
Gis Vector Raster Images Vector And Raster Data Gis Vector And Hot Spatial data observations focus on locations. every house, every tree, and every city has its own unique latitude and longitude coordinates. the two primary types of spatial data are vector and raster data in a gis. but what is the difference between raster and vector data? when should we use raster and when should we use vector features? find out more about the spatial data models commonly used. Explore the key differences between gis vector and raster data, and how each type supports diverse spatial analysis tasks.

Vector Vs Raster In Gis What S The Difference Gis Geography Geographic information system (gis) is a powerful tool for capturing, analyzing, and presenting spatial data. it is widely used in various fields, including urban planning, environmental management, and natural resource management. two fundamental data models used in gis are raster and vector data models. Vector vs raster model ― a simplified representation of a phenomenon or a system. gis data model ― the records that represent the geographic locations and distribution features of natural phenomenon and social phenomenon. it includes natural geographic data and social economic data. vector data model figure 1. vector data representation. The main difference between raster and vector data is that the raster data represents data as a cell or a grid matrix while vector data represents data using sequential points or vertices. geographic information system (gis) is a computer based tool or technology to manage, analyze and display geographically referenced information. users can visualize, and understand the relationships between. This article will give a detailed look at vector data vs raster data. after reading this, you should be able to make a sound decision on which to use.
Raster Vs Vector Data Formats In Gis Equator The main difference between raster and vector data is that the raster data represents data as a cell or a grid matrix while vector data represents data using sequential points or vertices. geographic information system (gis) is a computer based tool or technology to manage, analyze and display geographically referenced information. users can visualize, and understand the relationships between. This article will give a detailed look at vector data vs raster data. after reading this, you should be able to make a sound decision on which to use. The difference between vector and raster data in gis in this article, we will cover the fundamental differences between raster and vector data. geospatial data can be represented using either vector data type or raster. the two data types are very different in their internal representation, the operations you can do on them as well as their look and feel. the figures below show a. Understanding the difference between vector and raster data is fundamental for gis. these two types of spatial data are the backbone of gis analyses and mapping, each with its unique characteristics, advantages, and applications.
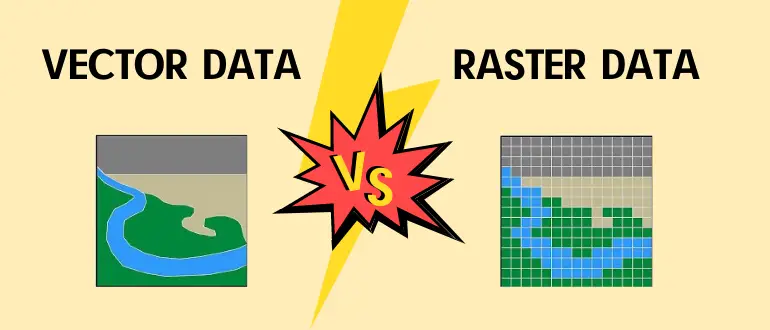
Raster Versus Vector Gis The difference between vector and raster data in gis in this article, we will cover the fundamental differences between raster and vector data. geospatial data can be represented using either vector data type or raster. the two data types are very different in their internal representation, the operations you can do on them as well as their look and feel. the figures below show a. Understanding the difference between vector and raster data is fundamental for gis. these two types of spatial data are the backbone of gis analyses and mapping, each with its unique characteristics, advantages, and applications.

12 Gis Vector Raster Images Vector And Raster Data Gis Vector And

12 Gis Vector Raster Images Vector And Raster Data Gis Vector And

12 Gis Vector Raster Images Vector And Raster Data Gis Vector And