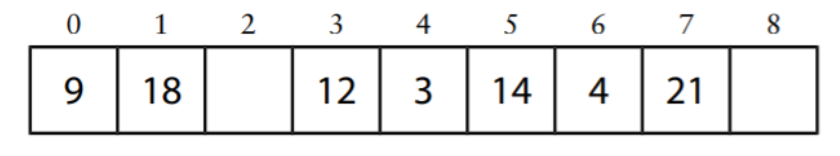
Solved Suppose You Have The Following Hash Table Chegg Computer science computer science questions and answers suppose a hash table is using linear probing to resolve collisions. if the hash table with 300 slots currently has a load factor of 0.55 (ie, λ=0.55 ), what is the probability of a collision occurring when a new item is added? notes: you can assume uniformly distributed hash function. However, because we’re using linear probing as our collision resolution algorithm, our hash table results in the following state after inserting all elements in : now, let’s dive into the linear probing algorithm and learn how we obtained the previous state in our hash table.
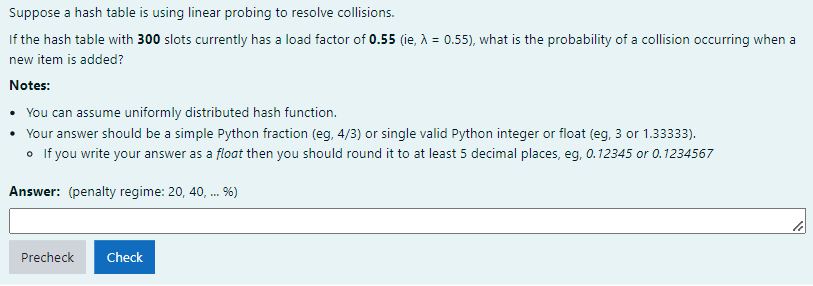
Solved Suppose A Hash Table Is Using Linear Probing To Chegg Exercise 3.2: suppose that our hash function for the table below is a simple mod function: h(x) = x mod table size and we use linear probing to resolve collisions. Implementation : please refer program to implement hash table using open addressing 2. quadratic probing if you observe carefully, then you will understand that the interval between probes will increase proportionally to the hash value. quadratic probing is a method with the help of which we can solve the problem of clustering that was. This is how the linear probing collision resolution technique works. challenges and solutions in linear probing clustering: one issue with linear probing is clustering, where a bunch of occupied spots clump together, slowing down the insertion and search processes. to minimize clustering, the table should have enough empty spots and use a good hash function that spreads items evenly. infinite. The simplest open addressing method is called linear probing: when there is a collision (when we hash to a table index that is already occupied with a key different from the search key), then we just check the next entry in the table (by incrementing the index).

Solved Suppose A Hash Table Is Using Linear Probing To Chegg This is how the linear probing collision resolution technique works. challenges and solutions in linear probing clustering: one issue with linear probing is clustering, where a bunch of occupied spots clump together, slowing down the insertion and search processes. to minimize clustering, the table should have enough empty spots and use a good hash function that spreads items evenly. infinite. The simplest open addressing method is called linear probing: when there is a collision (when we hash to a table index that is already occupied with a key different from the search key), then we just check the next entry in the table (by incrementing the index). The question you might be looking for : given the input (4371, 1323, 6173, 4199, 4344, 9679, 1989) and a hash function of h (x)=x (mod 10) show the resulting: a. separate chaining hash table (note: to make insertion easy to show, just add new element at the end of linked list) b. hash table using linear probing c. hash table using quadratic. The hash function we are using is the following: h (k) = k mod 9. suppose you have the following hash table, implemented using open addressing and linear probing. the hash function we are using is the following: h (k) = k mod 9 there are 3 steps to solve this one.

Solved Suppose You Have The Following Hash Table Chegg The question you might be looking for : given the input (4371, 1323, 6173, 4199, 4344, 9679, 1989) and a hash function of h (x)=x (mod 10) show the resulting: a. separate chaining hash table (note: to make insertion easy to show, just add new element at the end of linked list) b. hash table using linear probing c. hash table using quadratic. The hash function we are using is the following: h (k) = k mod 9. suppose you have the following hash table, implemented using open addressing and linear probing. the hash function we are using is the following: h (k) = k mod 9 there are 3 steps to solve this one.
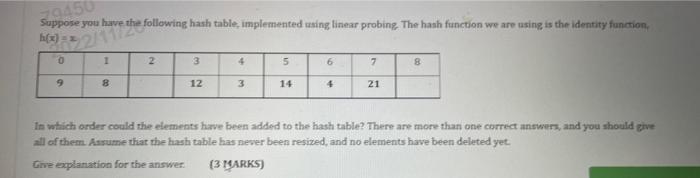
Solved Suppose You Have The Following Hash Table Chegg