
Vector Vs Raster What S The Difference Between Gis Spatial Data Types Vector data is not made up of a grid of pixels. instead, vector graphics are comprised of vertices and paths. the three basic symbol types for vector data are points, lines, and polygons (areas). because cartographers use these symbols to represent real world features in maps, they often have to decide based on the level of detail on the map. Staged products the topographic maps and geographical information system (gis) data provided in the national map are pre generated into downloadable products often available in multiple formats. the vector datasets include: the national hydrography dataset (s), watershed boundary dataset, governmental boundary units, transportation, structures, elevation contours and geographic names. raster.

Vector Vs Raster What S The Difference Between Gis Spatial Data Types Within the spatial referenced data group, the gis data can be further classified into two different types: vector and raster. most gis software applications mainly focus on the usage and manipulation of vector geodatabases with added components to work with raster based geodatabases. Understanding the difference between vector and raster data is fundamental for gis. these two types of spatial data are the backbone of gis analyses and mapping, each with its unique characteristics, advantages, and applications. Geographic information system (gis) is a powerful tool for capturing, analyzing, and presenting spatial data. it is widely used in various fields, including urban planning, environmental management, and natural resource management. two fundamental data models used in gis are raster and vector data models. The difference between vector and raster data in gis in this article, we will cover the fundamental differences between raster and vector data. geospatial data can be represented using either vector data type or raster. the two data types are very different in their internal representation, the operations you can do on them as well as their look and feel. the figures below show a.
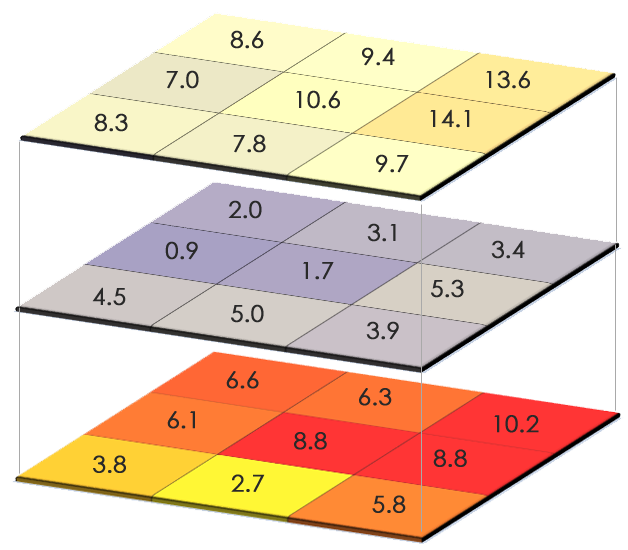
Vector Vs Raster What S The Difference Between Gis Spatial Data Types Geographic information system (gis) is a powerful tool for capturing, analyzing, and presenting spatial data. it is widely used in various fields, including urban planning, environmental management, and natural resource management. two fundamental data models used in gis are raster and vector data models. The difference between vector and raster data in gis in this article, we will cover the fundamental differences between raster and vector data. geospatial data can be represented using either vector data type or raster. the two data types are very different in their internal representation, the operations you can do on them as well as their look and feel. the figures below show a. Raster giss raster giss (grid cell) work by storing attribute data as grid cell values. grid cells are an ideal data structure for applications involving terrain analysis. they have superior analytical power to vector gis, but grid cell map presentation tends to be less attractive than vector map presentation. Since most input data is in vector form, data must undergo vector to raster conversion. besides increased processing requirements this may introduce data integrity concerns due to generalization and choice of inappropriate cell size. most output maps from grid cell systems do not conform to high quality cartographic needs.
Vector Vs Raster What S The Difference Between Gis Spatial Data Types Raster giss raster giss (grid cell) work by storing attribute data as grid cell values. grid cells are an ideal data structure for applications involving terrain analysis. they have superior analytical power to vector gis, but grid cell map presentation tends to be less attractive than vector map presentation. Since most input data is in vector form, data must undergo vector to raster conversion. besides increased processing requirements this may introduce data integrity concerns due to generalization and choice of inappropriate cell size. most output maps from grid cell systems do not conform to high quality cartographic needs.
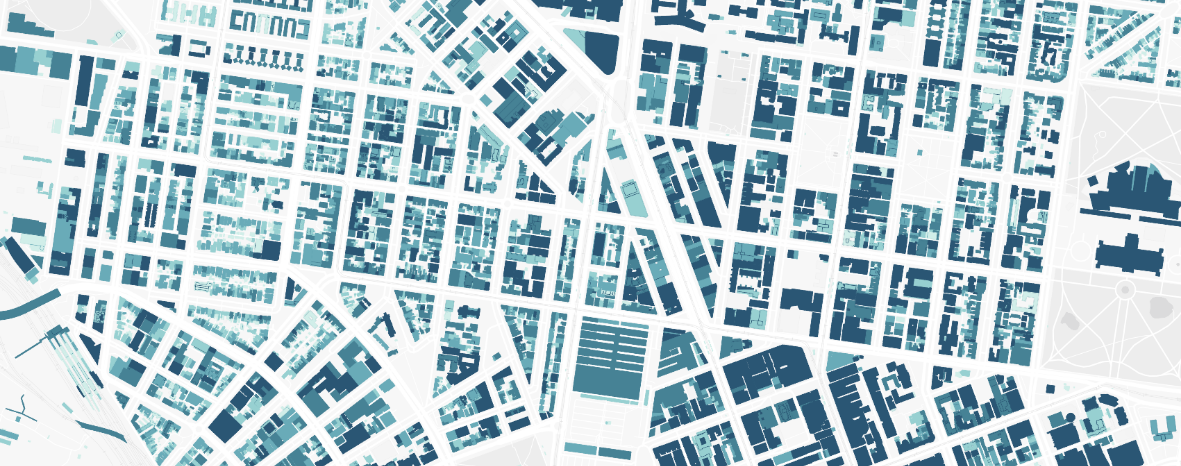
Raster Vs Vector Data The Ultimate Guide Atlas

Raster Vs Vector Data The Ultimate Guide Atlas

Vector And Raster Data Gis