Comoving Proper Distance Transverse Comoving Distance The proper distance dp d p is the distance between two regions of space at a constant cosmological time. as the universe expands, the proper distance between two comoving observers increases over time. this notion of distance is purely theoretical, because we cannot see where an object is 'right now'. In standard cosmology, comoving distance and proper distance (or physical distance) are two closely related distance measures used by cosmologists to define distances between objects. comoving distance factors out the expansion of the universe, giving a distance that does not change in time except due to local factors, such as the motion of a galaxy within a cluster. [1] proper distance.
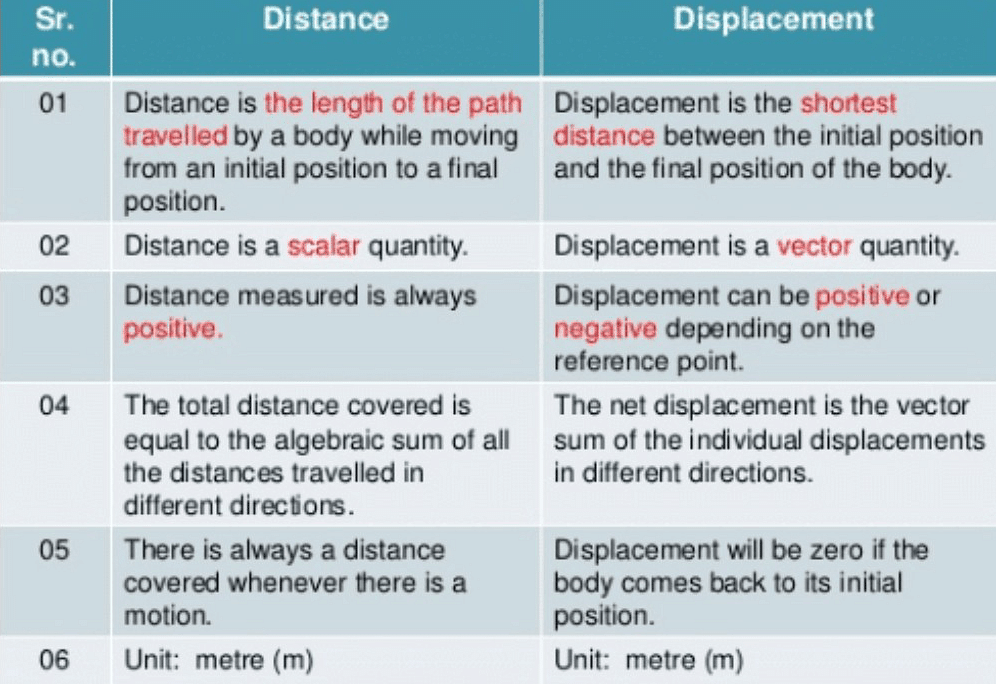
Difference Between Distance And Displacement In Physics Edurev Class The comoving distance changes if the proper distances change due to a factor other than the expansion of the universe as the universe expands, the proper distance to the galaxy increases but the comoving distance does not change. The comoving distance happens to be equivalent to the proper motion distance (hence the name dm), defined as the ratio of the actual transverse velocity (in distance over time) of an object to its proper motion (in radians per unit time) (weinberg 1972, pp. 423 424). the proper motion distance is plotted in figure 1. Notice that these distances are larger than ct, the distance travelled by a photon in time t. how could this be? the reason lies in our definition of proper distance, as the distance between two events measured in a frame of reference where those two events happen at the same time. to understand this, consider a photon in emitted at comoving radial coordinate rhor at time t = 0. we want to. In this informative video, we will explain the essential concepts of proper distance and comoving distance in cosmology. understanding these two types of distances is fundamental for grasping how.
Difference Between Distance And Displacement Notice that these distances are larger than ct, the distance travelled by a photon in time t. how could this be? the reason lies in our definition of proper distance, as the distance between two events measured in a frame of reference where those two events happen at the same time. to understand this, consider a photon in emitted at comoving radial coordinate rhor at time t = 0. we want to. In this informative video, we will explain the essential concepts of proper distance and comoving distance in cosmology. understanding these two types of distances is fundamental for grasping how. Comoving angular diameter distance: this is simply the angular diameter distance divided by the scale factor. we will reserve da d a for comoving angular diameter distance. the comoving angular diameter distance between r = 0 r = 0 and r = d r = d is da = d d a = d. I'm utterly confused by co moving distance, transverse comoving distance and proper distance. is comoving distance = proper distance? then what is transverse comoving distance? here's what i know so far: the frw metric can either be expressed as ds^2 = c^2dt^2 a^2(t) \\left[ \\frac{dr^2}{1 kr^2}.
Difference Between Distance And Displacement Comoving angular diameter distance: this is simply the angular diameter distance divided by the scale factor. we will reserve da d a for comoving angular diameter distance. the comoving angular diameter distance between r = 0 r = 0 and r = d r = d is da = d d a = d. I'm utterly confused by co moving distance, transverse comoving distance and proper distance. is comoving distance = proper distance? then what is transverse comoving distance? here's what i know so far: the frw metric can either be expressed as ds^2 = c^2dt^2 a^2(t) \\left[ \\frac{dr^2}{1 kr^2}.
Difference Between Distance And Displacement