Solved Problem 4 The Power Flow Problem Of The System Shown Chegg All values are given as per unit values with respect to the same base. provide the detailed procedure for solving] the power flow problem: 5.1 the first iteration of the gs method 5.2 the first iteration of the nr method 5.3 the first iteration of the decoupled method 5.4 solve the dc power flow problem. 4. (18 pts) a two bus power system is interconnected by a transmission line having series admittance of y12=0.304 j01.88 pu and total line charging of ycharging=j0.064 pu. bus 2 is a load bus with specified demand as pd pu and qd pu. bus 1 is a generator bus with specified terminal voltage magnitude of |v1| pu. we desire to solve the power flow problem for this system.
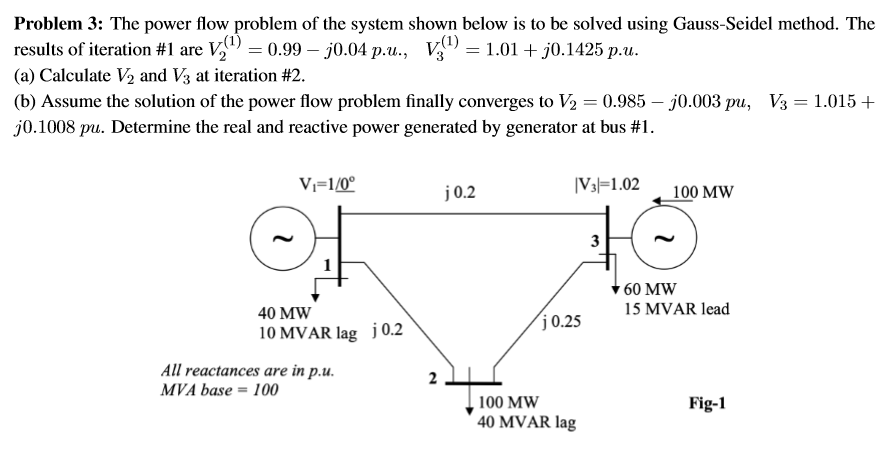
Problem 3 The Power Flow Problem Of The System Shown Chegg The most common power system analysis tool is the power flow (also known sometimes as the load flow) power flow determines how the power flows in a network also used to determine all bus voltages and all currents because of constant power models, power flow is a nonlinear analysis technique power flow is a steady state analysis tool. Can’t simply solve must employ numerical, iterative solution methods power system analysis to determine bus voltages and power flows is called power flow analysis or load flow analysis consider the one line diagram for a simple power system system includes: generators buses transformers treated as equivalent circuit impedances in per unit. In this example we have actually solved our first power flow problem by the newt on raphson method . this is because the two nonlinear equations of the example are the power flow equations for the simple system shown in the figure. The document summarizes the gauss seidel method for solving power flow problems. it describes power flow equations relating the voltage, current, real power, and reactive power at each bus. it provides the steps of the gauss seidel iteration process which solves for the unknown voltage magnitudes and angles at load buses in an electrical network by using initial estimates and successively.
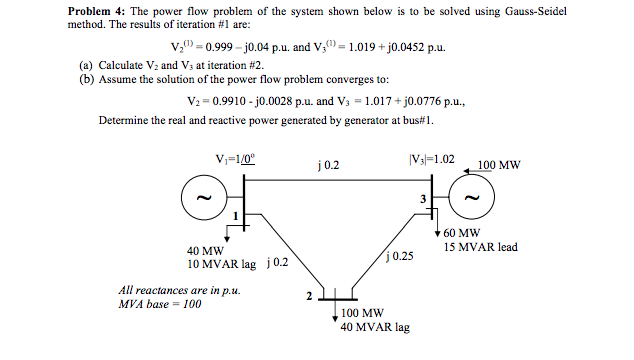
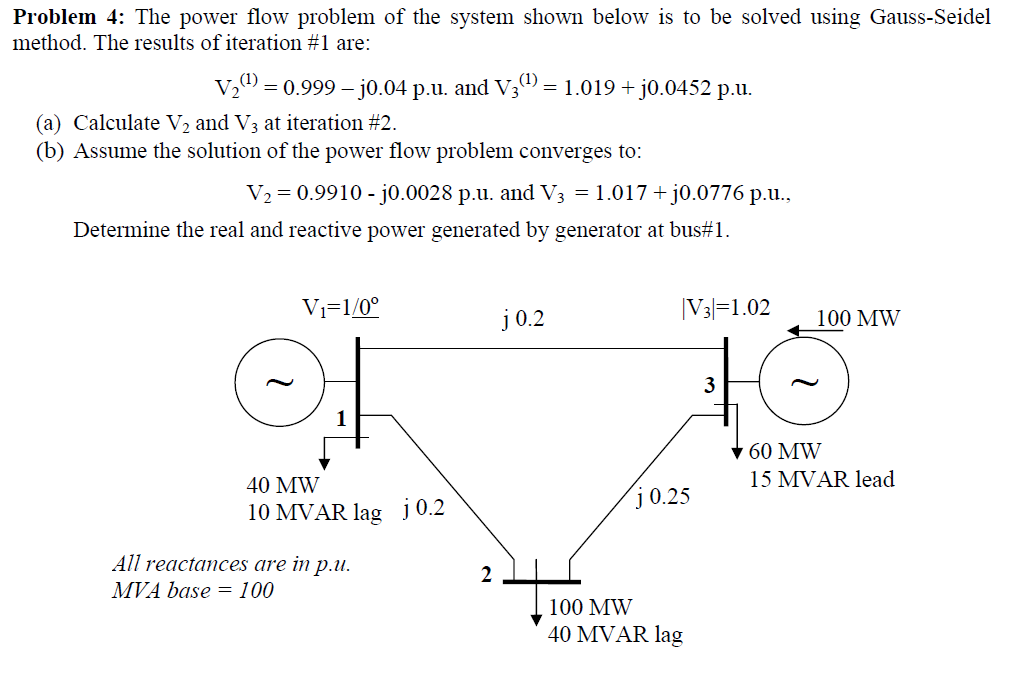
Solved Problem 4 The Power Flow Problem Of The System Shown Chegg In this example we have actually solved our first power flow problem by the newt on raphson method . this is because the two nonlinear equations of the example are the power flow equations for the simple system shown in the figure. The document summarizes the gauss seidel method for solving power flow problems. it describes power flow equations relating the voltage, current, real power, and reactive power at each bus. it provides the steps of the gauss seidel iteration process which solves for the unknown voltage magnitudes and angles at load buses in an electrical network by using initial estimates and successively. Download the cases needed for the assignment (pw simulator 5.0 or later format) one line diagram, together with the bus and line data, of a 5 bus power system is shown below; the system will be referred to as utility a. solve the following problems using thepowerworld simulator and the original data file 454 0.pwb and the one line diagram file 454 0.pwd. Engineering electrical engineering electrical engineering questions and answers problem 4: the power flow problem of the system shown below is to be solved using gauss seidel method. the results of iteration #1 are: v2 (1) = 0.999 j0.04 p. u. and v3 (1) = 1.019 j0.0452 pu (a) calculate v2 and v3 at iteration #2.
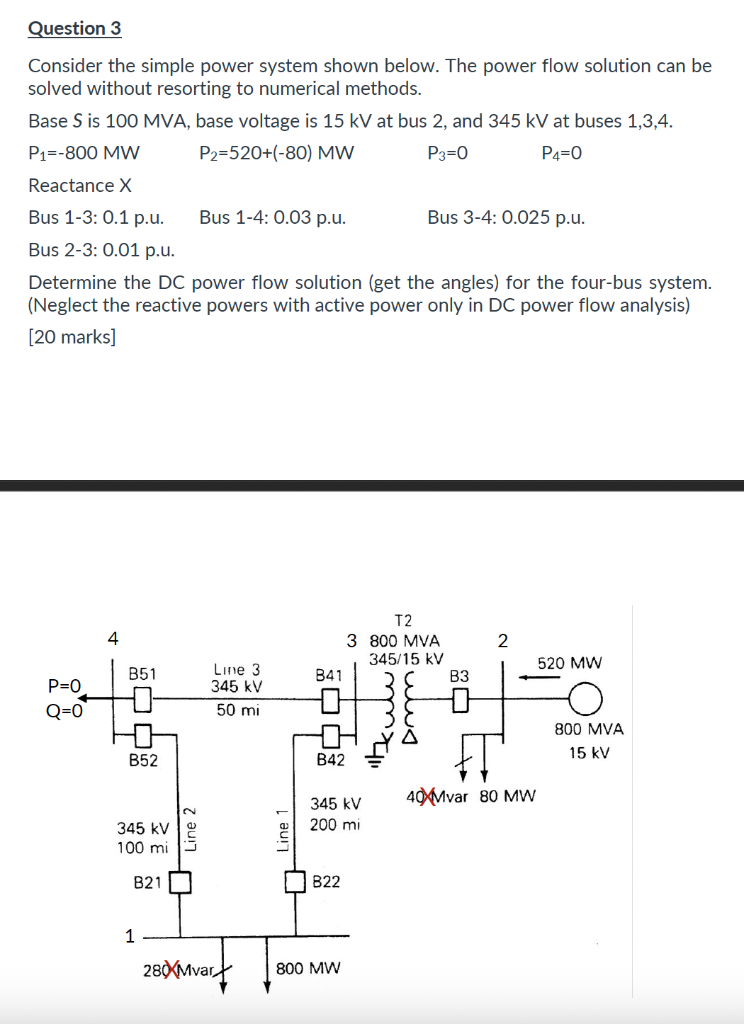
Solved Question 3 Consider The Simple Power System Shown Chegg Download the cases needed for the assignment (pw simulator 5.0 or later format) one line diagram, together with the bus and line data, of a 5 bus power system is shown below; the system will be referred to as utility a. solve the following problems using thepowerworld simulator and the original data file 454 0.pwb and the one line diagram file 454 0.pwd. Engineering electrical engineering electrical engineering questions and answers problem 4: the power flow problem of the system shown below is to be solved using gauss seidel method. the results of iteration #1 are: v2 (1) = 0.999 j0.04 p. u. and v3 (1) = 1.019 j0.0452 pu (a) calculate v2 and v3 at iteration #2.
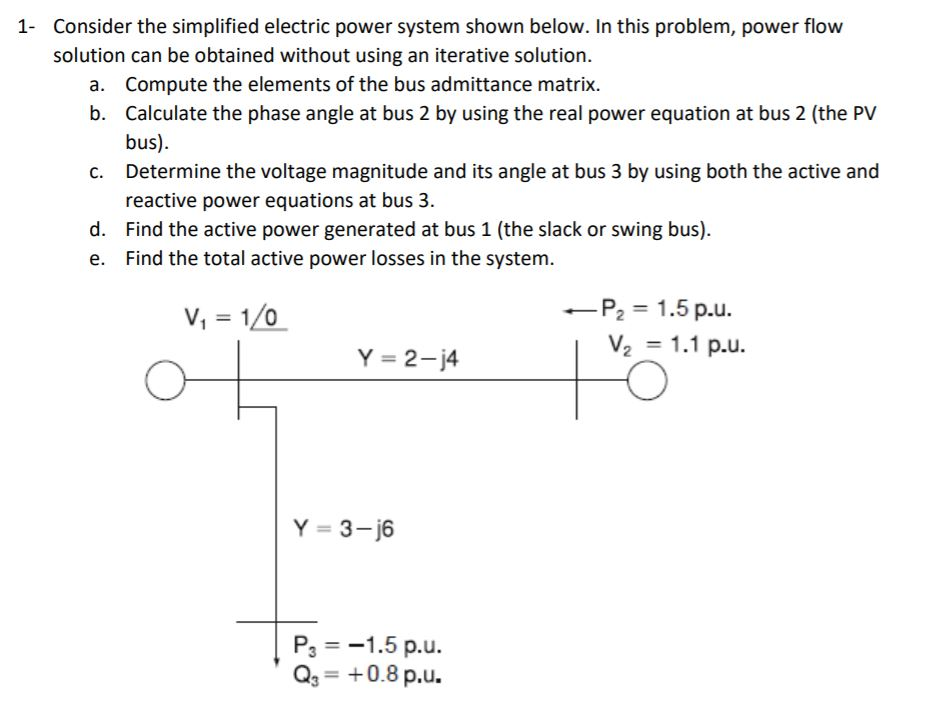
Solved Consider The Simplified Electric Power System Shown Chegg