
Rotor Synchronous Motor And How Does It Work Rotating Magnetic Field The term “ synchronous motor ” derives from the rotor’s speed matching the speed of the rotating magnetic field. it is a fixed speed motor because it has only one speed, which is synchronous speed. A synchronous motor is an electric motor that synchronizes with the stator's rotating magnetic field. it offers several benefits, such as constant speed operation, high efficiency, and power factor correction capabilities.

Synchronous Motor Wikipedia The Free Encyclopedia Pdf Electric A synchronous motor is a type of ac motor whose rotor rotates at the same speed as the rotating magnetic field. the stator’s magnetic field revolves at a speed that depends on the supply frequency known as synchronous speed. A permanent magnet synchronous motor (pmsm) uses permanent magnets embedded in the rotor to create a constant magnetic field. the stator carries windings connected to an ac electricity supply to produce a rotating magnetic field (as in an asynchronous motor). at synchronous speed the rotor poles lock to the rotating magnetic field. pmsms are similar to brushless dc motors. neodymium magnets. Synchronous motor a dc supply powers the rotor's permanent magnetic coils for synchronous motors. when an ac source delivers power to the stator, it generates a rotating magnetic field, or rmf. the rotor's poles are polarity different. due to their differing polarities, the rotor magnetic field and stator rmf lock when they interact, causing the rotor to begin rotating at a synchronous speed. Synchronous motor is a type of alternating current motor. the speed of rotation (synchronism speed) is constant and is synchronized with the frequency of the electrical voltage to which it is connected and the number of pairs of poles of the motor. these are typically three phase motors, but small power synchronous motors are often powered by the common single phase voltage available in homes.

Rotating Magnetic Field Rmf And Its Properties 57 Off Synchronous motor a dc supply powers the rotor's permanent magnetic coils for synchronous motors. when an ac source delivers power to the stator, it generates a rotating magnetic field, or rmf. the rotor's poles are polarity different. due to their differing polarities, the rotor magnetic field and stator rmf lock when they interact, causing the rotor to begin rotating at a synchronous speed. Synchronous motor is a type of alternating current motor. the speed of rotation (synchronism speed) is constant and is synchronized with the frequency of the electrical voltage to which it is connected and the number of pairs of poles of the motor. these are typically three phase motors, but small power synchronous motors are often powered by the common single phase voltage available in homes. A 3 phase synchronous motor is a type of motor powered by a three phase ac supply, which creates a rotating magnetic field in the stator. the rotor is excited with dc and locks into synchronism with the rotating magnetic field, ensuring constant speed operation. The speed of the synchronous motor is determined by the number of magnetic poles and the line frequency.as the name implies, synchronous motors run in synchronism with revolving field. the speed of rotation is therefore tied to the frequency of the source.
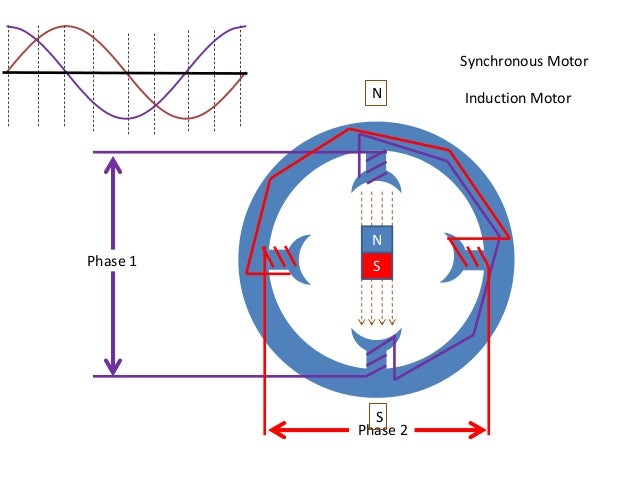
Rotating Magnetic Field A 3 phase synchronous motor is a type of motor powered by a three phase ac supply, which creates a rotating magnetic field in the stator. the rotor is excited with dc and locks into synchronism with the rotating magnetic field, ensuring constant speed operation. The speed of the synchronous motor is determined by the number of magnetic poles and the line frequency.as the name implies, synchronous motors run in synchronism with revolving field. the speed of rotation is therefore tied to the frequency of the source.