
Pain Management Options For Bone Fractures Guardian Liberty Voice Fractures represent common acute painful injuries that warrant deliberate evidenced based pain management strategies. fractures are best managed with a multi modal pain strategy that relies on non opioid modalities and medications as the first line treatment, and reserves limited opioid use for breakthrough pain. fracture pain management strategies can be categorized into 3 groups: non. For this reason, adequate pain management during both the acute trauma phase and the extended recovery period of orthopedic patients is necessary to improve the quality of life of the patients and for successful bone healing. the reasons why fracture pain persists during and following the healing process are poorly understood.

Pain Management During Labor Clinical Sciences Osmosis Video Library The literature is still inconclusive regarding superiority of either spinal or general anesthesia during operative treatment. fracture pain control is complex and multifactorial, requiring nuanced clinical judgment in the face of mixed clinical findings. keywords: ankle fracture; distal radius fracture; hip fracture; long bone fracture; pain. The pain medication recommendations are divided into 3 clinical scenarios—major musculoskeletal injury procedure (eg, operative fixation of long bone or complex joint fracture, extensive soft tissue injury or surgery, etc.), minor musculoskeletal injury procedure (eg, operative fixation of small bone or simple joint fracture, minimal soft. Key takeaway effective pain management for broken bones involves a combination of medications, regional anesthesia techniques, and non pharmacological approaches, tailored to the individual patient's needs and fracture type. Fracture pain control is complex and multifactorial, requiring nuanced clinical judgment in the face of mixed clinical findings. this article provides an overview of the management of pain associated with fractures, with an emphasis on updates to the literature within the past 3 years.
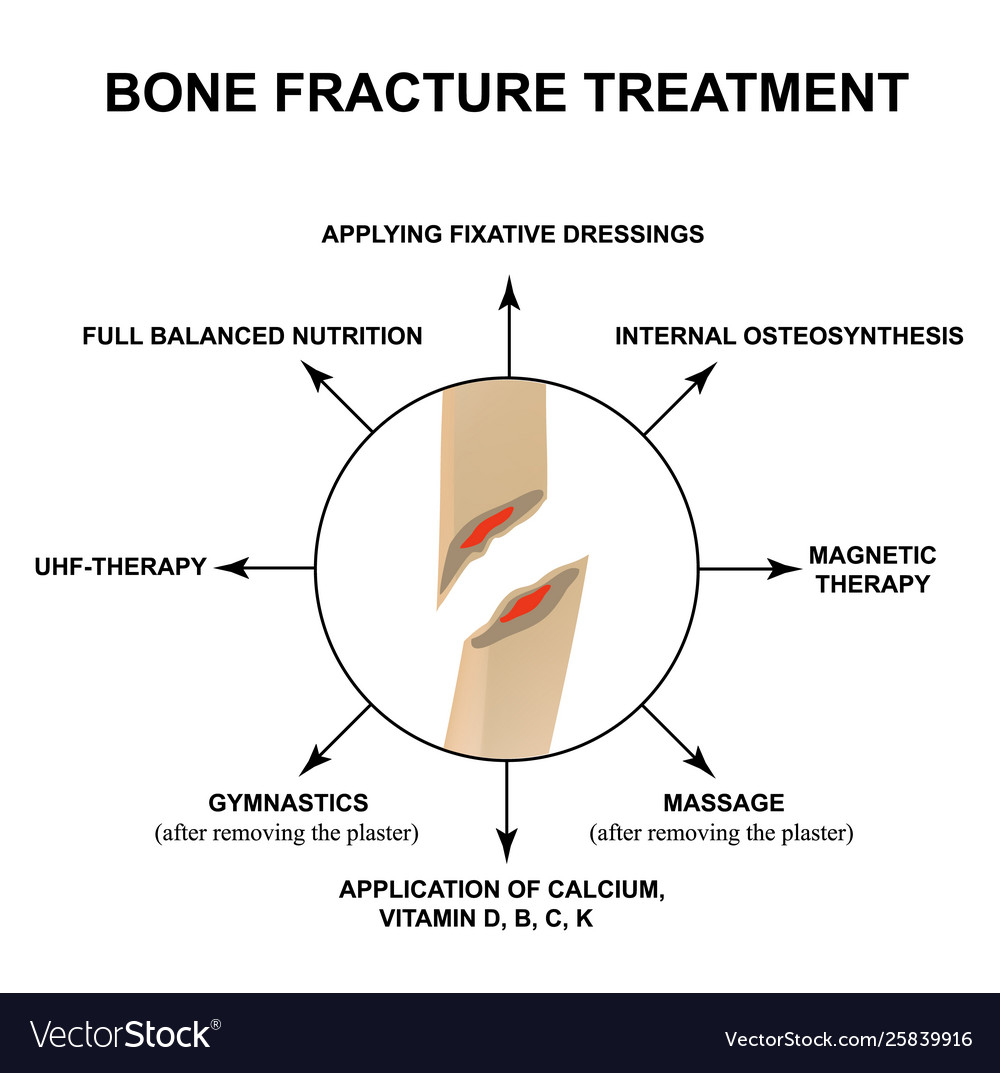
Treatment Bone Fractures Fracture Royalty Free Vector Image Key takeaway effective pain management for broken bones involves a combination of medications, regional anesthesia techniques, and non pharmacological approaches, tailored to the individual patient's needs and fracture type. Fracture pain control is complex and multifactorial, requiring nuanced clinical judgment in the face of mixed clinical findings. this article provides an overview of the management of pain associated with fractures, with an emphasis on updates to the literature within the past 3 years. Initial pharmacological management of pain in adults (16 or over) 1.1.4 for the initial management of pain in adults (16 or over) with suspected long bone fractures of the legs (tibia, fibula) or arms (humerus, radius, ulna), offer:. Effective pain management is essential in fracture healing. non pharmacological methods offer a holistic approach to alleviate discomfort and enhance recovery. these techniques, from traditional acupuncture to modern tens, provide diverse options for managing fracture pain, promoting a comfortable and efficient healing journey in orthopaedic care.

Research Released On Pain Management For Long Bone Fractures Initial pharmacological management of pain in adults (16 or over) 1.1.4 for the initial management of pain in adults (16 or over) with suspected long bone fractures of the legs (tibia, fibula) or arms (humerus, radius, ulna), offer:. Effective pain management is essential in fracture healing. non pharmacological methods offer a holistic approach to alleviate discomfort and enhance recovery. these techniques, from traditional acupuncture to modern tens, provide diverse options for managing fracture pain, promoting a comfortable and efficient healing journey in orthopaedic care.
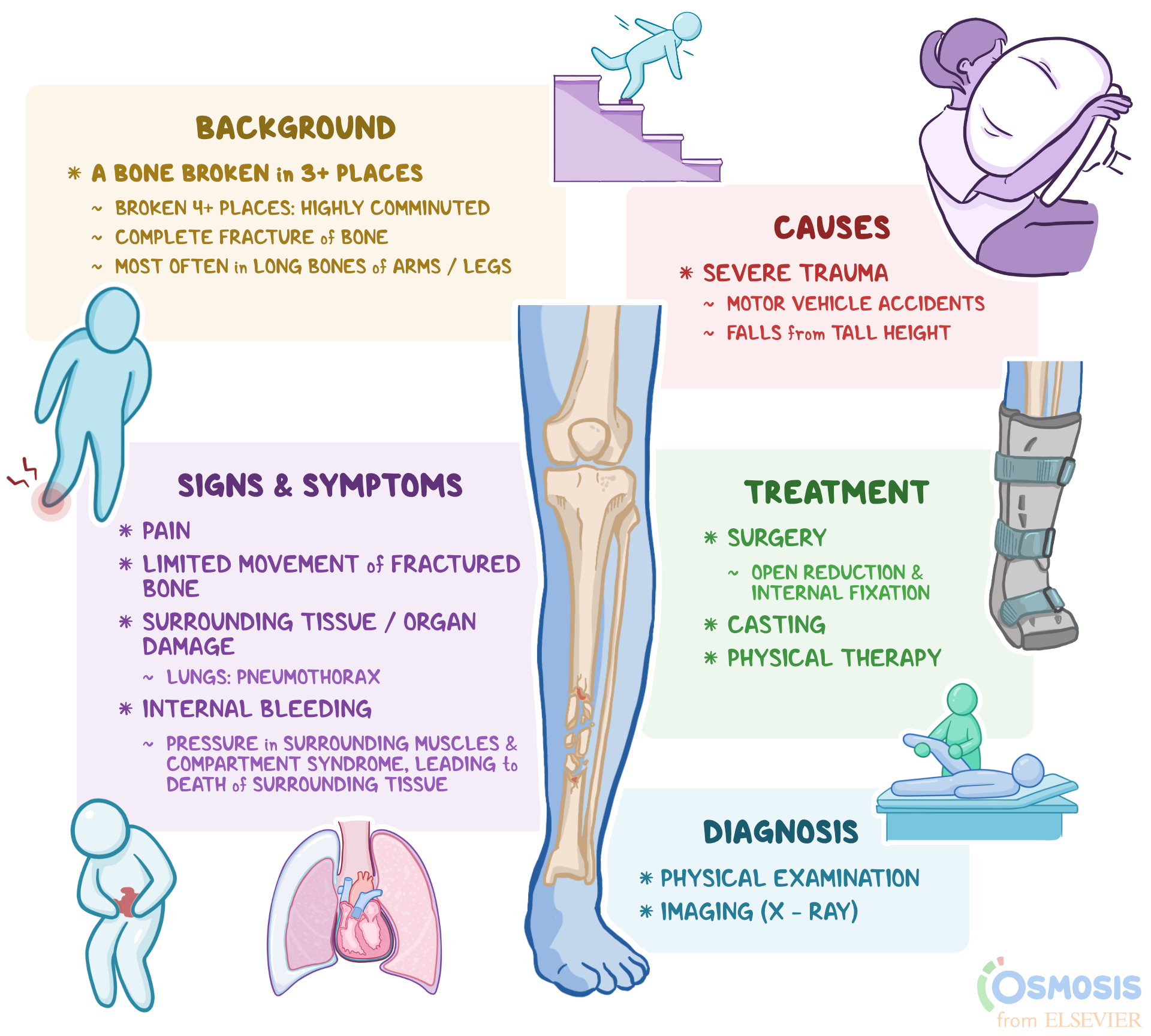
Comminuted Fracture What Is It Examples And More Osmosis
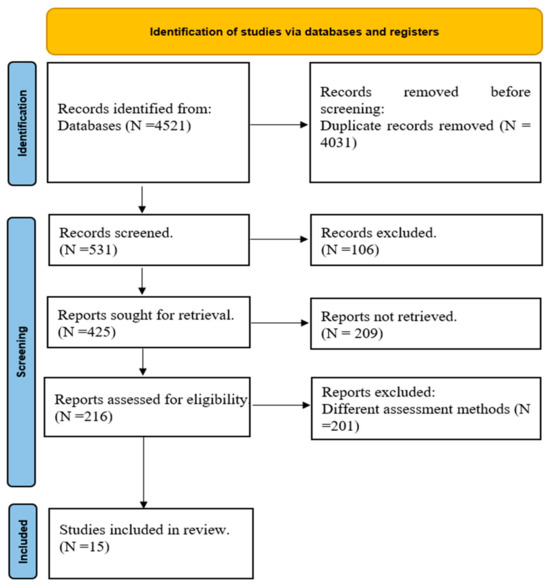
Novel Techniques For Musculoskeletal Pain Management After Orthopedic

Management Of Pain Associated With Fractures Current Osteoporosis Reports