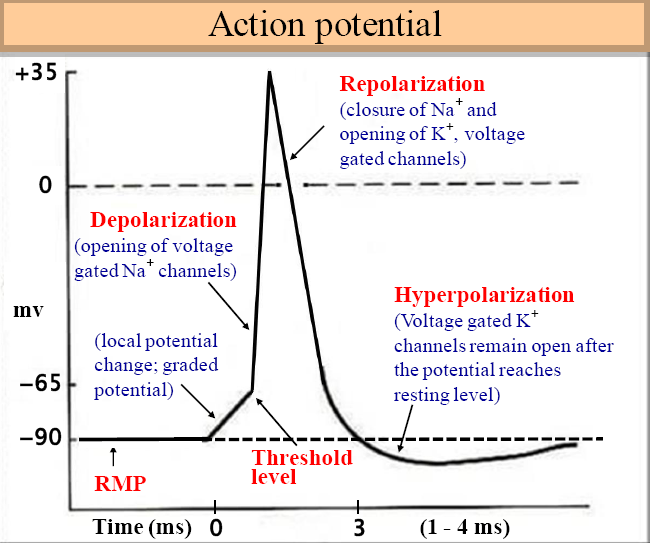
Action Potential Howmed Figure 12.23 graph of action potential plotting voltage measured across the cell membrane against time, the action potential begins with depolarization, followed by repolarization, which goes past the resting potential into hyperpolarization, and finally the membrane returns to rest. This article discusses action potential definition, steps and phases. click now to start with physiology 101 at kenhub!.

Anatomy Physiology Nervous System Action Potential By Mrs Monton Makes The functions of the nervous system—sensation, integration, and response—depend on the functions of the neurons underlying these pathways. to understand how neurons are able to communicate, it is necessary to describe the role of an excitable membrane in generating these signals. the basis of this communication is the action potential, which demonstrates how changes in the membrane can. Action potential is a brief reversal of membrane potential in which the membrane potential changes from 70mv to 30mv the action potential has three main stages: depolarization, repolarization, and hyperpolarization. depolarization is caused when positively charged sodium ions rush into a neuron with the opening of voltage gated sodium channels. Integrated human anatomy and physiology part 2 (not updated) the action potential objective 5 construct a model of the action potential. this trace shows the characteristic shape of the action potential. time is shown on the x axis (abscissa, horizontal axis). Figure 4.13 graph of action potential plotting voltage measured across the cell membrane against time, the action potential begins with depolarization, followed by repolarization, which goes past the resting potential into hyperpolarization, and finally the membrane returns to rest. the question is, now, what initiates the action potential?.

Anatomy And Physiology Action Potential Notes Phases Of An Action Integrated human anatomy and physiology part 2 (not updated) the action potential objective 5 construct a model of the action potential. this trace shows the characteristic shape of the action potential. time is shown on the x axis (abscissa, horizontal axis). Figure 4.13 graph of action potential plotting voltage measured across the cell membrane against time, the action potential begins with depolarization, followed by repolarization, which goes past the resting potential into hyperpolarization, and finally the membrane returns to rest. the question is, now, what initiates the action potential?. Action potential, the brief (about one thousandth of a second) reversal of electric polarization of the membrane of a nerve cell (neuron) or muscle cell. in the neuron an action potential produces the nerve impulse, and in the muscle cell it produces the contraction required for all movement. Figure 7. graph of action potential plotting voltage measured across the cell membrane against time, the action potential begins with depolarization, followed by repolarization, which goes past the resting potential into hyperpolarization, and finally the membrane returns to rest.

Anatomy And Physiology Action Potential Notes Phases Of An Action Action potential, the brief (about one thousandth of a second) reversal of electric polarization of the membrane of a nerve cell (neuron) or muscle cell. in the neuron an action potential produces the nerve impulse, and in the muscle cell it produces the contraction required for all movement. Figure 7. graph of action potential plotting voltage measured across the cell membrane against time, the action potential begins with depolarization, followed by repolarization, which goes past the resting potential into hyperpolarization, and finally the membrane returns to rest.

Action Potential Anatomy

Anatomy And Physiology Action Potential Notes Phases Of An Etsy