
Wi Fi Real Max Speed Bandwidth Throughput Bitrate Wi fi real max speed bandwidth throughput bitrate by marketing team may 22, 2014 classic hotspot, cloud management, wireless hardware being tanaza a multi vendor wi fi cloud management platform, we are often asked by users which is the maximum speed reachable by the wi fi routers access points. typical question:. In this article, we show the realistic speeds that wi fi 5 and wi fi 6 achieve in the real world, with real world devices that are available now. we show how speeds for both wi fi 5 and wi fi 6 are substantially affected by signal level, the channel bandwidth adopted and the mimo capabilities of devices.

Wi Fi Real Max Speed Bandwidth Throughput Bitrate Interference other wireless networks and devices in the same frequency in the same area affect performance shared bandwidth available bandwidth is shared between all users on the same wireless network. in addition, net ip layer throughput of wifi is typically 60% of the air link rate due to wifi being half duplex with acks, and being csma ca. 450 mbps on 2.4ghz is absolutely not going to happen. the max phy on a 2 stream 802.11n mimo client is going to be 173.3 mbps, which means that under ideal conditions your throughput might occasionally break 100mbps. 802.11ax will get you up to 286.8 mbps. Protocol overhead: each 20mhz wi fi channel has maximum phy bitrate of around 72mbps, but due to wi fi protocol overhead, real throughput will only be around 60% to 80% of that. When testing a client to ap connection speed, it is important to differentiate the speeds between the client device to the ap itself, and the speeds for the client device to the internet when distinguishing bandwidth concerns in a network.
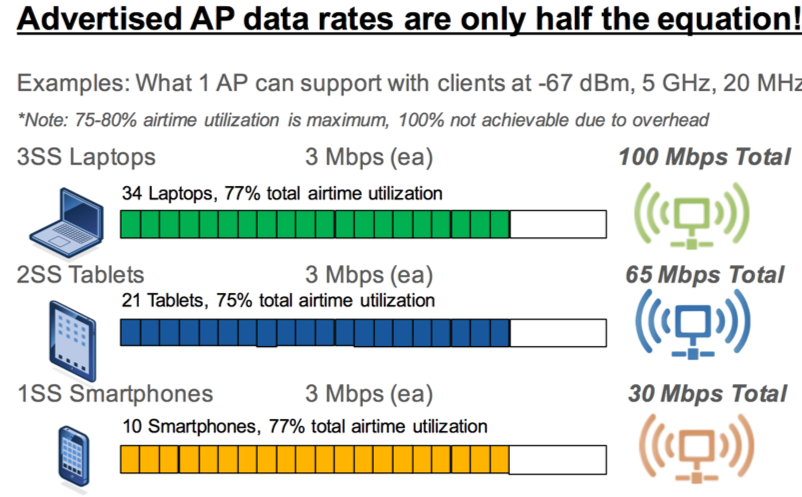
Wi Fi Throughput Divergent Dynamics Protocol overhead: each 20mhz wi fi channel has maximum phy bitrate of around 72mbps, but due to wi fi protocol overhead, real throughput will only be around 60% to 80% of that. When testing a client to ap connection speed, it is important to differentiate the speeds between the client device to the ap itself, and the speeds for the client device to the internet when distinguishing bandwidth concerns in a network. Conclusion: choosing the right wi fi bandwidth setting depends heavily on your environment and needs. in dense areas with lots of wi fi networks, sticking to 20 or 40 mhz may offer more stable connections. for those in less crowded spaces or requiring high data throughput, 80 or even 160 mhz channels might be beneficial. The blog post discusses the new sets of data rates that became available with 802.11ax (wi fi 6) and explains how these wi fi data rates are calculated. feel free to take a look at it to learn more about this topic. in this post, we will update the sets of wi fi data rates to include the new data rates provided by the new 802.11be (wi fi 7.

Differences Between Wifi Throughput Bandwidth And Data Rates Conclusion: choosing the right wi fi bandwidth setting depends heavily on your environment and needs. in dense areas with lots of wi fi networks, sticking to 20 or 40 mhz may offer more stable connections. for those in less crowded spaces or requiring high data throughput, 80 or even 160 mhz channels might be beneficial. The blog post discusses the new sets of data rates that became available with 802.11ax (wi fi 6) and explains how these wi fi data rates are calculated. feel free to take a look at it to learn more about this topic. in this post, we will update the sets of wi fi data rates to include the new data rates provided by the new 802.11be (wi fi 7.
Available Bandwidth Requested Bitrate And Segment Throughput A