
Time Complexity Part 1 May 18 Pdf Time complexity: o (log (log n)) auxiliary space: o (1) how to find the time complexity of an algorithm? now let us see some other examples and the process to find the time complexity of an algorithm: example: let us consider a model machine that has the following specifications: single processor 32 bit sequential execution 1 unit time for arithmetic and logical operations 1 unit time for. In this guide, you have learned what time complexity is all about, how performance is determined using the big o notation, and the various time complexities that exists with examples.
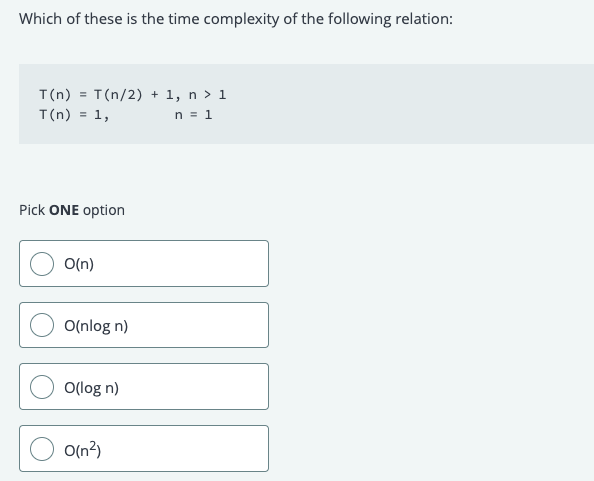
Solved Which Of These Is The Time Complexity Of The Chegg A simple example of o(1) might be return 23; whatever the input, this will return in a fixed, finite time. a typical example of o(n log n) would be sorting an input array with a good algorithm (e.g. mergesort). Time complexity is represented by o (parameter), where parameter can be a constant, a single variable, a quadratic variable, etc. time complexity expresses an approximation of the time to execute a certain task. for example, let's assume that we want to execute console.log('hi') in different ways and measure the time to do it. o (1) time between executions remains (almost) constant. When the running time of an algorithm increases non linearly o (n^2) with the length of the input, it is said to have a non linear time complexity. in general, nested loops fall into the o (n)*o (n) = o (n^2) time complexity order, where one loop takes o (n) and if the function includes loops inside loops, it takes o (n)*o (n) = o (n^2). Understanding time complexity concept figure table of contents 1. introduction definition of time complexity importance in algorithm design 2. understanding big o notation definition and.

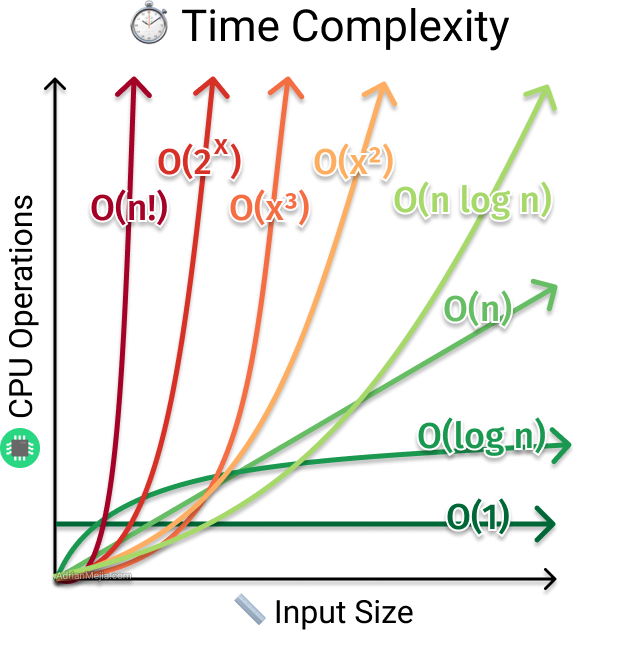
Chapter 1 Complexity Pdf Time Complexity Computational Complexity When the running time of an algorithm increases non linearly o (n^2) with the length of the input, it is said to have a non linear time complexity. in general, nested loops fall into the o (n)*o (n) = o (n^2) time complexity order, where one loop takes o (n) and if the function includes loops inside loops, it takes o (n)*o (n) = o (n^2). Understanding time complexity concept figure table of contents 1. introduction definition of time complexity importance in algorithm design 2. understanding big o notation definition and. O (2^n) – exponential time – execution time blows up rapidly the "n" refers to the input size. so o (n) equals linear time complexity – doubling the inputs doubles the runtime. big o notation also ignores constants and lower order terms. this simplifies analysis to focus on the long term growth rate as inputs scale towards infinity. Master the fundamentals of big o notation and time complexity analysis. learn about o (1), o (n), o (log n), o (n²), and o (2ⁿ) with practical examples and real world applications.

Understanding Time Complexity Examples O 1 O N O N 2 Course Hero O (2^n) – exponential time – execution time blows up rapidly the "n" refers to the input size. so o (n) equals linear time complexity – doubling the inputs doubles the runtime. big o notation also ignores constants and lower order terms. this simplifies analysis to focus on the long term growth rate as inputs scale towards infinity. Master the fundamentals of big o notation and time complexity analysis. learn about o (1), o (n), o (log n), o (n²), and o (2ⁿ) with practical examples and real world applications.

Solved What Will Be The Time Complexity Of The Following Chegg

Solved Note Your Solution Should Have O N Time Complexity Chegg
Understanding Time Complexity Through Visual Examples Peerdh