
Synchronous Motor Pdf Pdf Electric Motor Electrical Engineering A synchronous electric motor is an ac motor distinguished by a rotor spinning with coils passing magnets at the same rate as the alternating current and resulting magnetic field which drives it. Synchronous motors there are numerous applications where an electric motor must have an exact shaft rotation. timing devices and tape drives are applications where exact shaft rotation is necessary. an ac synchronous motor is one where the shaft rotation is exactly the same as the magnetic field rotation. for a 60 hz 2 pole motor the field rotates at 3600 rpm and for a 4 pole motor the field.

Motors Synchronous Pdf Electric Motor Electrical Connector Permanent magnet brushless dc motors rollers drive circuits, applications. unit 5 permanent magnet synchronous motors . construction and types, principle of operation, emf and torque equation, phasor diagram torque speed characteristics, power controllers self control, vector control, microprocessor based control, applications. In the synchronous motor, the basic magnetic field is obtained by direct current excitation rather than through the air gap from the armature, as is the case with induction motors. comparatively large air gaps are used, making practicable the manufacture, even in relatively low horsepower ratings of low speed synchronous motors. To understand the basic concept of a synchronous motor, look at figure 6 1, which shows a two pole synchronous motor. 1lle field current if of the motor produces a steady state magnetic field hr. a three phase set of voltages is applied to the stator orthe machine, which produces a three phase current flow in the windings. The document discusses synchronous motors. it explains that they run at synchronous speed, which is determined by supply frequency. they are not self starting and require methods like reducing frequency, using an external prime mover, or adding a damper winding to start. dc excitation is used to provide a steady magnetic field for the rotor so that torque production remains unidirectional as.

Synchronous Motor Pdf Power Inverter Electric Power System To understand the basic concept of a synchronous motor, look at figure 6 1, which shows a two pole synchronous motor. 1lle field current if of the motor produces a steady state magnetic field hr. a three phase set of voltages is applied to the stator orthe machine, which produces a three phase current flow in the windings. The document discusses synchronous motors. it explains that they run at synchronous speed, which is determined by supply frequency. they are not self starting and require methods like reducing frequency, using an external prime mover, or adding a damper winding to start. dc excitation is used to provide a steady magnetic field for the rotor so that torque production remains unidirectional as. A synchronous motor is started as induction motor till it runs 2 to 5% below the synchronous speed. afterwards, excitation is switched on and the rotor pulls into step with the synchronously rotating stator field. Introduction synchronous motors is called so because the speed of the rotor of this motor is same as the rotating magnetic field.
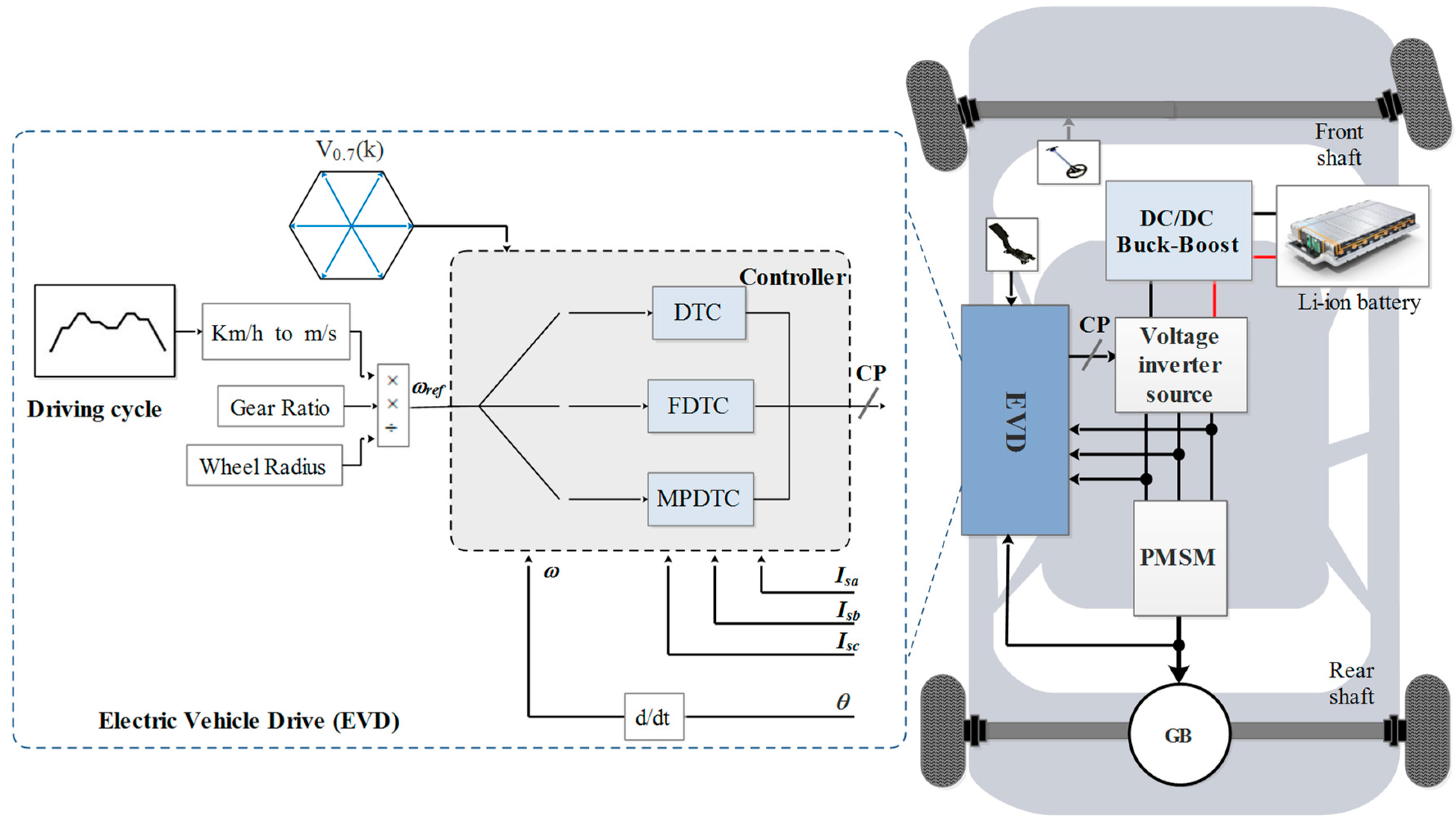
A Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor For Traction Applications Of A synchronous motor is started as induction motor till it runs 2 to 5% below the synchronous speed. afterwards, excitation is switched on and the rotor pulls into step with the synchronously rotating stator field. Introduction synchronous motors is called so because the speed of the rotor of this motor is same as the rotating magnetic field.