
The Forgetting Curve Peersite The forgetting curve is one of the most well known and established findings in memory research. knowing the pattern of memory change over time can provide insight into underlying cognitive mecha nisms. the default understanding is that forgetting follows a continuous, negatively accelerating func tion, such as a power function. The ebbinghaus forgetting curve, also known as the ebbinghaus memory curve, displays how we retain information.

The Forgetting Curve Peersite A representation of the forgetting curve showing retained information halving after each day the forgetting curve hypothesizes the decline of memory retention in time. this curve shows how information is lost over time when there is no attempt to retain it. [1] a related concept is the strength of memory that refers to the durability that memory traces in the brain. the stronger the memory. Ebbinghaus' forgetting curve is a memory model that shows how we lose information over time. luckily, there are various ways to combat it!. The science behind learning forgetting curve the german psychologist hermann ebbinghaus was the first to hypothesize and study (in 1885) the now famous forgetting curve – often referred to as ebbinghaus' forgetting curve. he noticed that at the time of learning, or taking in new information, a learner "knows" 100% of the material. We present a successful replication of ebbinghaus’ classic forgetting curve from 1880 based on the method of savings. one subject spent 70 hours learning lists and relearning them after 20 min, 1 hour, 9 hours, 1 day, 2 days, or 31 days. the results are similar to ebbinghaus' original data. we analyze the effects of serial position on forgetting and investigate what mathematical equations.
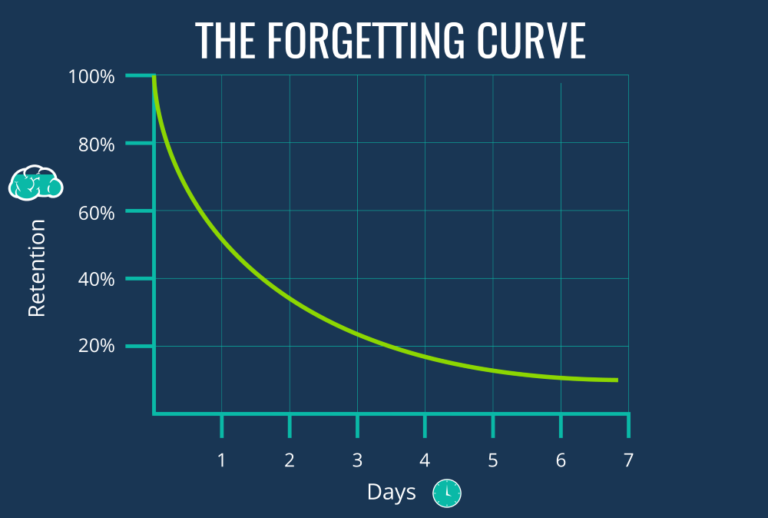
How To Overcome The Forgetting Curve And Improve Your Memory The science behind learning forgetting curve the german psychologist hermann ebbinghaus was the first to hypothesize and study (in 1885) the now famous forgetting curve – often referred to as ebbinghaus' forgetting curve. he noticed that at the time of learning, or taking in new information, a learner "knows" 100% of the material. We present a successful replication of ebbinghaus’ classic forgetting curve from 1880 based on the method of savings. one subject spent 70 hours learning lists and relearning them after 20 min, 1 hour, 9 hours, 1 day, 2 days, or 31 days. the results are similar to ebbinghaus' original data. we analyze the effects of serial position on forgetting and investigate what mathematical equations. The forgetting curve hermann ebbinghaus (1850 1909) was a german psychologist who founded the experimental psychology of memory. ebbinghaus’ research was groundbreaking at the time, and his work (though he was not a prolific writer) was generally well received. in recognition of his work in psychology, the “forgetting curve”—the loss of learned information—is sometimes referred to as. 1. the form of the forgetting curve and the fate of memories the search for a general quantitative description of the “forgetting curve”, the nonlinear function relating the observed probability of memory retention (r) and the delay or lag between study and test (t), is one of experimental psychology’s oldest problems (ebbinghaus, 1885 1974).

Curve Of Forgetting Teaching Matters The forgetting curve hermann ebbinghaus (1850 1909) was a german psychologist who founded the experimental psychology of memory. ebbinghaus’ research was groundbreaking at the time, and his work (though he was not a prolific writer) was generally well received. in recognition of his work in psychology, the “forgetting curve”—the loss of learned information—is sometimes referred to as. 1. the form of the forgetting curve and the fate of memories the search for a general quantitative description of the “forgetting curve”, the nonlinear function relating the observed probability of memory retention (r) and the delay or lag between study and test (t), is one of experimental psychology’s oldest problems (ebbinghaus, 1885 1974).

Understanding The Forgetting Curve Top 4 Insights For L D

Forgetting Curve

The Forgetting Curve