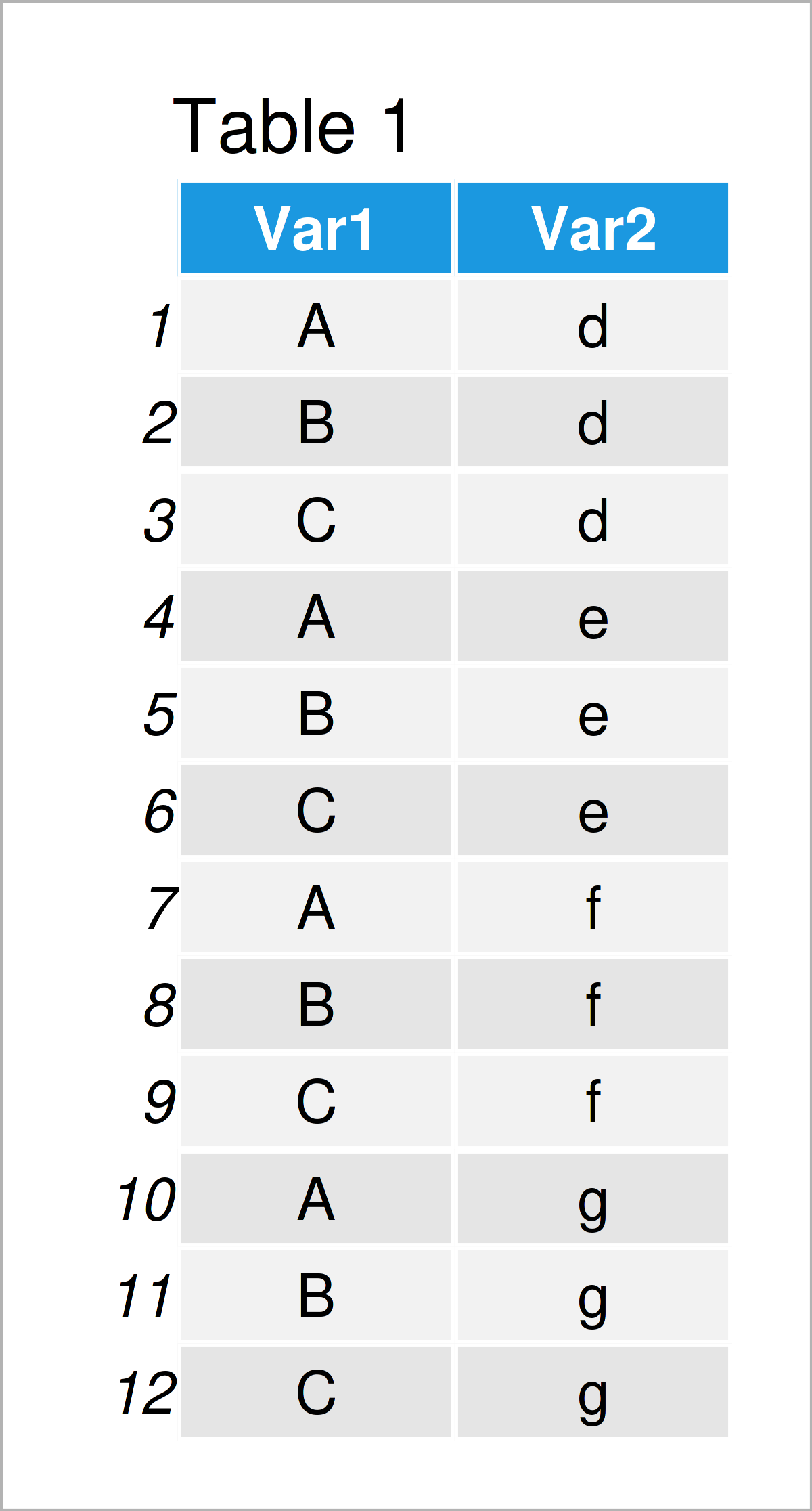
Expand Grid Function In R Example All Combinations Of Factor Variables 2 i am using rep and expand.grid with lists, but the output is not what i expected. the documentation isn't clear on how expand.grid works with lists. could someone explain how the two functions work together? rep replicates the elements of a vector x x < c(0, 1) rep(x, 2) # 0 1 0 1 so it replicates vector list elements. however, when i run it. Expand() generates all combination of variables found in a dataset. it is paired with nesting() and crossing() helpers. crossing() is a wrapper around expand grid() that de duplicates and sorts its inputs; nesting() is a helper that only finds combinations already present in the data. expand() is often useful in conjunction with joins: use it with right join() to convert implicit missing.

Expand Grid Function In R Example All Combinations Of Factor Variables This tutorial explains how to use the expand.grid() function in r to create a data frame, including several examples. Expand.grid: create a data frame from all combinations of factor variables description create a data frame from all combinations of the supplied vectors or factors. see the description of the return value for precise details of the way this is done. usage expand.grid(…, keep.out.attrs = true, stringsasfactors = true) arguments. Usage expand.grid( , keep.out.attrs = true, stringsasfactors = true) arguments value a data frame containing one row for each combination of the supplied factors. the first factors vary fastest. the columns are labelled by the factors if these are supplied as named arguments or named components of a list. the row names are ‘automatic’. See also complete () for a common application of expand: completing a data frame with missing combinations. expand grid () is low level that doesn't deduplicate or sort values.
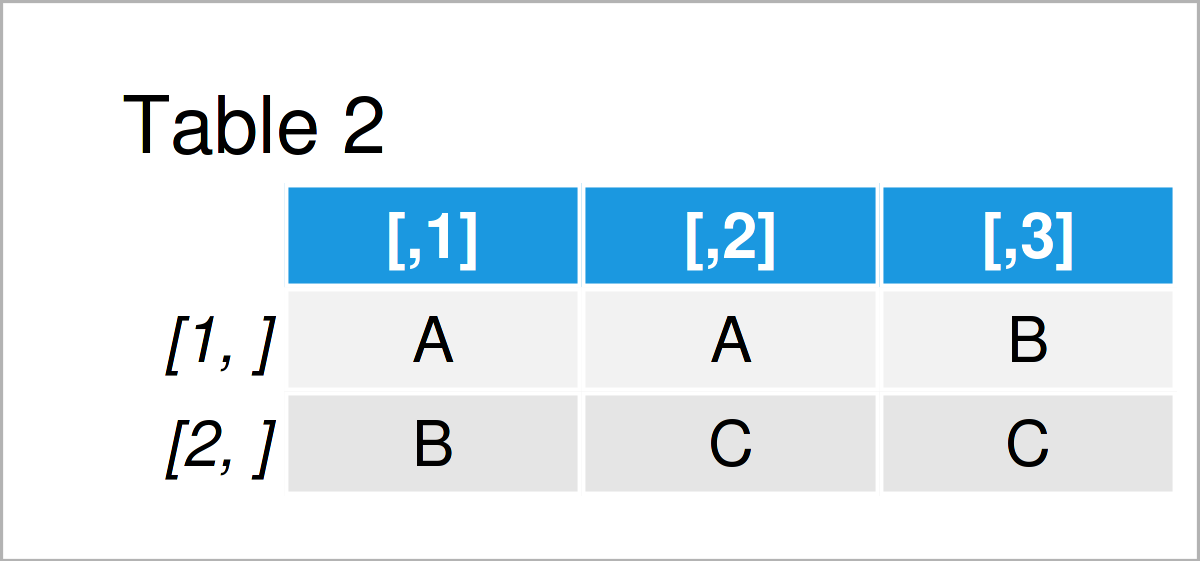
Non Redundant Version Of Expand Grid In R No Duplicate Combinations Usage expand.grid( , keep.out.attrs = true, stringsasfactors = true) arguments value a data frame containing one row for each combination of the supplied factors. the first factors vary fastest. the columns are labelled by the factors if these are supplied as named arguments or named components of a list. the row names are ‘automatic’. See also complete () for a common application of expand: completing a data frame with missing combinations. expand grid () is low level that doesn't deduplicate or sort values. What is the expand.grid () function? it is a function in r’s base system, meaning that it is already there when you install r for the first time, and does not even require any additional package. Df < expand.grid(a=1:2, b=1:2, c=1:2,) but this somehow feels inelegant. i tried using df < expand.grid(rep(1:2, 3)) but this produced a single column where the numbers 1 and 2 were repeated 3 times, instead of a grid. is there a way to get expand.grid to work with my input, or is there an easy way of doing what i'm asking for using another.

Non Redundant Version Of Expand Grid In R No Duplicate Combinations What is the expand.grid () function? it is a function in r’s base system, meaning that it is already there when you install r for the first time, and does not even require any additional package. Df < expand.grid(a=1:2, b=1:2, c=1:2,) but this somehow feels inelegant. i tried using df < expand.grid(rep(1:2, 3)) but this produced a single column where the numbers 1 and 2 were repeated 3 times, instead of a grid. is there a way to get expand.grid to work with my input, or is there an easy way of doing what i'm asking for using another.

Grid R Expanddong