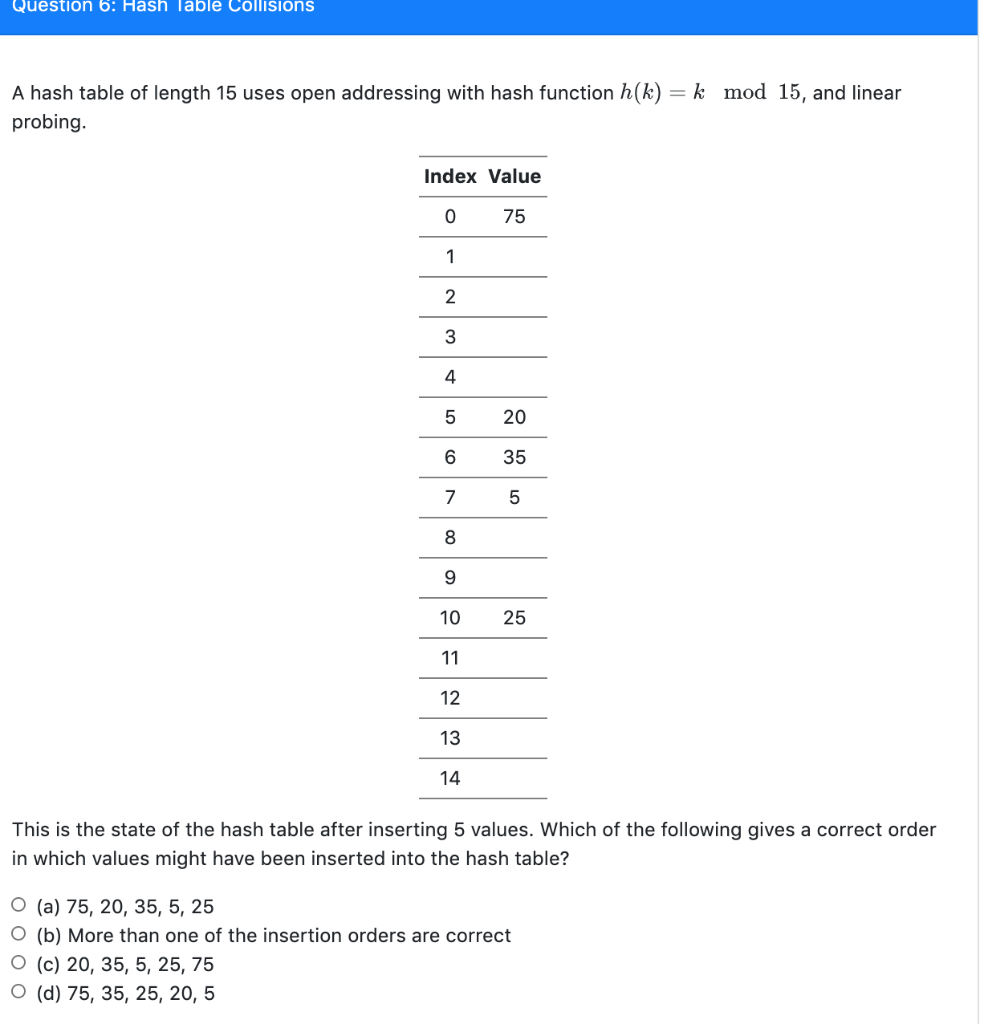
Solved Question 6 Hash Table Collisions A Hash Table Of Chegg Question 6: hash table collisions a hash table of length 15 uses open addressing with hash function h (k) = k mod 15, and linear probing. index value 0 75 1 2 3 4 5 20 6 35 7 5 00 9 10 25 11 12 13 14 this is the state of the hash table after inserting 5 values. Open addressing is a method for handling collisions. in open addressing, all elements are stored in the hash table itself. so at any point, the size of the table must be greater than or equal to the total number of keys (note that we can increase table size by copying old data if needed). this approach is also known as closed hashing.
Solved Question 6 Hash Table Collisions A Hash Table Of Chegg 11.2 6 suppose we have stored n keys in a hash table of size m, with collisions resolved by chaining, and that we know the length of each chain, including the length l of the longest chain. describe a procedure that selects a key uniformly at random from among the keys in the hash table and returns it in expected time o (l. (1 1 α)). Hash tables deal with collisions in one of two ways. option 1: by having each bucket contain a linked list of elements that are hashed to that bucket. this is why a bad hash function can make lookups in hash tables very slow. option 2: if the hash table entries are all full then the hash table can increase the number of buckets that it has and then redistribute all the elements in the table. For 4 the probe function yields slots 0 1 = 1, 0 3 = 3 and 0 6 = 6. c) [10 points] suppose that collisions are resolved by using double hashing (see the course notes), with the secondary hash function reverse(key), which reverses the digits of the key and returns that value; for example, reverse(7823) = 3287. C. hash table using quadratic probing: with quadratic probing, we increment the index by successive squares if there is a collision until an empty slot is found.

Solved Analysis Of Collisions In Hash Tables Consider A Chegg For 4 the probe function yields slots 0 1 = 1, 0 3 = 3 and 0 6 = 6. c) [10 points] suppose that collisions are resolved by using double hashing (see the course notes), with the secondary hash function reverse(key), which reverses the digits of the key and returns that value; for example, reverse(7823) = 3287. C. hash table using quadratic probing: with quadratic probing, we increment the index by successive squares if there is a collision until an empty slot is found. Computer science questions and answers 3. hash tables: dealing with collisions in a hash table, when two keys hash to the same location, we have a collision. there are multiple strategies for handling collisions: • separate chaining each location in the table stores a chain (typically a linked list) of all keys that hashed to that location. Learn hashing mcq questions and answers with easy and logical explanations in data structure. hashing mcq question provides all type of technical mcq questions which is important for technical exams, campus exams and other entrance examination.

Solved 3 Hash Tables Dealing With Collisions In A Hash Chegg Computer science questions and answers 3. hash tables: dealing with collisions in a hash table, when two keys hash to the same location, we have a collision. there are multiple strategies for handling collisions: • separate chaining each location in the table stores a chain (typically a linked list) of all keys that hashed to that location. Learn hashing mcq questions and answers with easy and logical explanations in data structure. hashing mcq question provides all type of technical mcq questions which is important for technical exams, campus exams and other entrance examination.