
Off The Bell Curve 4.1 the normal distribution here, you will look at the concept of normal distribution and the bell shaped curve. the peak point (the top of the bell) represents the most probable occurrences, while other possible occurrences are distributed symmetrically around the peak point, creating a downward sloping curve on either side of the peak point. A bell shaped curve, also known as a normal distribution or gaussian distribution, is a symmetrical probability distribution in statistics. it represents a graph where the data clusters around the mean, with the highest frequency in the center, and decreases gradually towards the tails.

Bell Curve Psychological Testing Normal Distribution The Myth Of The What is the bell curve? the bell curve is a simple way to look at how student performance on things like reading, math, or even social skills behavior, is spread out across a large group. it can tell you where your child’s performance lies in comparison to that of other children their age and help you beter understand their test scores. If 100 five year olds take the test and the average score (mean) and most common score (mode) is 100, the sample has produced a bell curve (normal distribution) with 100 at the 50th percentile. this would be right at the top of the bell curve. Conclusion 🔗 the normal distribution curve is a powerful tool in educational evaluation and psychological assessment. its symmetrical, bell shaped pattern provides valuable insights into how students are performing, both individually and as a group. Spg's bell curve graphic is a great visual resource for educators to use when discussing standardized testing results with families.
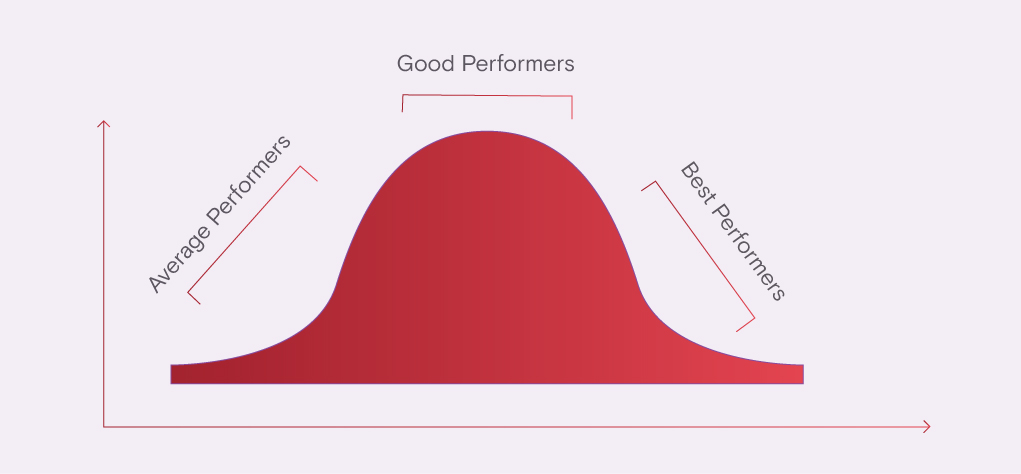
Change Management Bell Curve Conclusion 🔗 the normal distribution curve is a powerful tool in educational evaluation and psychological assessment. its symmetrical, bell shaped pattern provides valuable insights into how students are performing, both individually and as a group. Spg's bell curve graphic is a great visual resource for educators to use when discussing standardized testing results with families. The bell curve represents a normal distribution, the green area is where you’d accept the null hypothesis (h 0 ), and the red area is the “rejection zone,” where you’d favor the alternative hypothesis (ha ). the vertical blue line represents the threshold value or “critical value,” beyond which you’d reject h 0 . But in many cases the data tends to be around a central value, with no bias left or right, and it gets close to a "normal distribution" like this: the blue curve is a normal distribution. the yellow histogram shows some data that follows it closely, but not perfectly (which is usual).

Bell Curve Psychological Testing Normal Distribution The Myth Of The The bell curve represents a normal distribution, the green area is where you’d accept the null hypothesis (h 0 ), and the red area is the “rejection zone,” where you’d favor the alternative hypothesis (ha ). the vertical blue line represents the threshold value or “critical value,” beyond which you’d reject h 0 . But in many cases the data tends to be around a central value, with no bias left or right, and it gets close to a "normal distribution" like this: the blue curve is a normal distribution. the yellow histogram shows some data that follows it closely, but not perfectly (which is usual).